Abstract
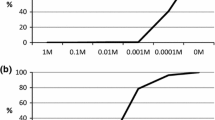
Brazil is one of the greatest producers of orange and its orange juice processing industry produces large volumes of solid and liquid waste daily. As an efficient use of the residues from citrus industry, production of bioethanol is highlighted. However, the generation of bioethanol produces a liquid effluent as a by-product, known as vinasse. The objective of this study was to evaluate the toxicity of an effluent from citrus industries, orange vinasse, when applied to soil using Allium cepa seeds. The evaluation was performed by means of germination, root growth, and genotoxic and mutagenic parameters. The EC50 (effectiveness concentration) and ½ EC50, defined in the germination test, were used for genotoxicity tests. Toxicity was observed in dilutions above 40%, which was responsible for reducing the germination speed index. Genotoxicity was observed only using the EC50 and mutagenicity was not detected. According to the results, orange vinasse showed toxicity similar to the sugar cane vinasse, so caution is suggested in the disposal of this effluent into the environment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini, R. J., Anderson, D., Douglas, G. R., et al. (2000). IPCS guidelines for the monitoring of genotoxic effects of carcinogens in humans. Mutation Research, Reviews in Mutation Research, 463(2), 111–172.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils (2nd ed.). Glasgow: Blackie Academic & Professional.
Alves, P. R. L., Natal-da-Luz, T., Sousa, J. P., & Cardoso, E. J. (2015). Ecotoxicological characterization of sugarcane vinasses when applied to tropical soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 526, 222–232.
Araújo-Neto S. E., de Ramos J. D., & Mendonça V. (2002). Desenvolvimento de mudas de maracujazeiro-amarelo em diferentes substratos e recipientes. In: Congresso Brasileiro de Fruticultura. Belém, PA. Brazil (in Portuguese).
Awan, A. T., Tsukamoto, J., & Tasic, L. (2013). Orange waste as a biomass for 2G-ethanol production using low cost enzymes and co-culture fermentation. RSC Advances, 3, 25071–25078.
Barros, J. R. M., Barros, A. L. M., & Cypriano, M. P. (2016). O mercado citricultural no Brasil e as suas novas perspectivas. Available on: http://www.citrusbr.com/download/biblioteca/CitrusBR_Livro_Concecitrus_2016.pdf. Accessed on July 23rd, 2019.
Becaro, A. A., Siqueira, M. C., Puti, F. C., de Moura, M. R., Correa, D. S., Marconcini, J. M., & Ferreira, M. D. (2017). Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticle/carboxymethyl cellulose on Allium cepa. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(7), 352.
Borboa, L., & Torre, C. (1996). The genotoxicity of Zn (II) and Cd (II) in Allium cepa root meristematic cells. The New Phytologist, 134(3), 481–486.
Brusick, D. (1986). Genotoxic effects in cultured mammalian cells produced by low pH treatment conditions and increased ion concentrations. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 8(6), 879–886.
CETESB - Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental. (2009). Qualidade das águas interiores no estado de São Paulo. Available on: http://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-interiores/wp-content/uploads/sites/32/2013/11/variaveis.pdf. Accessed 27 June.
CETESB - Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental. (2014). Decisão de Diretoria nº 045/2014/E/C/I. Available from: https://sites.usp.br/sef/wp-content/uploads/sites/52/2015/03/47-CETESB2014_Valores_Orientadores_solo_agua.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2018.
Chojnacka, K., Chojnacki, A., Górecka, H., & Górecki, H. (2005). Bioavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. The Science of the Total Environment, 337(1), 175–182.
Christofoletti, C. A., Pedro-Escher, J., Correia, J. E., Marinho, J. F. U., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2013a). Sugarcane vinasse: environmental implications of its use. Waste Management, 33(12), 2752–2761.
Christofoletti, C. A., Pedro-Escher, J., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2013b). Assessment of the genotoxicity of two agricultural residues after processing by diplopods using the Allium cepa assay. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224(4), 1–14.
Christofoletti, C. A., Francisco, A., Pedro-Escher, J., Gastaldi, V. D., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2016). Diplopods as soil bioindicators of toxicity after application of residues from sewage treatment plants and ethanol industry. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 22, 1098–1110.
Citrosuco. (2016a). Relatório de Sustentabilidade Safra 2015–2016. Available on: http://www.citrosuco.com.br/sustentabilidade/relatorio-de-sustentabilidade.html. Acessed on March 4th, 2018.
Citrosuco. (2016b). Subprodutos da indústria cítrica. Available on: http://www.citrosuco.com.br/pt/produtos.php#subprodutos. Accessed on February 10th, 2017.
Coelho, M. P. M., Moreira-de-Sousa, C., Souza, R. B., Ansoar-Rodríguez, Y., Silva-Zacarin, E. C., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2017). Toxicity evaluation of vinasse and biosolid samples in diplopod midgut: heat shock protein in situ localization. Environemental Science and Pollution Research, 24(27), 22007–22017.
CONAMA – Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. (2011). Resolução n. 430. Available on: http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=646. Accessed on July 23th, 2019.
Correia, J. E., Christofoletti, C. A., Marcato, A. C. C., Marinho, J. F. U., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2017). Histopathological analysis of tilapia gills (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) exposed to sugarcane vinasse. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 135, 319–326.
Das, P., Samantaray, S., & Rout, G. R. (1997). Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environmental Pollution, 98, 29–36.
España-Gamboa, E., Minagos-Cortes, J., Barahona-Perez, L., Dominguez-Maldonado, J., Hernández-Zarate, G., & Alzate-Gaviria, L. (2011). Vinasse: characterization and treatments. Waste Management and Research, 29(12), 1235–1250.
Farrell, M., Perkins, W. T., Hobbs, P. J., Griffith, G. W., & Jones, D. L. (2010). Migration of heavy metals in soil as influenced by compost amendments. Environmental Pollution, 158(1), 55–64.
Felisbino, K., Santos-Filho, R., Piancini, L. D., Cestari, M. M., & Leme, D. M. (2018). Mesotrione herbicide does not cause genotoxicity, but modulates the genotoxic effects of atrazine when assessed in mixture using a plant test system (Allium cepa). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 150, 83–88.
Fenech, M., & Morley, A. A. (1985). Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutation Research/Environmental Mutagenesis and Related Subjects, 147(1–2), 29–36.
Ferreira-Leitao, V., Gottschalk, L. M. F., Ferrara, M. A., Nepomuceno, A. L., Molinari, H. B. C., & Bon, E. P. (2010). Biomass residues in Brazil: availability and potential uses. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 1(1), 65–76.
Francisco, A., Christofoletti, C. A., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2014). Evaluation of allowed parameters for nickel in freshwater bodies using the Allium cepa test. Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde, 35, 49–60.
Freire, W. J., & Cortez, L. A. (2000). Vinhaça de cana-de-açúcar. Agropec., 203 (in Portuguese).
Garcia, C. F. H., Souza, R. B., De Souza, C. P., Christofoletti, C. A., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2017). Toxicity of two effluents from agricultural activity: comparing the genotoxicity of sugar cane and orange vinasse. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 216–221.
Gianchini, C. F., & Ferraz, M. V. (2009). Benefícios da utilização de vinhaça em terras de plantio de cana-de-açúcar – Revisão de Literatura. Rev Cient Eletrôn de Agron, 3, 1–15 (in Portuguese).
Gjorgieva, D., Kadifkova-Panovska, T., Mitrev, S., Kovacevik, B., Kostadinovska, E., Bačeva, K., & Stafilov, T. (2012). Assessment of the genotoxicity of heavy metals in Phaseolus vulgaris L. as a model plant system by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 47(3), 366–373.
Haq, I., Kumar, S., Raj, A., Lohani, M., & Satyanarayana, G. N. V. (2017). Genotoxicity assessment of pulp and paper mill effluent before and after bacterial degradation using Allium cepa test. Chemosphere, 169, 642–650.
ISO- International Organization For Standardization, (2004). Soil quality—determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora – Part 1 and Part 2.
Jansen, L. L., & Cronin, E. H. (1953). Halogeton on trial. Utah Farm & Home Science, 14, 38–39.
Justice, O. L., & Reece, M. H. (1954). A review of literature and investigation on the effects of hydrogen-ion concentration on the germination of seeds. Proceedings of the Association of Official Seed Analysts, 44, 144–149.
Karaouzas, I., Cotou, E., Albanis, T. A., Kamarianos, A., Skoulikidis, N. T., & Giannakou, U. (2011). Bioassays and biochemical biomarkers for assessing olive mill and citrus processing wastewater toxicity. Environmental Toxicology, 26(6), 669–676.
Kekec, G., Sakcali, M. S., & Uzonur, I. (2010). Assessment of genotoxic effects of boron on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by using RAPD analysis. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84(6), 759–764.
Kim, R. Y., Yoon, J. K., Kim, T. S., Yang, J. E., Owens, G., & Kim, K. R. (2015). Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: definitions and practical implementation—a critical review. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(6), 1041–1061.
Leme, D. M., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2009). Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: a review on its application. Mutation Research, 682(1), 71–81.
Marinho, J. F. U., Correia, J. E., de Castro Marcato, A. C., Pedro-Escher, J., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2014). Sugar cane vinasse in water bodies: impact assessed by liver histopathology in tilapia. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 110, 239–245.
Musgrove, E., Seaman, M., & Hedley, D. (1987). Relationship between cytoplasmic pH and proliferation during exponential growth and cellular quiescence. Experimental Cell Research, 172(1), 65–75.
Navarro, S., Vela, N., & Navarro, G. (2007). An overview on the environmental behaviour of pesticide residues in soils. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 5(3), 357–375.
OECD- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. (2003). Guideline 208. Terrestrial plant test: 208; Seedling emergence and seedling growth test.
Oliveira, J. P. W., Dos Santos, R. N., Pibernat, C. C., & Boeira, J. M. (2012). Genotoxicity and physical chemistry analysis of waters from Sinos River (RS) using Allium cepa and Eichhornia crassipesas bioindicators. Biochemistry and Biotechnology Reports, 1(1), 15–22.
Palmieri, M. J., Luber, J., Andrade-Vieira, L. F., & Davide, L. C. (2014). Cytotoxic and phytotoxic effects of the main chemical components of spent pot-liner: a comparative approach. Mutation Research, 763, 30–35.
Pedro-Escher, J., Maziviero, G. T., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2014). Mutagenic action of sugar cane vinasse in the Tradescantia Pallida test system. Journal of Ecosystem and Ecography, 4(2), 145.
Pedro-Escher, J., Christofoletti, C. A., Ansoar-Rodríguez, Y., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2016). Sugarcane vinasse, a residue of ethanol industry: toxic, cytotoxic and genotoxic potential using the Allium cepa test. Journal of Environmental Protection, 7(5), 602–612.
Rajiv, S., Jerobin, J., Saranya, V., Nainawat, M., Sharma, A., Makwana, P., & Mukherjee, A. (2016). Comparative cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of cobalt (II, III) oxide, iron (III) oxide, silicon dioxide, and aluminum oxide nanoparticles on human lymphocytes in vitro. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 35(2), 170–183.
Ramalho, J. F. G. P., & Sobrinho, N. M. B. A. (2001). Metais pesados em solos cultivados com cana-de-açúcar pelo uso de resíduos agroindustriais. Rev Florest Amb, 8(1), 120–129 (in Portuguese).
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1997). Allium cepa anaphase-telophase root tip chromosome aberration assay on N–methyl-N-nitrosourea, maleic hydrazide, sodium azide, and ethyl methanesulfonate. Mutation Research, 390, 121–127.
Rezzadori K., & Benedetti S. (2009). Proposições para valorização de resíduos do processamento do suco de laranja. In: International workshop advances in cleaner production. São Paulo, SP, 1–11 (in Portuguese).
Rieuwerts, J. S., Thornton, I., Farago, M. E., & Ashmore, M. R. (1998). Factors influencing metal bioavailability in soils: preliminary investigations for the development of a critical loads approach for metals. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 10(2), 61–75.
Russel, P. J. (2002). Chromosomal mutation. In B. Cummings (Ed.), Genetics (2nd ed., pp. 595–621). San Francisco: Pearson Education Inc.
Santos, C. B., Longhi, S. J., Hoppe, J. M., & Moscovich, F. A. (2000). Efeito do volume de tubetes e tipos de substratos na qualidade de mudas de Cryptomeria japonica (L.F.). Cienc Florest, 10(2), 1–15 (in Portuguese).
Saverini, M., Catanzaro, I., Sciandrello, G., Avellone, G., Indelicato, S., Marcì, G., & Palmisano, L. (2012). Genotoxicity of citrus wastewater in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and efficiency of heterogeneous photocatalysis by TiO2. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 108, 8–15.
Sociedade Nacional de Agricultura. (2014). Available on: http://www.sna.agr.br/etanol-da-laranja-pode-entrar-no-mercado-em-dois-anos/ . Accessed on August 28th, 2018.
Souguir, D., Ferjani, E., Ledoigt, G., & Goupil, P. (2008). Exposure of Vicia faba and Pisum sativum to copper-induced genotoxicity. Protoplasma, 233(3–4), 203.
Souza R. B., Moreira-de-Sousa C., Christofoletti C. A., Souza C. P., & Fontanetti C. S. (2017a). Impacto de resíduos (vinhaça e biossólido) lançados no cultivo de cana-de-açúcar em representantes da fauna edáfica. In: Fontanetti C.S., & Correa O.B. (eds) Cana-de-açúcar e seus impactos: uma visão acadêmica. 1st edn. Brazil: Canal 6, pp 197–214 (in Portuguese).
Souza, R. B., De Souza, C. P., Bueno, O. C., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2017b). Genotoxicity evaluation of two metallic-insecticides using Allium cepa and Tradescantia pallida: a new alternative against leaf-cutting ants. Chemosphere, 168, 1093–1099.
Steinkellner, H., Mun-Sik, K., Helma, C., et al. (1998). Genotoxic effects of heavy metals: comparative investigation with plant bioassays. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 31(2), 183–191.
Stubbendieck, J. (1974). Effect of pH on germination of three grass species. Journal of Range Management, 27(1), 78–79.
Tavares, V. B., Sivieri, K., Ceron, C. R., et al. (1998). Utilização do resíduo líquido de indústria de processamento de suco de laranja como meio de cultura de Penicillium citrinum: depuração biológica do resíduo e produção de enzima. Quim Nova, 21(6), 722–725 (in Portuguese).
USEPA- United States Environmental Protection Agency. (1996). Ecological effects test guidelines (OPPTS 850.4200): Seed germination/root elongation toxicity test.
Valerio, M. E., Garcia, J. F., & Peinado, F. M. (2007). Determination of phytotoxicity of soluble elements in soils, based on a bioassay with lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). The Science of the Total Environment, 378, 63–66.
Vries W., Groenenberg J.E., Lofts S., Tipping E., & Posch M. (2012). Critical loads of heavy metal for soils. In: Alloway B.J., & Trevors J.T. (eds) Heavy metals in soil. 3rd ed. Springer, pp 211-240.
Wilkins, M. R., Widmer, W. W., Grohmann, K., & Cameron, R. G. (2007). Hydrolysis of grapefruit peel waste with cellulase and pectinase enzymes. Bioresource Technology, 98(8), 1596–1601.
Wise, S. S., Schuler, J. H., Katsifis, S. P., & Wise, J. P., Sr. (2003). Barium chromate is cytotoxic and genotoxic to human lung cells. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 42(4), 274–278.
Yi, M., Yi, H., Li, H., & Wu, L. (2010). Aluminum induces chromosome aberrations, micronuclei, and cell cycle dysfunction in root cells of Vicia faba. Environmental Toxicology, 25(2), 124–129.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Dejanira de Franceschi de Angelis and Dilza Aparecida Nalin de Oliveira Leite for helping in the preparation of the orange vinasse.
Funding
This study received funding from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP, process n. 2014/17998-7 and 2012/50197-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, C.F.H., de Souza, R.B., de Souza, C.P. et al. Effluent from Citrus Industry: Toxic Parameters of Orange Vinasse. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 201 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4260-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4260-4