Abstract
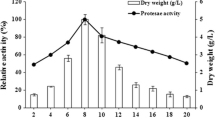
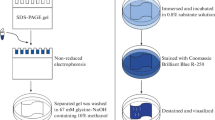
Streptomyces violaceoruber produces two different classes of mycelium, the substrate and the aerial mycelium. Since proteases have been associated with morphological turnover processes in other Streptomyces species, the presence of excretory/secretory proteolytic activities was investigated here in S. violaceoruber culture supernatants. Various polypeptide bands, with apparent molecular masses ranging from 40 to 180 kDa, were detected in soy trypticase broth (STB) culture media supernatants following 72 h of growth, using Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Zymograms showed the presence of five proteolytic enzymes (Spvio1–5), which migrated as bands of 167.7, 130.7, 110.7, 48.3 and 40.9 kDa, respectively. The characterization of these proteases by specific inhibitors showed that Spvio1–4 belong to the serine protease group and Spvio5 corresponds to a cysteine protease. Additionally, Spvio2 and 5 were inhibited by a mixture of EDTA and EGTA, indicating that both require divalent cations. The protease pattern obtained in STB enriched with glucose was identical to that obtained in STB. However, Spvio3 and 4 were absent when nitrogen was added to the culture medium. Cell death was fluorescently detected following 72 h of S. violaceoruber growth in STB and in STB that was enriched with glucose. On the contrary, no cell death was detected in nitrogen-enriched STB media. Additionally, the formation of the aerial mycelium was impaired in solid cultures of STB media enriched with nitrogen. These results demonstrate that the composition of the media influences the morphological turnover of the colony and the pattern of excreted/secreted proteases from S. violaceoruber, and suggest that Spvio3 and 4 are involved in the aerial mycelium formation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bresollier P, Letourneau F, Urdaci M, Verneuil B (1999) Purification and characterization of keratolytic serine proteinase from Streptomyces albidoflvus. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2570–2576
Böckle B, Galunski B, Muller R (1995) Characterization of a keratolytic serine proteinase from Streptomyces pactum DSM 40530. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3705–3710
El Kirat K, Prigent A, Chauvet J, Roux B, Besson F (2003) Transphosphatidylation activity of Streptomyces chromofuscus phospholipase D in biomimetic membranes. Eur J Biochem 270:4523–4530
Fernandez M, Sanchez J (2001) Viability staining and terminal deoxyribonucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling of the mycelium in submerged cultures of Streptomyces antibioticus ETH7451. J Microbiol Methods 47:293–298
Fernandez M, Sanchez J (2002) Nuclease activities and cell death processes associated with the development of surface cultures of Streptomyces antibioticus ETH7451. Microbiology 148:405–412
Gibb GD, Strohl WR (1988) Physiological regulation of protease activity in Streptomyces peucetius. Can J Microbiol 34:187–190
Ginther CL (1978) Sporulation and the production of serine protease and cephamycin C by Streptomyces sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 15:522–526
Gunther CL (1979) Sporulation and the production of serine protease and cephamycin C by Streptomyces lactamdurams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 15:522–526
Hale VM, McGrew B, Carlson, Schottel J (1992) Heterologous expression and secretion of a Streptomyces scabies esterase in Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 174:2431–2439
Kim I, Lee K (1995) Physiological roles of leupeptin and extracellular proteases in mycelium development of Streptomyces exfoliatus SMF13. Microbiology 141:1017–1025
Kim I, Lee K (1996) Trypsin-like protease of Streptomyces exfoliatus SMF13 a potential agent in mycelial differentiation. Microbiology 142:1797–1806
Khetan A, Hu W, Sherman D (2000) Heterogeneous distribution of lysine 6 aminotransferase during cephamycin C biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus demonstrated using green fluorescent protein as a reporter. Microbiology 146:1869–1880
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lounes A, Lebrihi A, Benslimane C, Lefebvre G, Germain P (1995) Glycerol effect on Spiramycin production and valine catabolism in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Curr Microbiol 31:304–311
Martin J, Demain A (1980) Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev 44:230–251
Mendez C, Braña AF, Manzanal MB, Hardisson C (1985) Role of substrate mycelium. Can J Microbiol 31:446–450
Nicieza R, Huergo J, Connolly B, Sanchez J (1999) Purification, characterization, and role of nucleases and serine proteases in Streptomyces differentiation. Analogies with the biochemical processes described in late steps of eukaryotic apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:20366–20375
Taddei A, Tremarias MM, Hartung de Capriles C (1998) Viability studies on actinomycetes. Mycopathologia 143:161–164
Wildermuth H (1970) Development and organization of the aerial mycelium in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol 60:43–50
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from FONACIT No. S1-97003714 and DAAD 227.1044010082 to Antonieta Taddei, and FONACIT No. 2000001639 to Jose Bubis. Juan Giarrizzo is a recipient of a graduate school fellowship from FONACIT and a graduate research assistantship from Decanato de Investigación y Desarrollo, Universidad Simón Bolívar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giarrizzo, J., Bubis, J. & Taddei, A. Influence of the culture medium composition on the excreted/secreted proteases from Streptomyces violaceoruber . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 553–558 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9260-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9260-z