Abstract
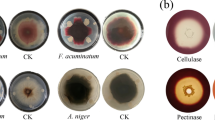
Exiguobacterium acetylicum strain 1P (MTCC 8707) is a rhizospheric, Gram positive, rod shaped, yellow pigmented bacterium isolated from an apple orchard rhizospheric soil, on nutrient agar plates incubated at 4°C. The species level identification was arrived on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The sequence showed 98% similarity with sequences of E. acetylicum available in the public domain. The strain was positive for siderophore and HCN production. In separate invitro assays it was found to inhibit the growth and development of Rhizoctoniasolani, Sclerotium rolfsii, Pythium and Fusarium oxysporum. The volatile compound produced by the bacterium was found to be the most potent in inhibiting the hyphal development of R. solani, S. rolfsii, Pythium and F. oxysporum by 45.55, 41.38, 28.92 and 39.74% respectively. Commonly observed deformities caused by the diffusible and volatile compounds produced by the bacterium included hyphal inhibition, constriction and deformation. Under pot culture conditions the bacterium improved the germination and early growth parameters of pea (Pisum sativum) in the presence of R. solani and S. rolfsii.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bais HP, Park SW, Weir TL et al (2004) How plants communicate using the underground information superhighway. Trends Plant Sci 9:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2003.11.008
Bakker AW, Schipper B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90037-X
Barnett SJ, Roget DK, Ryder MH (2006) Suppression of Rhizoctonia solani AG-8 induced disease on wheat by the interaction between Pantoea, Exiguobacterium and Microbacteria. Aust J Soil Res 44:331–342. doi:10.1071/SR05113
Bloemberg GV, Lugtenberg BJJ (2001) Molecular basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:343–350. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00183-7
Burr TJ, Ceaser A (1984) A beneficial plant bacteria. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 2:1–20
Chaurasia B, Pandey A, Palni LMS et al (2005) Diffusible and volatile compounds produced by an antagonistic Bacillus subtilis cause structural deformations in pathogenic fungi in vitro. Microbiol Res 160:75–81. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2004.09.013
Collins CH, Lyne PM (1980) Microbiological methods. Butterworth and Co. (Publishers) Ltd, London
De Weger LA, vander Bij AJ, Dekkers LC et al (1995) Colonization of the rhizosphere of crop plants by plant-beneficial pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17:221–228
Defago G, Haas D (1990) Pseudomonas as antagonists of soilborne plant pathogens: mode of action and genetic analysis. Soil Biochem 6:249–291
Duffy BK, Defago G (1999) Environmental factors modulating antibiotic and siderophore biosynthesis by Pseudomonas fluorescens biocontrol strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2429–2438
Gerhardson B (2002) Biological substitutes for pesticides. Trends Biotechnol 20:338–343. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(02)02021-8
Glick B (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Haas D, Defago G (2005) Biological control of soil borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:307–319. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1129
Huang HC, Hoes JA (1976) Penetration and infection in S. sclerotium by C. minitans. Can J Bot 54:406–410
Kasana R, Yadav S (2007) Isolation of a psychrotrophic Exiguobacterium sp SKPB5 (MTCC 7803) and characterization of its alkaline protease. Curr Microbiol 54(3):117–121. doi:10.1007/s00284-006-0402-1
Kloepper JW, Ryu CM, Zhang S (2004) Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94:1259–1266. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1259
Knudston KE, Haas EJ, Iwen PC et al (2001) Characterization of a Gram-positive non spore forming Exiguobacterium like organism isolated from a western Colorado (USA) hot spring. Abstr: Annu Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1(92):30
Loper JE, Henkels MD (1997) Availability of iron to Pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizosphere and bulk soil evaluated with an ice nucleation reporter gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:99–105
Loper JE, Henkels MD (1999) Utilization of heterologous siderophores enhances levels of iron available to Pseudomonas putida in the rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5357–5363
Miteva VI, Sheridan PP, Brenchly JE (2004) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of microorganisms isolated from a deep Greenland glacier ice core. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:202–213. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.1.202-213.2004
Negi YK, Garg SK, Kumar J (2005) Cold tolerant fluorescent Pseudomonas isolates from Garhwal Himalayas as potential plant growth promoting and biocontrol agents in pea. Curr Sci 89:2151–2156
Nowak J, Shulaev V (2003) Priming for transplant stress resistance in in vitro propagation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:107–124. doi:10.1079/IVP2002403
O’Sullivan DJ, O’Gara F (1992) Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiol Rev 56:662–676
Ovadis M, Liu X, Gavriel S, Ismailov Z, Chet I, Chernin L (2004) The global regulator genes from biocontrol strain Serratia plymouthica IC1270: cloning, sequencing and functional studies. J Bacteriol 186:4986–4993. doi:10.1128/JB.186.15.4986-4993.2004
Pandey A, Palni LMS, Coulomb N (1997) Antifungal activity of bacteria isolated from rhizosphere of established tea bushes. Microbiol Res 152:105–112
Pandey A, Palni LMS, Hebbar KP (2001) Suppression of damping-off in maize seedling by Pseudomonas corrugata. Microbiol Res 156:191–194. doi:10.1078/0944-5013-00102
Pandey A, Trivedi P, Kumar B et al (2006) Soil microbial diversity from the Himalaya: need for documentation and conservation. NBA Bulletin no 5. National Biodiversity Authority Chennai, Tamilnadu, India, p 64
Raaijmakers JM, Vlami M, de Souza JT (2002) Antibiotic production by bacterial biocontrol agents. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:537–547. doi:10.1023/A:1020501420831
Reiter B, Pfeifer U, Schwab H, Sessitsch A (2002) Response of endophytic bacterial communities in potato plant to infection with Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2261–2268. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.5.2261-2268.2002
Rodriguez DF, Goris J, Vishnivetskaya et al (2006) Characterization of Exiguobacterium isolates from the Siberian permafrost. Description of Exiguobacterium sibiricum sp. nov. Extremophiles 10:285–294. doi:10.1007/s00792-005-0497-5
Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH et al (2004) Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:1017–1026. doi:10.1104/pp.103.026583
Samanta SK, Dutta S (2004) Potential of native plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the management of Sclerotinia stem rot of mustard. J Mycol Plant Pathol 34:761–768
Schillinger U, Lucke FK (1989) Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus strain isolated from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1901–1906
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:40–47. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Wada M, Yoshizumi A, Furukawa Y et al (2004) Cloning and expression of Exiguobacterium sp F42 gene encoding a new short chain dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the stereo selective reduction of ethyl 3-oxo 3-(2- thienyl) propanoate to ethyl(S)- 3-hydroxy-3 (2-thienyl) propanoate. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 7:1481–1488. doi:10.1271/bbb.68.1481
Yumoto I, Hishinuma-Narisawa M, Hirota K et al (2004) Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans sp. nov., a novel alkaliphile exhibiting high catalase activity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2013–2017. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63129-0
Zhang L, Birch RG (1997) Mechanisms of biocontrol by Pantoea dispersa of sugar cane leaf scald disease caused by Xanthomonas albilineans. J Appl Microbiol 82:448–454. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00135.x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, through the project “Application of Microorganisms in Agriculture and Allied Sectors”. Dr. Anita Pandey, GBPIHED, Almora and Dr. Deeksha Joshi, VIHA, Almora, are acknowledged for providing the plant pathogenic fungal cultures used in this study. Sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene was performed at the Institute of Microbial Technology, Chandigarh, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvakumar, G., Joshi, P., Nazim, S. et al. Exiguobacterium acetylicum strain 1P (MTCC 8707) a novel bacterial antagonist from the North Western Indian Himalayas. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 131–137 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9874-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9874-4