Abstract
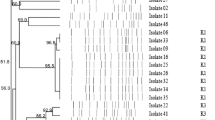
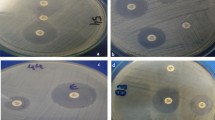
The aim of this study was to investigate the antibiotic susceptibility profiles and the presence of extended-spectrum-β-lactamases (ESBLs) in Pseudomonas fluorescens isolates from coastal waters of the Kaštela Bay, Croatia. Twenty-two water samples were collected during 2009. Isolates were tested for susceptibilities to 13 antibiotics by Etest. ESBL production was confirmed by double-disk synergy test carried out on Mueller–Hinton agar plates containing efflux pump inhibitor Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide dihydrochloride. PCR and DNA sequencing analysis were used to identify ESBL-encoding genes. The transferability of cephalosporin resistance was tested by conjugation experiments. Genetic relatedness of ESBL-producing isolates was determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. Out of 185 P. fluorescens isolates recovered, 70 (37.8%) demonstrated multiresistance phenotype with highest rates of resistance to tetracycline (61.6%), aztreonam (31.9%), meropenem (17.3%), ceftazidime (15.1%) and cefotaxime (12.4%). Ten (5.4%) isolates were identified as ESBL producers. All isolates carried chromosomally located bla TEM-116 gene. RAPD analysis identified four different genotypes. Here, we demonstrated a baseline profiles of antimicrobial resistance of P. fluorescens from coastal waters of the Kaštela Bay, Croatia. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the presence of TEM-type ESBL in P. fluorescens, indicating this bacterium as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes with clinical relevance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balsalobre LC, Dropa M, de Oliveira DE, Lincopan N, Mamizuka EM, Matté GR, Matté MH (2010) Presence of bla TEM-116 gene in environmental isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas jandaei from Brazil. Braz J Microbiol 41:718–719
Baquero F, Martinez JL, Canton R (2008) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:260–265
Bedenić B, Schmidt H, Herold S, Monaco M, Plecko V, Kalenić S, Katić S, Skrlin-Subić J (2005) Epidemic and endemic spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing SHV-5 beta-lactamase in Dubrava University Hospital, Zagreb, Croatia. J Chemother 17:367–375
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2006) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 7th edn. Document M7-A7, vol 26, no. 2. CLSI, Wayne, PA, USA
David J, Lemeland MF, Boyer S (2008) Emergence of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: about 24 cases at Rouen University Hospital. Path Biol 56: 429– 434
Dubois V, Arpin C, Dupart V, Scavelli A, Coulange L, André C, Fischer I, Grobost F, Brochet J-P, Lagrange I, Dutilh B, Jullin J, Noury P, Larribet G, Quentin C (2008) β-lactam and aminoglycoside resistance rates and mechanisms among Pseudomonas aeruginosa in French general practice (community and private healthcare centres). J Antimicrob Chemother 62:316–323
Falagas ME, Karageorgopoulos DE (2009) Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing organisms. J Hosp Infect 73:345–354
Fishwick D, Paul T, Elms J, Robinson E, Crook B, Gallagher F, Lennox R, Curran A (2005) Respiratory symptoms, imunology and organism identification in contaminated metalworking fluid workers. What you see is not what you get. Occup Med 55:238–241
Gershman MD, Kennedy DJ, Noble-Wang J, Kim C, Gullion J, Kacica M, Jensen B, Pascoe N, Saiman L, McHale J, Wilkins M, Schoonmaker-Bopp D, Clayton J, Arduino M, Srinivasan A (2008) Multistate outbreak of Pseudomonas fluorescens bloodstream infection after exposure to contaminated heparinized saline flush prepared by a compounding pharmacy. Clin Infec Dis 47:1372–1379
Girlich D, Poirel L, Nordmann P (2010) Novel Ambler class A carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase from a Pseudomonas fluorescens isolate from the Seine River, Paris, France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:328–332
Girlich D, Poirel L, Nordmann P (2011) Diversity of clavulanic acid-inhibited extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Aeromonas spp. from the Seine River, Paris. France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:1256–1261
Hearn EM, Dennis JJ, Gray MR, Foght JM (2003) Identification and characterization of the emhABC efflux system for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Pseudomonas fluorescens cLP6a. J Bacteriol 185:6233–6240
Jacoby GA, Bush K (2005) β-Lactam resistance in the 21st century. In: White DG, Alekshun MN, McDermott PF (eds) Frontiers in antimicrobial resistance: a tribute to Stuart B. Levy. ASM Press, Washington, DC, p 570
Jakšić Ž, Batel R, Bihari N, Mičić M, Zahn RK (2005) Adriatic coast as a microcosm for global genotoxic marine contamination- a long-term field study. Mar Poll Bull 50:1314–1327
Jeong SH, Bae IK, Lee JH, Sohn SG, Kang GH, Jeon GJ, Kim YH, Jeong BC, Lee SH (2004) Molecular characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases produced by clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli from a Korean nationwide survey. J Clin Microbiol 42:2902–2906
Jiang X, Zhang Z, Li M, Zhou D, Ruan F, Lu Y (2006) Detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother 50:2990–2995
Koh TH, Wang GCY, Sng LH (2004) IMP-1 and a novel metallo- β-lactamase, VIM-6, in fluorescent pseudomonads isolated in Singapore. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:2334–2336
Lachmayr KL, Kerkhof LJ, Dirienzo AG, Cavanaugh CM, Ford TE (2009) Quantifying nonspecific TEM beta-lactamase (blaTEM) genes in a wastewater stream. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:203–211
Lahlaoui H, Dahmen S, Moussa MB, Omrane B (2011) First detection of TEM-116 extended- spectrum β-lactamase in a Providencia stuartii isolate from a Tunisian hospital. Indian J Med Microbiol 29:258–261
Literacka E, Bedenic B, Baraniak A, Fiett J, Tonkic M, Jajic-Bencic I, Gniadkowski M (2009) blaCTX-M genes in Escherichia coli strains from Croatian hospitals are located in new (blaCTX-M-3a) and widely spread (blaCTX-M-3a and blaCTX-M-15) genetic structures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:1630–1635
Machado E, Coque TM, Cantón R, Sousa JC, Silva D, Ramos M, Rocha J, Ferreira H, Peixe L (2009) Leakage into Portuguese aquatic environments of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:616–618
Michaux C, Fre`re J-M, Docquier JD, Vandenberghe I, Samyn B, Pierrard A, Feller G, Charlier P, Van Beeumen J, Wouters J (2008) Crystal structure of a cold-adapted class C β-lactamase. FEBS J 275:1687–1697
Pal KK, Tilak KV, Saxena AK, Dey Dey R, Singh CS (2001) Suppression of maize root diseases caused by Macrophomina phaseolina, Fusarium moniliforme and Fusarium graminearum by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol Res 156:209–223
Pappas G, Karavasilis V, Christou L, Tsianos EV (2006) Pseudomonas fluorescens infections in clinical practice. Scand J Infect Dis 38:68–70
Paterson DL, Hujer KM, Hujer AM, Yeiser B, Bonomo MD, Rice LB, Bonomo RA, International Klebsiella Study Group (2003) Extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream isolates from seven countries: dominance and widespread prevalence of SHV- and CTX-M-type β-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3554–3560
Pellegrini C, Mercuri PS, Celenza G, Galleni M, Segatore B, Sacchetti E, Volpe R, Amicosante G, Perilli M (2009) Identification of bla IMP-22 in Pseudomonas spp. in urban wastewater and nosocomial environments: biochemical characterization of a new IMP metallo-enzyme variant and its genetic location. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:901–908
Petroni A, Corso A, Melano R, Cacace ML, Bru AM, Rossi A, Galas M (2002) Plasmidic extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor in Argentina. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:1462–1468
Picão RC, Poirel L, Demarta A, Petrini O, Corvaglia AR, Nordmann P (2008) Expanded-spectrum β-lactamase PER-1 in an environmental Aeromonas media isolate from Switzerland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:3461–3462
Poirel L, Naas T, Guibert M, Chaibi EB, Labia R, Nordmann P (1999) Molecular and biochemical characterization of VEB-1, a novel class A extended-spectrum β-lactamase encoded by an Escherichia coli integron gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:573–581
Poirel L, Le Thomas I, Naas T, Karim A, Nordmann P (2000) Biochemical sequence analyses of GES-1, a novel class A extended-spectrum β-lactamase and the class 1 integron In52 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:622–632
Pontes DS, Pinheiro FA, Lima-Bittencourt CI, Guedes RLM, Cursino L, Barbosa F, Santos FR, Chartone-Souza E, Nascimento AMA (2009) Multiple antimicrobial resistance of Gram-negative bacteria from natural oligotrophic lakes under distinct anthropogenic influence in a tropical region. Microb Ecol 58:762–772
Rodríguez-Baño J, Navarro MD, Romero L, Martínez-Martínez L, Muniain MA, Perea EJ, Pérez-Cano R, Pascual A (2004) Epidemiology and clinical features of infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in nonhospitalized patients. J Clin Microbiol 42:1089–1094
Romero EDV, Padilla TP, Hernandez AH, Grande RP, Vazquez MF, Garcia IG, Garcia-Rodriguez JA, Munoz Bellido JL (2007) Prevalence of clinical isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. producing multiple extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 59:433–437
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Laboratory Press, New York
Sevillano E, Valderrey C, Canduela MJ, Umaran A, Calvo F, Gallego L (2006) Resistance to antibiotics in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pathol Biol 54:493–497
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tonkić M, Mohar B, Šiško-Kraljević K, Meško-Meglič K, Goić-Barišić I, Novak A, Kovačić A, Punda-Polić V (2010) High prevalence and molecular characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Proteus mirabilis strains in southern Croatia. J Med Microbiol 59:1185–1190
Vignoli R, Varela G, Mota MI, Cordeiro NF, Power P, Ingold E, Gadea P, Sirok A, Schelotto F, Ayala JA, Gutkind G (2005) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains carrying genes encoding the PER-2 and TEM-116 extended-spectrum β-lactamases isolated from children with diarrhea in Uruguay. J Clin Microbiol 43:2940–2943
Wright GD (2010) Antibiotic resistance in the environment: a link to the clinic? Curr Opin Microbiol 13:589–594
Zhang XX, Zhang T, Fang HH (2009) Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:397–414
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Ministry of Science, Education and Sports, Republic of Croatia, project “Faecal indicator and potential pathogens in coastal and marine waters“, Grant 177-0000000-3182 and project “Mechanisms of maintenance genome stability in higher plants”, Grant 177-1191196-0829.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maravić, A., Skočibušić, M., Šamanić, I. et al. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles and first report of TEM extended-spectrum β-lactamase in Pseudomonas fluorescens from coastal waters of the Kaštela Bay, Croatia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 2039–2045 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1006-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1006-5