Abstract
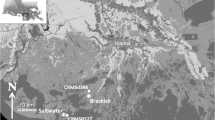
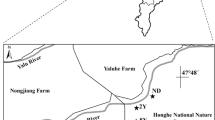
The wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are experiencing serious degradation, with more than 90,000 hectares of marshland converted to wet meadow or meadow after 40 years of drainage. However, little is known about the effects of wetland conversion on soil C stocks and the quality of soil organic carbon (SOC) (defined by the proportion of labile versus more resistant organic carbon compounds). SOC, microbial biomass carbon, light fraction organic carbon (LFOC), dissolved organic carbon, and the chemical composition of SOC in the soil surface layer (0–10 cm), were investigated along a wetland degradation gradient (marsh, wet meadow, and meadow). Wetland degradation caused a 16 % reduction in the carbon stocks from marsh (178.7 ± 15.2 kg C m−2) to wet meadow (150.6 ± 21.5 kg C m−2), and a 32 % reduction in C stocks of the 0–10 cm soil layer from marsh to meadow (122.2 ± 2.6 kg C m−2). Wetland degradation also led to a significant reduction in SOC quality, represented by the lability of the carbon pool as determined by a density fractionation method (L LFOC), and a significant increase in the stability of the carbon pool as reflected by the alkyl-C:O-alkyl-C ratio. 13C NMR spectroscopy showed that the labile form of C (O-alkyl-C) declined significantly after wetland degradation. These results assist in explaining the transformation of organic C in these plateau wetland soils and suggest that wetland degradation not only caused SOC loss, but also decreased the quality of the SOC of the surface soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SOM:
-
Soil organic matter
- SOC:
-
Soil organic carbon
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- C:N:
-
Carbon to nitrogen ratio
- BD:
-
Soil bulk density
- LFOC:
-
Light fraction organic carbon
- LFN:
-
Light fraction nitrogen
- MBC:
-
Microbial biomass carbon
- MBN:
-
Microbial biomass nitrogen
- DOC:
-
Dissolved organic carbon
- DON:
-
Dissolved organic nitrogen
- 13C CP/MAS NMR:
-
Solid-state 13C cross polarization with magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance
- DO C:N:
-
DOC-to-DON ratio
- LF C:N:
-
LFOC-to-LFN ratio
References
Ågren GI (2000) Temperature dependence of old soil organic matter. J Human Environ 29(1):55
Almendros G, Dorado J, González-Vila FJ, Blanco MJ, Lankes U (2000) 13C NMR assessment of decomposition patterns during composting of forest and shrub biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 32(6):793–804
Arevalo CBM, Bhatti JS, Chang SX, Jassal RS, Sidders D (2010) Soil respiration in four different land use systems in north central Alberta, Canada. J Geophys Res 115(G1):G01003. doi:10.1029/2009jg001006
Arevalo CBM, Chang SX, Bhatti JS, Sidders D (2012) Mineralization potential and temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon under different land uses in the parkland region of Alberta, Canada. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76(1):241–251. doi:10.2136/sssaj2011.0126
Bai J, Ouyang H, Wang Q, Gao H, Ding Q (2009) Changes in landscape patterns of alpine wetlands in Roige plateau before and after drainage. Trans CSAE 25(Supp 1):64–68 (in Chinese with english abstract)
Baldock JA, Oades JM, Nelson PN, Skene TM, Golchin A, Clarke P (1997) Assessing the extent of decomposition of natural organic materials using solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Aust J Soil Res 35(5):1061–1084. doi:10.1071/S97004
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17(6):837–842
Chen CR, Xu ZH, Mathers NJ (2004) Soil carbon pools in adjacent natural and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68(1):282–291. doi:10.2136/sssaj2004.2820
Chen H, Gao Y, Yao S, Ning W, Wang Y, Luo P, Tian J (2008) Spatiotemporal variation of methane emissions from alpine wetlands in Zoige Plateau. Acta Ecol Sin 28(7):3425–3437
Christ MJ, David MB (1996) Temperature and moisture effects on the production of dissolved organic carbon in a spodosol. Soil Biol Biochem 28(9):1191–1199
Craine JM, Fierer N, McLauchlan KK (2010) Widespread coupling between the rate and temperature sensitivity of organic matter decay. Nat Geosci 3 (12):854–857. doi:10.1038/ngeo1009
Dai KO, Johnson C, Driscoll C (2001) Organic matter chemistry and dynamics in clear-cut and unmanaged hardwood forest ecosystems. Biogeochemistry 54(1):51–83. doi:10.1023/a:1010697518227
Dignac M-F, Knicker H, Kögel-Knabner I (2002) Effect of N content and soil texture on the decomposition of organic matter in forest soils as revealed by solid-state 13CPMAS NMR spectroscopy. Org Geochem 33(12):1715–1726
Ding W, Cai Z, Wang D (2004) Preliminary budget of methane emissions from natural wetlands in China. Atmos Environ 38(5):751–759
Faz Cano A, Mermut AR, Ortiz R, Benke MB, Chatson B (2002) 13C CP/MAS NMR spectra of organic matter as influenced by vegetation, climate, and soil characteristics in soils from Murcia, Spain. Can J Soil Sci 82(4):403–411. doi:10.4141/S02-031
Fierer N, Craine JM, McLauchlan K, Schimel JP (2005) Litter quality and the temperature sensitivity of decomposition. Ecology 86(2):320–326
Fissore C, Giardina CP, Kolka RK, Trettin CC (2009) Soil organic carbon quality in forested mineral wetlands at different mean annual temperature. Soil Biol Biochem 41(3):458–466. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.11.004
Godde M, David MB, Christ MJ, Kaupenjohann M, Vance GF (1996) Carbon mobilization from the forest floor under red spruce in the northeastern USA. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1181–1189
Hartley IP, Ineson P (2008) Substrate quality and the temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1567–1574
Haynes RJ (2005) Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: an overview. Adv Agron 85:221–268
Helfrich M, Ludwig B, Buurman P, Flessa H (2006) Effect of land use on the composition of soil organic matter in density and aggregate fractions as revealed by solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Geoderma 136(1–2):331–341
Huang Z, Xu Z, Chen C, Boyd S (2008) Changes in soil carbon during the establishment of a hardwood plantation in subtropical Australia. For Ecol Manag 254(1):46–55
Huo L, Chen Z, Zou Y, Lu X, Guo J, Tang X (2013) Effect of Zoige alpine wetland degradation on the density and fractions of soil organic carbon. Ecol Eng 51:287–295. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.020
Inubushi K, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1991) Soil microbial biomass C, N and ninhydrin-N in aerobic and anaerobic soils measured by the fumigation-extraction method. Soil Biol Biochem 23(8):737–741
Janzen HH, Campbell CA, Brandt SA, Lafond GP, Townley-Smith L (1992) Light fraction organic matter in soils from long term crop rotations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:1799–1806
Kayranli B, Scholz M, Mustafa A, Hedmark Å (2010) Carbon storage and fluxes within freshwater wetlands: a critical review. Wetlands 30(1):111–124
Kirschbaum MUF (2006) The temperature dependence of organic-matter decomposition—still a topic of debate. Soil Biol Biochem 38(9):2510–2518
Laik R, Kumar K, Das DK, Chaturvedi OP (2009) Labile soil organic matter pools in a calciorthent after 18 years of afforestation by different plantations. Appl Soil Ecol 42(2):71–78
Leifeld J, Kögel K (2005) Soil organic matter fractions as early indicators for carbon stock changes under different land-use? Geoderma 124:143–155
Lorenz K, Lal R, Preston CM, Nierop KGJ (2007) Strengthening the soil organic carbon pool by increasing contributions from recalcitrant aliphatic bio(macro)molecules. Geoderma 142(1–2):1–10
Lu R (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis methods. Chinese Agricultural Scientific and Technology Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Luan J, Xiang C, Liu S, Luo Z, Gong Y, Zhu X (2010) Assessments of the impacts of Chinese fir plantation and natural regenerated forest on soil organic matter quality at Longmen mountain, Sichuan, China. Geoderma 156(3–4):228–236
Luan J, Liu S, Wang J, Zhu X, Shi Z (2011) Rhizospheric and heterotrophic respiration of a warm-temperate oak chronosequence in China. Soil Biol Biochem 43(3):503–512
Luan J, Liu S, Wang J, Zhu X (2013) Factors affecting spatial variation of annual apparent Q10 of soil respiration in two warm temperate forests. PLoS One 8(5):e64167. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064167
Mathers NJ, Mendham DS, O’connell AM, Grove TS, Xu Z, Saffigna PG (2003) How does residue management impact soil organic matter composition and quality under Eucalyptus globulus plantations in southwestern Australia? For Ecol Manag 179(1–3):253–267
McLauchlan K, Hobbie S (2004) Comparison of labile soil organic matter fractionation techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68(2):1616–1625
Miller AE, Schimel JP, Meixner T, Sickman JO, Melack JM (2005) Episodic rewetting enhances carbon and nitrogen release from chaparral soils. Soil Biol Biochem 37(12):2195–2204
Neff JC, Asner GP (2001) Dissolved organic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems: synthesis and a model. Ecosystems 4(1):29–48
Paul EA, Morris SJ, Conant RT, Plante AF (2006) Does the acid hydrolysis-incubation method measure meaningful soil organic carbon pools? Soil Sci Soc Am J 70(3):1023–1035. doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0103
Plante AF, Fernández JM, Haddix ML, Steinweg JM, Conant RT (2011) Biological, chemical and thermal indices of soil organic matter stability in four grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43(5):1051–1058
Russell AE, Cambardella CA, Ewel JJ, Parkin TB (2004) Species, rotation, and life-form diversity effects on soil carbon in experimental tropical ecosystems. Ecol Appl 14(1):47–60. doi:10.1890/02-5299
Schmidt MWI, Knicker H, Hatcher PG, Kogel-Knabner I (1997) Improvement of 13C and 15N CPMAS NMR spectra of bulk soils, particle size fractions and organic material by treatment with 10% hydrofluoric acid. Eur J Soil Sci 48(2):319–328
Six J, Elliott ET, Paustian K, Doran JW (1998) Aggregation and soil organic matter accumulation in cultivated and native grassland soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:1367–1377
Six J, Callewaert P, Lenders S (2002a) Measuring and understanding carbon storage in afforested soils by physical fractionation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66(6):1981–1987
Six J, Contant RT, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002b) Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 241:155–176
Skjemstad JO, Swift RS, McGowan JA (2006) Comparison of the particulate organic carbon and permanganate oxidation methods for estimating labile soil organic carbon. Soil Res 44(3):255–263. doi:10.1071/SR05124
Smith P (2005) An overview of the permanence of soil organic carbon stocks: influence of direct human-induced, indirect and natural effects. Eur J Soil Sci 56(5):673–680
Song CC, Wang LL, Guo YD, Song YY, Yang GS, Li YC (2011) Impacts of natural wetland degradation on dissolved carbon dynamics in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeastern China. J Hydrol 398(1–2):26–32
Sparling GP, Feltham CW, Reynolds J, West AW, Singleton P (1990) Estimation of soil microbial c by a fumigation-extraction method: use on soils of high organic matter content, and a reassessment of the kec-factor. Soil Biol Biochem 22(3):301–307
Sparling G, Vojvodic-Vukovic M, Schipper LA (1998) Hot-water-soluble C as a simple measure of labile soil organic matter: the relationship with microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 30(10/11):1469–1472
Sun G (1998a) Formation and evolvement of marsh. Territ Nat Res 4:33–35 (in Chinese with english abstract)
Sun GY (1998b) Swamps and peat in Hengduan mountains. Comprehensive scientific expedition for Tibetan of Chinese Academy Sciences. Science Press, Beijing
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19(6):703–707
von Lützow M, Kögel-Knabner I, Ekschmitt K, Flessa H, Guggenberger G, Matzner E, Marschner B (2007) SOM fractionation methods: relevance to functional pools and to stabilization mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 39(9):2183–2207
Wang D, Ding W, Wang Y (2003) Influence of major environmental factors on difference of methane emission from Zoige Plateau and Sanjiang Plain wetland. Wetl Sci 1(1):63–67 (in Chinese)
Wang G, Li Y, Wang Y, Chen L (2007a) Typical alpine wetland system changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years. Acta Geogr Sin 62(5):481–491 (in Chinese with english abstract)
Wang G, Wang Y, Li Y, Cheng H (2007b) Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Catena 70(3):506–514. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2007.01.001
Wang C, Long R, Wang Q, Liu W, Jing Z, Zhang L (2010a) Fertilization and litter effects on the functional group biomass, species diversity of plants, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity of two alpine meadow communities. Plant Soil 331(1):377–389
Wang H, Liu S-R, Mo J-M, Wang J-X, Makeschin F, Wolff M (2010b) Soil organic carbon stock and chemical composition in four plantations of indigenous tree species in subtropical China. Ecol Res 25(6):1071–1079
Wang J, Dodla S, DeLaune R, Hudnall W, Cook R (2011) Soil carbon characteristics in two Mississippi river deltaic marshland profiles. Wetlands 31(1):157–166
Whiting GJ, Chanton JP (2001) Greenhouse carbon balance of wetlands: methane emission versus carbon sequestration. Tellus B 53(5):521–528
Wu J (2012) Response of peatland development and carbon cycling to climate change: a dynamic system modeling approach. Environ Earth Sci 65(1):141–151. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1073-1
Xiang S, Guo R, Wu N, Sun S (2009) Current status and future prospects of Zoige Marsh in eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol Eng 35(4):553–562. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.02.016
Xu X, Luo Y, Zhou J (2012) Carbon quality and the temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition in a tallgrass prairie. Soil Biol Biochem 50:142–148. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.03.007
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of Dangzhou Hamo, Ta Baima, as well as the Roige National Wetland Reserve for their assistance in field sampling. We would also like to thank Professor Max Finlayson and three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on this manuscript. Thanks to Beverly Young and Sarah Furlotte for their improvements on the language.
Funding
This study was funded by the Research Institute of Forestry New Technology (CAFINT2011C09), the Chinese Ministry of Finance (No. 201204201), and China’s National Natural Science Foundation (No. 31200370). J Wu would like to thank Humber River Basin research initiative, Agricultural Research Initiative of NL, and Grenfell Campus’s Start-up research fund for research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, J., Cui, L., Xiang, C. et al. Soil carbon stocks and quality across intact and degraded alpine wetlands in Zoige, east Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Wetlands Ecol Manage 22, 427–438 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-014-9344-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-014-9344-8