Abstract
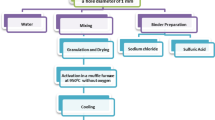
This work focuses on the preparation of eco-friendly adsorbents from waste pork bone to remove heavy metal ions. Two adsorbents, bone char (BC) and cellulose-modified BC (MCC-BC), are prepared successfully and characterized by FTIR, XRD, BET, and Zeta potential. The influences of pH, temperature, contact time, adsorbent dosage, and initial concentration of Pb (II) on the removal performance are investigated, and the maximum adsorption capacity of Pb (II) by BC and MCC-BC can reach 89.9 and 115.7 mg/g, respectively. By the analysis of kinetics, adsorption isotherms, and thermodynamics, combined with XPS characterization, the adsorption process is found to be spontaneous and endothermic, and the mechanisms are the chemical precipitation of CaxPb(10-x)(PO4)6(OH)2 via ion exchange of Ca (II) and Pb (II), accompanied by the coordination of Pb (II) with hydroxyl groups. Furthermore, MCC-BC can be regenerated with high adsorption efficiency after 5 adsorption/desorption cycles.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Hameed, M. M., Abuarab, M. E., Mottaleb, S. A., El-Bahbohy, R. M., & Bakeer, G. A. (2018). Comparative studies on growth and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution by Nostoc muscorum and Anabaena variabilis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165, 637–644.
Abouzeid, R. E., Khiari, R., El-Wakil, N., & Dufresne, A. (2019). Current state and new trends in the use of cellulose nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. Biomacromolecules, 20, 573–597.
Ajao, A. T., Mustapha, M. O., & Yakubu, S. E. (2019). Model for the treatment of refinery wastewater and expression of catabolic genes in fluidized bed bioreactor using mixed bacterial consortium. Pollution, 5, 179–187.
Aka, E. C., Nongbe, M. C., Ekou, T., Ekou, L., Coeffard, V., & Felpin, F. X. (2019). A fully bio-sourced adsorbent of heavy metals in water fabricated by immobilization of quinine on cellulose paper. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 84, 174–183.
Amiri, M. J., Abedi-Koupai, J., Eslamian, S. S., & Arshadi, M. (2015). Adsorption of Pb(II) and Hg(II) ions from aqueous single metal solutions by using surfactant-modified ostrich bone waste. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57, 16522–16539.
Bolisetty, S., Peydayesh, M., & Mezzenga, R. (2019). Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: review and analysis. Chemical Society Reviews, 48, 463–487.
Davoodi, S. M., Taheran, M., Brar, S. K., Galvez-Cloutier, R., & Martel, R. (2019). Hydrophobic dolomite sorbent for oil spill clean-ups: kinetic modeling and isotherm study. Fuel, 251, 57–72.
Dhilleswararao, V., Subbarao, M. V., & Muralikrishna, M. P. S. (2019). Removal of manganese (II) from aqueous solution by chemically activated Thuja Occidentalis leaves carbon (CATLC) as an adsorbent: adsorption equilibrium and kinetic studies. Phys. Chem. Res., 7, 11–26.
Estrella, M. B. d., Flores, S. T. d., Bonini, N. A., Gonzo, E., Pérez, N. P., & Arias, A. N. (2015). Rapid synthesis of nanometric cellulose hydroxyapatite. Procedia Materials Science, 8, 608–616.
Fayyaz, F., Rabbani, M., Rahimi, R., & Rassa, M. (2019). Preparation, characterization and photo-inactivation of cellulose nanocrystals impregnated with meso-tetrakis(4-nitrophenyl)porphyrin. Iran. Chem. Commun., 7, 53–62.
Gu, D. M., Guo, C. S., Hou, S., Lv, J. P., Zhang, Y., Feng, Q. Y., Zhang, Y., & Xu, J. (2019). Kinetic and mechanistic investigation on the decomposition of ketamine by UV-254 nm activated persulfate. Chemical Engineering Journal, 370, 19–26.
Hao, L., Lv, Y., & Song, H. (2017). The morphological evolution of hydroxyapatite on high-efficiency Pb(II) removal and antibacterial activity. Microchemical Journal, 135, 16–25.
Iriarte-Velasco, U., Sierra, I., Zudaire, L. & Ayastuy, J. L.: 2016, 'Preparation of a porous biochar from the acid activation of pork bones', Food bioprod. Process. 98, 341–353.
Jia, L. M., Shi, Y. H., Zhang, Q., & Xu, X. H. (2018). Green synthesis of ultrafine methyl-cellulose-derived porous carbon/MnO2 nanowires for asymmetric supercapacitors and flexible pattern stamping. Applied Surface Science, 462, 923–931.
Jung, K.-W., Lee, S. Y., Choi, J.-W., & Lee, Y. J. (2019). A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper (II) from aqueous media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 369, 529–541.
Kakavandi, B., Raofi, A., Peyghambarzadeh, S. M., Ramavandi, B., Niri, M. H., & Ahmadi, M. (2018). Efficient adsorption of cobalt on chemical modified activated carbon: characterization, optimization and modeling studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 111, 310–321.
Khallok, H., Ojala, S., Ezzahmouly, M., Elouahli, A., Gourri, E., Jamil, M., & Hatim, Z. (2019). Porous foams based hydroxyapatite prepared by direct foaming method using egg white as a pore promoter. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 55, 611–619.
Kousalya, G. N., Rajiv Gandhi, M., Sairam Sundaram, C., & Meenakshi, S. (2010). Synthesis of nano-hydroxyapatite chitin/chitosan hybrid biocomposites for the removal of Fe(III). Carbohydrate Polymers, 82, 594–599.
Lu, H. P., Li, Z. A., Gasco, G., Mendez, A., Shen, Y., & Paz-Ferreiro, J. (2018). Use of magnetic biochars for the immobilization of heavy metals in a multi-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ., 622-623, 892–899.
Mu, Y., Saffarzadeh, A., & Shimaoka, T. (2018). Utilization of waste natural fishbone for heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Journal of Cleaner Production, 172, 3111–3118.
Narwade, V. N., Khairnar, R. S., & Kokol, V. (2017). In situ synthesized hydroxyapatite—cellulose nanofibrils as biosorbents for heavy metal ions removal. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 26, 2130–2141.
Nayak, B., Samant, A., Patel, R., & Misra, P. K. (2017). Comprehensive understanding of the kinetics and mechanism of fluoride removal over a potent nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite surface. ACS Omega, 2, 8118–8128.
Ozer, C., Boysan, F., & Imamoglu, M. (2017). Efficient removal of Cd (II), Cu (II), Ni (II) and Pb(II) by polyamine polyurea polymer modified with 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde from synthetic and real wastewaters. Desalination and Water Treatment, 85, 320–329.
Phasuk, A., Srisantitham, S., Tuntulani, T., & Anutrasakda, W. (2017). Facile synthesis of magnetic hydroxyapatite-supported nickel oxide nanocomposite and its dye adsorption characteristics. Adsorption, 24, 157–167.
Ramos Guivar, J. A., Sanches, E. A., Bruns, F., Sadrollahi, E., Morales, M. A., López, E. O., & Litterst, F. J. (2016). Vacancy ordered γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles functionalized with nanohydroxyapatite: XRD, FTIR, TEM, XPS and mössbauer studies. Applied Surface Science, 389, 721–734.
Rashed, M. N., Toufeek, M. E. F., Eltaher, M. A. E., & Elbadry, A. O. (2019). Adsorption and leaching behavior of copper, zinc and lead ions by three different River Nile sediments at Aswan, Egypt. Pollution, 5, 99–114.
Rojas-Mayorga, C. K., Mendoza-Castillo, D. I., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., & Silvestre-Albero, J. (2016). Tailoring the adsorption behavior of bone char for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. Adsorption Science and Technology, 34, 368–387.
Samant, A., Nayak, B., & Misra, P. K. (2017). Kinetics and mechanistic interpretation of fluoride removal by nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite derived from Limacine artica shells. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5, 5429–5438.
Sun, R. X., Long, J., Sun, Z. Z., Li, C. Q., Wang, L. S., Zhang, H. X., & Chen, K. Z. (2014). Fabrication and lead ion removal property of magnetic hydroxyapatite composite with hierarchically urchin-like microstructure. Advances in Materials Research, 941-944, 666–671.
Wan, Y., Wang, J., Gama, M., Guo, R., Zhang, Q., Zhang, P., Yao, F. & Luo, H.: 2019, 'Biofabrication of a novel bacteria/bacterial cellulose composite for improved adsorption capacity', Compos part A: Appl. Sci. Manufac. 125, 105560.
Wang, J., Liu, M., Duan, C., Sun, J., & Xu, Y. (2019a). Preparation and characterization of cellulose-based adsorbent and its application in heavy metal ions removal. Carbohydrate Polymers, 206, 837–843.
Wang, X., He, J., & Huang, J. (2019b). Amino-modified hyper-cross-linked polymers with hierarchical porosity for adsorption of salicylic acid from aqueous solution. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 131, 1–8.
Wang, Y.-Y., Liu, Y.-X., Lu, H.-H., Yang, R.-Q., & Yang, S.-M. (2018). Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu (II), and Zn (II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 261, 53–61.
Wozniak, B., Szalaj, U., Chodara, A., Mizeracki, J., Lojkowski, M., Myszka, D., & Lojkowski, W. (2019). Mechanism for sonocoating a polymer surface with nano-hydroxyapatite. Materials Letters, 249, 155–159.
Xia, S. P., Song, Z. L., Jeyakumar, P., Shaheen, S. M., Rinklebe, J., Ok, Y. S., Bolan, N., & Wang, H. L. (2019). A critical review on bioremediation technologies for Cr (VI)-contaminated soils and wastewater. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 1027–1078.
Yang, W., Ping, P., Wang, L.-L., Bo-Yuan Chen, T., Chun-Yin Yuen, A., Zhu, S.-E., Wang, N.-N., Hu, Y.-L., Yang, P.-P., Sun, C., Zhang, C.-Y., Lu, H.-D., Chan, Q. N., & Yeoh, G.-H. (2018). Fabrication of fully bio-based aerogels via microcrystalline cellulose and hydroxyapatite nanorods with highly effective flame-retardant properties. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 1, 1921–1931.
Zhang, N., Zang, G. L., Shi, C., Yu, H. Q., & Sheng, G. P. (2016). A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu (II) removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 316, 11–18.
Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Wang, H., & Zhao, J. (2018). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using hydroxyapatite/calcium silicate hydrate (HAP/C-S-H) composite adsorbent prepared by a phosphate recovery process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 344, 53–61.
Zhou, Y., Li, S., Wang, D. & Han, X.: 2018, 'Electrospinning synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanofibers assembled from nanorods and their adsorption for heavy metal ions', Polish J. Environmental Studies 28, 981–988.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant no. 2242019k1G024) and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. KYCX18_0131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Luo, P. Preparation, Kinetics, and Adsorption Mechanism Study of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Modified Bone Char as an Efficient Pb (II) Adsorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 328 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04687-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04687-8