Abstract
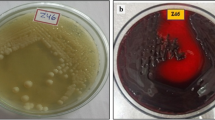
The biosorption of several toxic heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Co, Ni, Zn and Cu) by the exopolysaccharide (EPS) produced by Paenibacillus jamilae, a potential biosorbent for metal remediation and recovery was studied. Firstly, the biochemical composition of this bacterial polymer was determined. Glucose was the most abundant neutral sugar, followed by galactose, rhamnose, fucose and mannose. The polymer presented a high content of uronic acids (28.29%), which may serve as binding sites for divalent cations. The presence of carboxylic groups was also detected by infrared spectroscopy. The EPS presented an interesting affinity for Pb in comparison with the other five metals. Lead biosorption (303.03 mg g−1) was tenfold higher (in terms of mg of metal adsorbed per gram of EPS) than the biosorption of the rest of metals. Biosorption kinetics, the effect of pH and the effect of competitive biosorption were determined. Finally, we found that the EPS was able to precipitate Fe(III), but the EPS-metal precipitate did not form with Fe(II), Pb(II), Cd(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera M, Quesada MT, Guerra del Águila V, Morillo JA, Rivadeneyra MA, Ramos-Cormenzana A et al (2008) Characterisation of Paenibacillus jamilae strains that produce exopolysaccharide during growth on and detoxification of olive mill wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 99:5640–5644. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.032
Ahluwalia SS, Goyal D (2007) Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 98:2243–2257. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.12.006
Bramhachari PV, Dubey SK (2006) Isolation and characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Vibrio harveyi strain VB23. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:571–577. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.01967.x
Corzo J, León-Barrios M, Hernando-Rico V, Gutierrez-Navarro AM (1994) Precipitation of metallic cations by the acidic exopolysaccharides from Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium (Chamaecytisus) strain BGA-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4531–4535
Díaz-Marrero AR, Santamaría M, Hernández J, Corzo J (2004) Coprecipitation of Th4+ and the purified extracellular polysaccharide produced by bacterium Bradyrhizobium (Chamaecytisus) strain BGA-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:356–362
Freire-Nordi CS, Vieira AAH, Nakaie CR, Nascimento OR (2005) Effect of polysaccharide capsule of the microalgae Staurastrum iversenii var. americanum on diffusion of charged and uncharged molecules, using EPR technique. Braz J Phys 36:75–82
Gadd GM (1996) Roles of microorganisms in the environmental fate of radionuclides. Endeavour 20:150–156. doi:10.1016/S0160-9327(96)10021-1
Geddie L, Sutherland IW (1993) Uptake of metals by bacterial polysaccharides. J Appl Bacteriol 74:467–472
Guibaud G, Tixier N, Boujou A, Baudu M (2003) Relation between extracellular polymer’s composition and its ability to complex Cd, Cu and Pb. Chemosphere 52:1701–1710. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00355-2
Guibaud G, Hullebusch E, Bordas F (2006) Lead and cadmium biosorption by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from activated sludges: pH-sorption edge tests and mathematical equilibrium modelling. Chemosphere 64:1955–1962. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.012
Gutnick DL, Bach H (2000) Engineering bacterial biopolymers for the biosorption of heavy metals; new products and novel formulations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:451–460. doi:10.1007/s002530000438
Kim SY, Kim JH, Kim CI, Oh O (1996) Metal adsorption of the polysaccharide produced from Methylobacterium organophilum. Biotechnol Lett 18:1161–1164. doi:10.1007/BF00128585
Lau TC, Wu XA, Chua H, Qian PY, Wong PK (2005) Effect of exopolysaccharides on the adsorption of metal ions by Pseudomonas sp. CU-1. Water Sci Technol 52:63–68
Lin S, Rayson GS (1998) Impact of surface modification on binding affinity distributions of Datura innoxia biomass to metal ions. Environ Sci Technol 32:1488–1493. doi:10.1021/es970843z
Loaëc M, Olier R, Guezennec J (1997) Uptake of lead, cadmium and zinc by a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide. Water Res 31:1171–1179. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00375-2
Lorenz H (1979) Binding forms of toxic heavy metals, mechanisms of entrance of heavy metals into food chain and possible measures to reduce levels in foodstuff. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 3:47–58. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(79)90059-9
Merroun ML, Ben Chekroun K, Arias JM, González MT (2003) Lanthanum fixation by Myxococcus xanthus: cellular location and extracellular polysaccharide observation. Chemosphere 52:113–120. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00220-0
Morillo JA, Aguilera M, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Monteoliva-Sánchez M (2006) Production of a metal binding exopolysaccharide by Paenibacillus jamilae using two-phase olive-mill waste as fermentation substrate. Curr Microbiol 53:189–193. doi:10.1007/s00284-005-0438-7
Morillo JA, Guerra del Águila V, Aguilera M, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Monteoliva-Sánchez M (2007) Production and chemical characterization of the exopolysaccharide produced by Paenibacillus jamilae grown on olive mill waste waters. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1705–1710. doi:10.1007/s11274-007-9418-3
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:730–750. doi:10.1007/s002530051457
Pagnanelli F, Papini MP, Toro L, Trifoni M, Vegliò F (2000) Biosorption of metal ions on Arthrobacter sp.: biomass characterization and biosorption modeling. Environ Sci Technol 34:2773–2778. doi:10.1021/es991271g
Paperi R, Micheletti E, De Philips R (2006) Optimization of copper sorbing-desorbing cycles with confined cultures of the exopolysaccharide-producing cyanobacterium Cyanospira capsulata. J Appl Microbiol 101:1351–1356. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03021.x
Pradhan S, Singh S, Rai LC (2007) Characterization of various functional groups present in the capsule of Microcystis and study of their role in biosorption of Fe, Ni and Cr. Bioresour Technol 98:595–601. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.02.041
Pulsawat W, Leksawasdi N, Rogers PL, Foster LJ (2003) Anions effects on biosorption of Mn(II) by extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) from Rhizobium etli. Biotechnol Lett 25:1267–1270. doi:10.1023/A:1025083116343
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati SA (2003) Removal of metal ions from aqueous solution by polysaccharide produced from Bacillus firmus. Water Res 37:4231–4235. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00418-4
Schmitt J, Flemming HC (1998) FTIR-spectroscopy in microbial and material analysis. Int Biodeter Biodegr 41:1–11. doi:10.1016/S0964-8305(98)80002-4
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Wang CM (2006) FTIR-spectral analysis of two photosynthetic H2-producing strains and their extracellular polymeric substances. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:204–210. doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0442-2
Veglio F, Beolchini F, Gasbarro A (1997) Biosorption of toxic metals: an equilibrium study using free cells of Arthrobacter sp. Process Biochem 32:99–105. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(96)00047-7
Volesky B (2001) Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: biosorption for the next century. Hydrometallurgy 59:203–221. doi:10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00160-2
Acknowledgements
This work was possible thanks to a FPI fellowship of the Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Spain) funded under the Project No. REN 2000-1502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morillo Pérez, J.A., García-Ribera, R., Quesada, T. et al. Biosorption of heavy metals by the exopolysaccharide produced by Paenibacillus jamilae . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2699–2704 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9800-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9800-9