Abstract
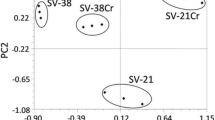
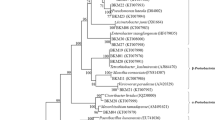
Four bacterial isolates were examined for their ability to increase the availability of water soluble Cu, Cr, Pb and Zn in soils and for their effect on metals uptake by Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis was used to show that the bacterial cultures were genetically diverse. Bacterial isolates S3, S28, S22 and S29 had 16S rRNA gene sequences that were most similar to Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pumilus, Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and Brevibacterium halotolerans based on 100% similarity in their 16S rDNA gene sequence, respectively. Filtrate liquid media that had supported B. pumilus and B. subtilis growth significantly increased Cr and Cu extraction from soil polluted with tannery effluent and from Cu-rich soil, respectively, compared to axenic media. The highest concentrations of Pb (0.2 g kg−1), Zn (4 g kg−1) and Cu (2 g kg−1) were accumulated in shoots of Z. mays grown on Cu-rich soil inoculated with Br. halotolerans. The highest concentration of Cr (5 g kg−1) was accumulated in S. bicolor roots grown in tannery-effluent-polluted soil inoculated with a mixed inoculum of bacterial strains. These results show that bacteria play an important role in increasing metal availability in soil, thus enhancing Cr, Pb, Zn and Cu accumulation by Z. mays and S. bicolor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RA, Delorme TA, Angle JS, Chaney RL, Ghanem K, Moawad H, Ghozlan HA (2003a) Phenotypic characterization of microbes in the rhizosphere of Alyssum murale. Int J Phytoremediation 5:367–379
Abou-Shanab RA, Angle JS, Delorme TA, Chaney RL, van Berkum P, Moawad H, Ghanem K, Ghozlan HA (2003b) Rhizobacterial effects on nickel extraction from soil and uptake by Alyssum murale. New Phytol 158:219–224
Abou-Shanab RA, Angle JS, Chaney RL (2006) Bacterial inoculants affecting nickel uptake by Alyssum murale from low, moderate and high Ni soils. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2882–2889
Abou-Shanab RAI, Angle JS, van Berkum P (2007) Chromate-tolerant bacteria for enhanced metal uptake by Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.). Int J Phytoremediation 9:91–105
Altschul SF, Thomas LM, Alejandro AS, Jinghui Z, Webb M, David JL (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSt-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Angle SJ, Chaney R, Rhee D (1993) Bacterial resistance to heavy metals related to extractable and total metal concentrations in soil and media. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1443–1446
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1999) Short protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, ISBN 0-471-32938-X
Belimov AA, Safronova VI, Sergeyeva TA, Egorova TN, Matveyeva VA, Tsyganov VE, Borisov AY, Tikhonovich IA, Kluge C, Preisfeld A, Dietz KJ, Stepanok VV (2001) Characterization of plant growth-prompting rhizobacteria isolated from polluted soils and containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can J Microbiol 47:642–652
Burd GI, Dixon DC, Click BR (1998) A plant growth promoting bacterium that decreases nickel toxicity in seedlings. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3663–3668
Chaney RL, Malik M, Lim YM, Brown SL, Brewer EP, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1997) Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:279–284
Chen YX, Wang YP, Lin Q, Luo YM (2005) Effect of copper-tolerant rhizosphere bacteria on mobility of copper in soil and copper accumulation by Elsholtzia splendens. Environ Int 31:861–866
Cheng S (2003) Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:192–198
Chlopecka A, Bacon JR, Wilson MJ, Kay J (1996) Heavy metals in the environment. J Environ Qual 25:69–79
Delorme TA, Gagliardi JV, Angle JS, Chaney RL (2001) Influence of the zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens J. & C. Presl. and the nonmetal accumulator Trifolium pratense L on soil microbial population. Can J Microbiol 67:190–197
De-Souza MP, Huang CPA, Chee N, Terry N (1999) Rhizosphere bacteria enhance that accumulation of selenium and mercury in wetland plants. Planata 209:259–263
Ernst WHO (1996) Bioavailability of heavy metals and decontamination of soil by plants. Appl Geochem 11:163–167
Forster J (1995) Determination of soil pH. In: Alef K, Nannipieri P (eds) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biotechnology. Academic press, San Diego, CA, pp 55, ISBN 0-12-513840-7
Ghaderian MYS, Anthony JEL, Baker AJM (2000) Seedling mortality of metal hyperaccumulator plants resulting from damping off by Pythium spp. New Phytol 146:219–224
Gilis A (1993) Interactie tussen verschillende potentieel toxische metalen (Zn, Cd, Ni en Al) en siderofoor-afhankelijke ijzer-opname in verschillende fluorescerende Pseudomonas stamen. Licentiaatsthesis, Brussels, Belgium
Glass DJ (1999) Economic potential of phytoremediation. In: Raskin I, Ensley BD (eds) Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, pp 15–31, ISBN0-47-1-(1925)4-6
Glick RB (2003) Phytoremediation: synergistic use of plants and bacteria to clean up the environment. Biotechnol Adv 21:383–393
Hassan MET (1996) Genetic mechanism of heavy metal resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CMG103. Ph.D Thesis, University of Karachi, Pakistan
Huyer M, Page W (1988) Zn2+ increases siderophore production in Azotobacter vinelandii. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2625–2631
Ibekwe AM, Angle JS, Chaney RL, van Berkum P (1995) Sewage sludge and heavy metal effects on nodulation and nitrogen fixation of legumes. J Environ Qual 24:1199–1204
Kukier U, Peters CA, Chaney RL, Angle JS, Roseberg RJ (2004) The effect of pH on metal accumulation in two Alyssum species. J Environ Qual 32:2090–2102
McGrath SP, Cunliffe CH (1985) A simplified method for the extraction of the metals Fe, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Ni, Cr, Co, and Mn from soils and sewage sludge. J Sci Food Agric 36:794–798
McGrath SP, Chaudri AM, Giller KE (1995) Long-term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants. J Ind Microbiol 14:94–104
Mengonii A, Barzanti R, Gonnelli C, Gabbrielli R, Bazzicalupo M (2001) Characterization of nickel-resistant bacteria isolated from serpentine soil. Environ Microbiol 3:691–698
Pulford ID, Watson C (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated land by trees–a Review. Environ Int 29:529–540
Ralph D, McClelland M, Welsh J, Baranton G, Perolat P (1993) Leptospira species categorized by arbitrary primed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and by mapped restriction polymorphism in PCR-amplified rRNA genes. J Bacteriol 175:973–981
Rhodes MW, Kator H, Kotob S, van Berkum P, Kaattari I, Vogelbein W, Quinn F, Floyd MM, Butler WR, Ottinger CA (2003) Mycobacterium shottsii sp. nov., a slowly growing species isolated from Chesapeake Bay striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:421–424
Schlegel HG, Cosson JP, Baker AM (1991) Nickel hyperaccumulating plants provide a niche for nickel-resistant bacteria. Botanical Acta 104:18–25
Selenska-pobell S, Otto A, Kutschke S (1998) Identification and discrimination of Thiobacilli using ARDREA, RAPD and Rep-APD. J Appl Bacteriol 84:1085–1091
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press Inc., San Diego, ISBN 0-12-652840-3
Tessier A, Campbell PGC (1988) Partitioning of trace metals in sediments. In: Kramer JR, Allen HE (eds) Metal speciation: theory, analysis and application. Lewis Publishers, Inc., Chelsea, MI, ISBN-10:0873711408
Trapp S, Karlson U (2001) Aspects of phytoremediation of organic pollutants. J Soils Sediments 1:1–7
van Berkum P, Beyene D, Eardly BD (1996) Phylogenetic relationships among Rhizobium species nodulating the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.).Int. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:240–244
van Berkum P, Fuhrmann JJ (2000) Evolutionary relationships among the soybean bradyrhizobia reconstructed from 168 rRNA gene and internally transcribed spacer region sequence divergence. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:2165–2172
van der Lelie D, Corbisier P, Diels L, Gilis A, Lodewyckx C, Mergeay M, Taghavi S, Spelmans N, Vangronsveld J (1999) The role of bacteria in the phytoremediation of heavy metals. In: Terry N, Banuelos E (eds) Phytoremediation of contaminated soil and water. G Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Fl, USA, pp 265–281, ISBN 1-56670-450-2
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Wenzel WW, Jockwer F (1999) Accumulation of heavy metals in plants grown on mineralized soils of the Austrian Alps. Environ Pollut 104:145–155
Whiting SN, De Souza M, Terry N (2001) Rhizosphere bacteria mobilize Zn for hyperaccumulator by Thlaspi caerulescens. Environ Sci Technol 35:3144–3150
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acid Res 18:6531–6535
Wollum AG (1982) Cultural methods for soil microorganisms. In: Page AL (Eds) Methods of soil analysis: chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Inc./Soil Science Society of America, Inc. Agronomy ASIN: B000KEKA20, pp. 781–802
Zavoda J, Cutright T, Szpak J, Fallon E (2001) Uptake, selectivity, and inhibition of hydroponic treatment of contaminants. J Environ Eng 127:502–508
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou-Shanab, R.A., Ghanem, K., Ghanem, N. et al. The role of bacteria on heavy-metal extraction and uptake by plants growing on multi-metal-contaminated soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 253–262 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9464-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9464-x