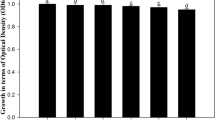
Abstract
Mung bean seedlings inoculated with Enterobacter asburiae PSI3, a gluconic acid-producing rhizosphere isolate, enhanced plant growth in the presence of phytotoxic levels of Cd2+ in gnotobiotic pot experiments as compared to the uninoculated Cd-treated plants. Addition of organic acids to Cd-stressed seedlings promoted root elongation. Hematoxylin competition assays showed that organic acids could displace Cd2+ from the Cd2+: hematoxylin complex in the same order of effectiveness as was found for restoration of root net elongation viz. oxalate > malate > succinate while gluconate was effective at higher concentrations. Root associated Cd2+, assessed by hematoxylin staining of roots was found to be reduced when roots were treated with organic acid. Cd stress increased antioxidant enzymes such as peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in mung bean roots while organic acid treatment suppressed the up-regulation of these enzymes by Cd.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arduini I, Godbold DL, Onnis A (1994) Cadmium and copper change root growth and morphology of Pinus pinea and Pinus pinaster seedlings. Physiol Plant 92:675–680. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1994.tb03039.x
Barea J-M, Pozo MJ, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2005) Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere. J Exp Bot 56:1761–1778. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri197
Baszynski T, Wajda L, Krol M, Wolinska D, Krupa Z, Tukendorf A (1980) Photosynthetic activity of Cd-treated tomato plants. Physiol Plant 48:365–370. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1980.tb03269.x
Belimov AA, Dietz K-J (2000) Effect of associative bacteria on element composition of barley seedlings grown in solution culture at toxic cadmium concentrations. Microbiol Res 155:113–121
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202005000100003
Burd GI, Dixon DG, Glick BR (1998) A plant growth promoting bacterium that decrease nickel toxicity in seedlings. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3663–3668
Burd GI, Dixon GD, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth promoting bacterium that decreases heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 46:237–245. doi:10.1139/cjm-46-3-237
Chiang P-N, Wang MK, Chiu CY, Chou S-Y (2006) Effects of cadmium amendments on low-molecular-weight organic acid exudates in rhizosphere soils of tobacco and sunflower. Environ Toxicol 21:479–488. doi:10.1002/tox.20210
Cieslinski G, Van Rees KCJ, Szmigielska AM, Krishnamurti GSR, Huang PM (1998) Low-molecular-weight organic acids in rhizosphere soils of durum wheat and their effect on cadmium bioaccumulation. Plant Soil 203:109–117. doi:10.1023/A:1004325817420
Delhaize E, Ryan PR, Randall PJ (1993) Aluminium tolerance in wheat. Plant Physiol 103:695–702
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreon V (2008) Improvement of Brassica napus growth under cadmium stress by cadmium-resistant rhizobacteria. Soil Biol Biochem 40:74–84. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.06.024
Diels L, van der Lelie N, Bastiaens L (2002) New developments in treatment of heavy metal contaminated soils. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 1:75–82. doi:10.1023/A:1015188708612
Gadd GM (2000) Bioremedial potential of microbial mechanisms of metal mobilization and immobilization. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:271–279. doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(00)00095-1
Glick BR (2003) Phytoremediation: synergistic use of plants and bacteria to clean up the environment. Biotechnol Adv 21:383–393. doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(03)00055-7
Goldstein AH (1986) Bacterial solubilization of mineral phosphates: historical perspective and future prospects. Am J Altern Agric 1:51–57
Goldstein AH (1995) Recent progress in understanding the molecular genetics and biochemistry of calcium phosphate solubilization by gram negative bacteria. Biol Agric Hortic 12:185–193
Gyaneshwar P, Parekh LJ, Archana G, Poole PS, Collins MD, Hutson RA et al (1999) Involvement of a phosphate starvation inducible glucose dehydrogenase in soil phosphate solubilisation by Enterobacter asburiae PSI3. FEMS Microbiol Lett 171:223–229. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13436.x
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanism for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.366.1
Han F, Shan X, Zhang S, Wen B, Owens G (2006) Enhanced cadmium accumulation in maize roots—the impact of organic acids. Plant Soil 289:355–368. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9145-9
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2003) Changes in protein and amino acid contents in two cultivars of rice seedlings with different apparent tolerance to cadmium. Plant Growth Regul 40:147–155. doi:10.1023/A:1024248021314
Inoune M, Ninomiya S, Tohoyama H, Joho M, Murayama T (1994) Different characteristics of roots in the cadmium tolerance and Cd-binding complex formation between mono- and dicotyledenous plants. J Plant Res 107:201–207. doi:10.1007/BF02344245
Johnson LB, Cunningham BA (1972) Peroxidase activity in healthy and leaf rust infected wheat leaves. Phytochemistry 11:547–551. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(72)80011-6
Jones DL, Dennis PG, Owen AG, van Hees PAW (2003) Organic acid behavior in soils—misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Plant Soil 248:31–41. doi:10.1023/A:1022304332313
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2006) Role of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 26:1–15. doi:10.1051/agro:2005055
Kochian LV, Pineros MA, Hoekenga OA (2005) The physiology, genetics and molecular biology of plant aluminum resistance and toxicity. Plant Soil 274:175–195. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-1158-7
Lucy M, Reed E, Glick BR (2004) Applications of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 86:1–25. doi:10.1023/B:ANTO.0000024903.10757.6e
Ma JF (2000) Role of organic acids in detoxification of aluminium in higher plant. Plant Cell Physiol 41:383–390
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autooxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x
Meharg AA (2005) Mechanisms of plant resistance to metal and metalloid ions and potential biotechnological applications. Plant Soil 274:163–174. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-0262-z
Metwally A, Safronova V, Belimov AA, Dietz KJ (2005) Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. J Exp Bot 56:167–178
Nigam R, Srivastva S, Prakash S, Srivastava MM (2000) Effect of organic acids on availability of cadmium in wheat. Chem Spec Bioavail 12:125–132. doi:10.3184/095422900782775481
Parker DR, Pedler JF (1998) Probing the malate hypothesis of differential aluminium tolerance in wheat by using other rhizotoxic ions as proxies for Al. Planta 205:389–396. doi:10.1007/s004250050335
Pineros MA, Magalhaes JV, Alves VMC, Kochian LV (2002) The physiology and biophysics of an aluminium tolerance mechanism based on root citrate exudation in maize. Plant Physiol 129:1194–1206. doi:10.1104/pp.002295
Pishchik VN, Vorobyev NI, Chernyaeva II, Timofeeva SV, Kozhemyakov AP, Alexeev YV et al (2002) Experimental and mathematical simulation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and plant interaction under cadmium stress. Plant Soil 243:173–186. doi:10.1023/A:1019941525758
Rani A, Shouche YS, Goel R (2008) Declination of copper toxicity in pigeon pea and soil system by growth-promoting Proteus vulgaris KNP3 Strain. Curr Microbiol 57:78–82. doi:10.1007/s00284-008-9156-2
Reed MLE, Glick BR (2005) Growth of canola (Brassica napus) in the presence of plant growth-promoting bacteria and either copper or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Can J Microbiol 51:1061–1069. doi:10.1139/w05-094
Rodrıguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339. doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(99)00014-2
Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Jones DL (2001) Function and mechanism of organic anion exudation from plant roots. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:527–556. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.527
Safronova VI, Stepanok VV, Engqvist GL, Alekseyev YV, Belimov AA (2006) Root-associated bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase improve growth and nutrient uptake by pea genotypes cultivated in cadmium supplemented soil. Biol Fertil Soils 42:267–272. doi:10.1007/s00374-005-0024-y
Saleem M, Arshad M, Hussain S, Bhatti AS (2007) Perspective of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) containing ACC deaminase in stress agriculture. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:635–648. doi:10.1007/s10295-007-0240-6
Schutzendubel A, Schwanz P, Teichmann T, Gross K, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Douglas L et al (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in antioxidative systems, hydrogen peroxide content, and differentiation in scots pine roots. Plant Physiol 127:887–898. doi:10.1104/pp.127.3.887
Sharma V, Kumar V, Archana G, Naresh Kumar G (2005) Substrate specificity of glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) of Enterobacter asburiae PSI3 and rock phosphate solubilization with GDH substrates as C sources. Can J Microbiol 51:477–482. doi:10.1139/w05-032
Singh OV, Labana S, Pandey G, Budhiaraja R, Jain RK (2003) Phytoremediation: an overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:405–412
Sinha S, Mukherjee SK (2008) Cadmium-induced siderophore production by a high Cd-resistant bacterial strain relieved Cd toxicity in plants through root colonization. Curr Microbiol 56:55–60. doi:10.1007/s00284-007-9038-z
Somashekaraiah BV, Padmaja K, Prasad ARK (1992) Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germinating seedlings of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorophyll degradation. Physiol Plant 85:85–89. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb05267.x
Tripura C, Reddy PS, Reddy MK, Sashidhar B, Podile AR (2007) Glucose dehydrogenase of a rhizobacterial strain of Enterobacter asburiae involved in mineral phosphate solubilization shares properties and sequence homology with other members of Enterobacteriacea. Indian J Microbiol 47:126–131. doi:10.1007/s12088-007-0025-7
Vassilev A, Vangronsveld J, Yordanov I (2002) Cadmium phytoextraction: present state biological background and research needs. Bulg J Plant Physiol 28:68–95
Acknowledgments
S. Shukla is grateful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for providing fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavita, B., Shukla, S., Naresh Kumar, G. et al. Amelioration of phytotoxic effects of Cd on mung bean seedlings by gluconic acid secreting rhizobacterium Enterobacter asburiae PSI3 and implication of role of organic acid. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2965–2972 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9838-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9838-8