Abstract
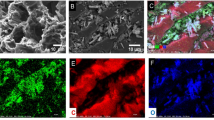
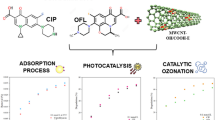
This paper presents a novel approach to remove ciprofloxacin from an aqueous solution using Fe3O4/C material by adsorption and then followed by a degradation process using several advanced oxidation technologies, i.e., heterogeneous Fenton and catalytic ozonation. Porous carbon material was synthesized through several stages, i.e., polymerization of resorcinol-formaldehyde and carbonization (800 °C). The properties of porous carbon (blank carbon and Fe/C) were characterized by N2-sorption analyzer, SEM-EDX, XRD, and TGA. The adsorption isotherm data were well described by the Langmuir isotherm model with ciprofloxacin uptake up to 208.31 mg g-1 and 189.38 mg g-1 at 30°C by Fe/C and blank carbon material, respectively. The maximum uptake was influenced by adsorption temperature and mesopore volume of material. After adsorbing the ciprofloxacin, the Fe/C material was contacted with H2O2 and ozone to produce hydroxyl radicals (OH*). The result showed that ciprofloxacin was degraded about 99.7% within 120 min at 30°C through heterogeneous Fenton oxidation. The degradation performance for the other two oxidation processes: catalytic ozonation and combined ozonation-Fenton (O3/H2O2), has been explored as well. The process using O3/H2O2 could degrade ciprofloxacin quickly. In addition, Fe/C material could be reused during cyclability test without significantly reducing the catalytic activity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akhtar, J., Amin, N. A. S., & Shahzad, K. (2016). A review on removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(27), 12842–12860. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1051121
Amelia, S., Sediawan, W. B., Prasetyo, I., Munoz, M., & Ariyanto, T. (2020). Role of the pore structure of Fe/C catalysts on heterogeneous Fenton oxidation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(1), 102921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102921
Ariyanto, T., Kurniasari, M., Laksmana, W. T., & Rochmadi, & Prasetyo, I. (2019a). Pore size control of polymer-derived carbon adsorbent and its application for dye removal. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(8), 4631–4636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2166-0
Ariyanto, T., Sarwendah, R. A. G., Amimmal, Y. M. N., Laksmana, W. T., & Prasetyo, I. (2019b). Modifying nanoporous carbon through hydrogen peroxide oxidation for removal of metronidazole antibiotics from simulated wastewater. Processes, 7(11), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110835
Avcı, A., İnci, İ., & Baylan, N. (2019). A comparative adsorption study with various adsorbents for the removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from water. Water Air Soil Pollut, 230(250). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4315-6
Beltrán, F. J. (2004). Ozone reaction kinetics for water and wastewater systems. In Lewis Publisher (Vol. 53, Issue 9). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Carabineiro, S. A. C., Thavorn-Amornsri, T., Pereira, M. F. R., Serp, P., & Figueiredo, J. L. (2012). Comparison between activated carbon, carbon xerogel and carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Catalysis Today, 186(1), 29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.08.020
Cuerda, E. M., Alexandre, M. F., & Fernandez, C. (2020). Antibiotics from water. An overview. Water, 12(102), 1–50.
Do, D. D. (1998). Adsorption Analysis:Equilibria and Kinetics (Vol. 2). Imperial College Press.
Epold, I. (2015). Degradation of Pharmaceuticals by Advanced Oxidation Technologies in Aqueous Matrices. Tallinn University of Technology.
Epold, I., Dulova, N., Veressinina, Y., & Trapido, M. (2012). Application of ozonation, UV photolysis, Fenton treatment and other related processes for degradation of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole in different aqueous matrices. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 15(2), 354–364. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2012-0215
Gu, C., & Karthikeyan, K. G. (2005). Sorption of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(23), 9166–9173. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051109f
Guo, Y., Qi, P. S., & Liu, Y. Z. (2017). A review on advanced treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 63(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/63/1/012025
Hoekstra, J., Beale, A. M., Soulimani, F., Versluijs-Helder, M., Van De Kleut, D., Koelewijn, J. M., Geus, J. W., & Jenneskens, L. W. (2016). The effect of iron catalyzed graphitization on the textural properties of carbonized cellulose: Magnetically separable graphitic carbon bodies for catalysis and remediation. Carbon, 107, 248–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.065
Igwegbe, C. A., Oba, S. N., Aniagor, C. O., Adeniyi, A. G., & Ighalo, J. O. (2021). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: A comprehensive review. In. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 93, 57–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.09.023
Jain, M., Yadav, M., Kohout, T., Lahtinen, M., Garg, V. K., & Sillanpää, M. (2018). Development of iron oxide/activated carbon nanoparticle composite for the removal of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. Water Resources and Industry, 20(Vi), 54–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2018.10.001
Jalil, M. E. R., Baschini, M., & Sapag, K. (2017). Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using pillared clays. Materials, 10(12), 17–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121345
Jiang, C., Zhang, X., Xu, X., & Wang, L. (2016). Magnetic mesoporous carbon material with strong ciprofloxacin adsorption removal property fabricated through the calcination of mixed valence Fe based metal-organic framework. Journal of Porous Materials, 23(5), 1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0188-x
Jin, X., Wu, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, Z., Liu, Y., Fang, M., & Min, X. (2018). Preparation of carbon-coated Fe3O4 porous particles and their adsorption properties of iron (III) ion. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 18(1), 306–317. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2017.082
Khader, E. H., Mohammed, T. J., Mirghaffari, N., Salman, A. D., Juzsakova, T., & Abdullah, T. A. (2021). Removal of organic pollutants from produced water by batch adsorption treatment. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02159-z
Kurniawan, I., Mariadi, P. D., & Huda, A. (2019). Hubungan Tingkat Penggunaan Antibiotik di Rumah Sakit dengan Potensi Cemaran Antibiotik di Perairan Umum. Prosiding Seminar Nasional II Hasil Litbangyasa Industri, 165–173.
Li, X., Wang, W., Dou, J., Gao, J., Chen, S., Quan, X., & Zhao, H. (2016). Dynamic adsorption of ciprofloxacin on carbon nanofibers: Quantitative measurement by in situ fluorescence. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 9, e14–e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.12.006
Lu, D., Xu, S., Qiu, W., Sun, Y., Liu, X., Yang, J., & Ma, J. (2020). Adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on functionalized spherical MCM-41 for water treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 264, 121644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121644
Mansouri, F., Chouchene, K., Roche, N., & Ksibi, M. (2021). Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption and advanced oxidation processes: State of the art and trends. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 11(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146659
Mao, H., Wang, S., Lin, J. Y., Wang, Z., & Ren, J. (2016). Modification of a magnetic carbon composite for ciprofloxacin adsorption. In Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 49, 179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.05.048
Mohd Zawawi, N., Hamzah, F., Veny, H., Mohd Rodhi, M. N., & Sarif, M. (2021). Chemical and Electrochemical properties of bamboo activated carbon activate using potassium hydroxide assisted by microwave-ultrasonic irradiation. ASEAN Journal of Chemical Engineering, 21(2), 211–224. https://doi.org/10.22146/ajche.64617
Munoz, M., Nieto-Sandoval, J., Álvarez-Torrellas, S., Sanz-Santos, E., Calderón, B., de Pedro, Z. M., Larriba, M., Fullana, A., García, J., & Casas, J. A. (2021). Carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles as reusable adsorbents for micropollutants removal from water. Separation and Purification Technology, 257, 117974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117974
Mutia, A. S. (2022). Adsorpsi dan degradasi ciprofloxacin pada air limbah simulasi dengan proses kombinasi fenton heterogen dan ozonasi katalitik. Universitas Gadjah Mada.
Prasetyo, I., Akbar, F., Prabandari, A. W., & Ariyanto, T. (2019). Fenton oxidation using easily recoverable catalyst (Fe3O4) as efficient approach to treat dyeing effluent in traditional industry. ASEAN Journal on Science and Technology for Development, 36(3), 103–108. https://doi.org/10.29037/ajstd.592
Rekhate, C. V., & Srivastava, J. K. (2020). Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater- A review. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 3, 100031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2020.100031
Ren, N., Wang, C., Wei, W., Li, J., Yue, X., & Qin, G. (2020). Ciprofloxacin adsorption on a mesoporous carbon prepared by a dual-template route. Desalination and Water Treatment, 192, 241–247. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25760
Sharma, P. C., Jain, A., Jain, S., Pahwa, R., & Yar, M. S. (2010). Ciprofloxacin: Review on developments in synthetic, analytical, and medicinal aspects. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 25(4), 577–589. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756360903373350
Tang, Y., Chen, Q., Li, W., Xie, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Chai, H., & Huang, Y. (2020). Engineering magnetic N-doped porous carbon with super-high ciprofloxacin adsorption capacity and wide pH adaptability. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388(October 2019), 122059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122059
Tu, Y. J., Premachandra, G. S., Boyd, S. A., Sallach, J. B., Li, H., Teppen, B. J., & Johnston, C. T. (2021). Synthesis and evaluation of Fe3O4-impregnated activated carbon for dioxin removal. Chemosphere, 263, 128263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128263
Wang, Y. X., Ngo, H. H., & Guo, W. S. (2015). Preparation of a specific bamboo based activated carbon and its application for ciprofloxacin removal. In Science of the Total Environment (Vol. 533, pp. 32–39). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.087
Wardani, R. K., Dahlan, K., Wahyudi, S. T., & Sukaryo, S. G. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticle magnetite for biomedical application. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2194(December). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5139869
Wu, Y., Zhou, S., Qin, F., Zheng, K., & Ye, X. (2010). Modeling the oxidation kinetics of Fenton’s process on the degradation of humic acid. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.036
Zazo, J. A., Pliego, G., Blasco, S., Casas, J. A., & Rodriguez, J. J. (2011). Intensification of the Fenton process by increasing the temperature. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50(2), 866–870. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101963k
Acknowledgements
The research was funded by Kurita Overseas Research Grant 2021 (21Pid077-17 T). A.S.M thanks to the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia for the LPDP master scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutia, A.S., Ariyanto, T. & Prasetyo, I. Ciprofloxacin Removal from Simulated Wastewater Through a Combined Process of Adsorption and Oxidation Processes Using Fe/C Adsorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05618-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05618-5