Abstract
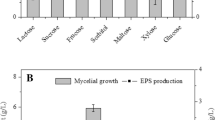
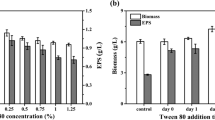
Maltose and yeast extract were the most favourable carbon and nitrogen sources for exopolysaccharide production by submerged culture of Shiraia bambusicola WZ-003, and initial maltose and yeast extract concentrations were at 30 and 3 g l−1, respectively. Plant oils could increase the mycelial growth and exopolysaccharide production in tested concentration. K+ and Mg2+ could enhance the mycelial growth and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis. The optimal cultivation temperature and initial pH were found to be 26°C and 6.0, respectively. Exopolysaccharide concentration reached 0.53 g l−1 in 15-l fermenter under optimal nutritional conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babitskaya VG, Shcherba VV, Pushkova TA, Smirnov DA (2005) Polysaccharides of Ganoderma lucidum: factors affecting their production. Appl Biochem Microbiol 41:169–173. doi:10.1007/s10438-005-0029-1
Bao XF, Wang XS, Dong Q, Fang JN, Li XY (2002) Structural features of immunologically active polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum. Phytochemistry 59:175–181. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00450-2
Chang MY, Tsai GJ, Houng JY (2006) Optimization of the medium composition for the submerged culture of Ganoderma lucidum by Taguchi array design and steepest ascent method. Enzyme Microb Technol 38:407–414. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.06.011
Chen Y, Zhang YX, Li MH, Zhao WM, Shi YH, Miao ZH et al (2005) Antiangiogenic activity of 11,11′-dideoxyverticillin, a natural product isolated from the fungus Shiraia bambusicola. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329:1334–1342. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.115
Cui FJ, Li Y, Xu ZH, Xu HY, Sun K, Tao WY (2006) Optimization of the medium composition for production of mycelial biomass and exo-polymer by Grifola frondosa GF9801 using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 97:1209–1216. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.005
Fang J, Yie C, Liu Y, Chu K, Pan W, Bao Q et al (1980) Shiraia bambusicola I. Isolation and identification of two polysaccharides, Sb1 and Sb2 from a species of ascomycetes. J Biochem Biophys 12:365–370 (in Chinese)
Jia XM, Xu XH, Zhuang BC, Lin HP (2006) The progress of biological research of medicinal fungus Shiraia bambusicola. Chin Microbiol 33:147–150 (in Chinese)
Kim SW, Hwang HJ, Xu CP, Na YS, Song SK, Yun JW (2002) Influence of nutritional conditions on the mycelial growth and exopolysaccharide production in Paecilomyces sinclairii. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:389–393. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2002.01105.x
Kim SW, Xu CP, Hwang HJ, Choi JW, Kim CW, Yun JW (2003) Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides from an enthomopathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris NG3. Biotechnol Prog 19:428–435. doi:10.1021/bp025644k
Lai GH, Fu LY (2000) Investigation on the host of Shiraia bambusicola. Chin Wild Plant Resour 19:8–11 (in Chinese)
Lee BC, Bae JT, Pyo HB, Choe TB, Kim SW, Hwang HJ et al (2003) Biological activities of the polysaccharides produced from submerged culture of the edible Basidiomycete Grifola frondosa. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:574–581. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00026-7
Liu F, Ooi VE, Chang ST (1997) Free radical scavenging activities of mushroom polysaccharide extracts. Life Sci 60:763–771. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(97)00004-0
Ma G, Khan SI, Jacob MR, Tekwani BL, Li Z, Pasco DS et al (2004) Antimicrobial and antileishmanial activities of hypocrellins A and B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:4450–4452. doi:10.1128/AAC.48.11.4450-4452.2004
Ohno N, Furukawa M, Miura N, Adachi Y, Motoi M, Yadomae T (2001) Antitumor β-glucan from the cultured fruit body of Agaricus blazei. Biol Pharm Bull 24:820–828. doi:10.1248/bpb.24.820
Park JP, Kim SW, Hwang HJ, Cho YJ, Yun JW (2002) Stimulatory effect of plant oils and fatty acids on the exo-biopolymer production in Cordyceps militaris. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:250–255. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00099-6
Yang FC, Liau CB (1998) Effects of cultivating conditions on the mycelial growth of Ganoderma lucidum in submerged flask cultures. Bioprocess Eng 19:233–236
Yang FC, Ke YF, Kuo SS (2000) Effect of fatty acids on the mycelia growth and polysaccharide formation by Ganoderma lucidum in shake flask cultures. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:295–301. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00213-1
Zhang J, Cao EH, Li JF, Zhang TC, Ma WJ (1998) Photodynamic effects of hypocrellin A on three human malignant cell lines by inducing apoptotic cell death. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 43:106–111
Zou X (2005) Optimization of nutritional factors for exopolysaccharide production by submerged cultivation of the medicinal mushroom Oudemansiella radicata. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1267–1271. doi:10.1007/s11274-005-1941-5
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Zhejiang Department of Science and Technology (Project No. 2007C23012), P.R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., He, G. Influence of nutritional conditions on exopolysaccharide production by submerged cultivation of the medicinal fungus Shiraia bambusicola . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2903–2907 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9832-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9832-1