Abstract
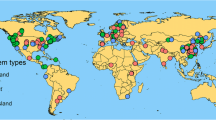
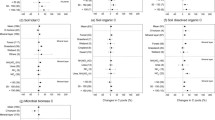
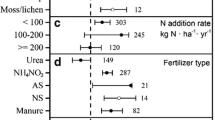
Although phosphorus (P) enrichment alone or in combination with other nutrients such as nitrogen (N) and potassium (K) due to anthropogenic activities may modify the nutrient pools and nutrient elemental ratios of terrestrial ecosystems, few studies have revealed the global effects of P alone or in combination with N and K enrichment on terrestrial ecosystems. In this study, we conducted a meta-analysis of the impacts of P addition alone or in combination with N and K on the C, N, and P pools and C/N/P ratios of plants, soils, and microbial biomass in terrestrial ecosystems. The results suggest that the following changes occurred: (1) P addition resulted in a significantly larger plant C pool, which was further enhanced when extra N and K were added. (2) The soil and microbial biomass C pools and the plant, soil, and microbial biomass N pools were minimally affected by P addition at the global scale but were noticeably affected when N and K were simultaneously added. (3) The P pools of the plants, soil, and microbial biomass were significantly and consistently enhanced by the addition of P, NP, and NPK. (4) The plant C/N, N/P, and C/P ratios were significantly reduced when P was added, while the C/N/P ratios in the soil and microbial biomass were minimally affected. These results, which show the inconsistent responses of plant, soil, and microbial biomass nutrient pools and elemental ratios to P, NP, and NPK addition, improve our understanding of terrestrial ecosystem functions under global change scenarios.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, R., Verhoeven, J. T. A., & Whigham, D. F. (1999). Plant-mediated controls on nutrient cycling in temperate fens and bogs. Ecology, 80, 2170–2181.
Bai, E., Li, S., Xu, W., Li, W., Dai, W., & Jiang, P. (2013). A meta-analysis of experimental warming effects on terrestrial nitrogen pools and dynamics. New Phytologist, 199, 441–451.
Bedada, W., Lemenih, M., & Karltun, E. (2016). Soil nutrient build-up, input interaction effects and plot level N and P balances under long-term addition of compost and NP fertilizer. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 218, 220–231.
Berg, B., & McClaugherty, C. (2014). Plant litter: decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Bracken, M. E., Hillebrand, H., Borer, E. T., Seabloom, E. W., Cebrian, J., Cleland, E. E., Elser, J. J., Gruner, D. S., Harpole, W. S., & Ngai, J. T. (2015). Signatures of nutrient limitation and co-limitation: Responses of autotroph internal nutrient concentrations to nitrogen and phosphorus additions. Oikos, 124, 113–121.
Cleveland, C. C., Townsend, A. R., & Schmidt, S. K. (2002). Phosphorus limitation of microbial processes in moist tropical forests: Evidence from short-term laboratory incubations and field studies. Ecosystems, 5, 0680–0691.
Corbin, J. D., Avis, P. G., & Wilbur, R. B. (2003). The role of phosphorus availability in the response of soil nitrogen cycling, understory vegetation and arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculum potential to elevated nitrogen inputs. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 147, 141–162.
Cusell, C., Kooijman, A., & Lamers, L. P. (2014). Nitrogen or phosphorus limitation in rich fens? Edaphic differences explain contrasting results in vegetation development after fertilization. Plant and Soil, 384, 153–168.
Danger, M., Daufresne, T., Lucas, F., Pissard, S., & Lacroix, G. (2008). Does Liebig’s law of the minimum scale up from species to communities. Oikos, 117, 1741–1751.
Elser, J. J., Bracken, M. E., Cleland, E. E., Gruner, D. S., Harpole, W. S., Hillebrand, H., Ngai, J. T., Seabloom, E. W., Shurin, J. B., & Smith, J. E. (2007). Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 10, 1135–1142.
Elser, J., Fagan, W., Kerkhoff, A., Swenson, N., & Enquist, B. (2010). Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytologist, 186, 593–608.
Feller, I. C., Lovelock, C. E., & McKee, K. L. (2007). Nutrient addition differentially affects ecological processes of Avicennia germinans in nitrogen versus phosphorus limited mangrove ecosystems. Ecosystems, 10, 347–359.
García-Palacios, P., Maestre, F. T., Kattge, J., & Wall, D. H. (2013). Climate and litter quality differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition across biomes. Ecology Letters, 16, 1045–1053.
Güsewell, S., Koerselman, W., & Verhoeven, J. T. (2003). Biomass N: P ratios as indicators of nutrient limitation for plant populations in wetlands. Ecological Applications, 13, 372–384.
Harpole, W. S., Ngai, J. T., Cleland, E. E., Seabloom, E. W., Borer, E. T., Bracken, M. E., Elser, J. J., Gruner, D. S., Hillebrand, H., & Shurin, J. B. (2011). Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecology Letters, 14, 852–862.
Hedges, L. V., Gurevitch, J., & Curtis, P. S. (1999). The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology, 80, 1150–1156.
Huang, W., Zhou, G., & Liu, J. (2012). Nitrogen and phosphorus status and their influence on aboveground production under increasing nitrogen deposition in three successional forests. Acta Oecologica, 44, 20–27.
Huang, J., Hu, B., Qi, K., Chen, W., Pang, X., Bao, W., & Tian, G. (2016). Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in a subalpine spruce plantation. European Journal of Soil Biology, 72, 35–41.
Iversen, C. M., Bridgham, S. D., & Kellogg, L. E. (2010). Scaling plant nitrogen use and uptake efficiencies in response to nutrient addition in peatlands. Ecology, 91, 693–707.
Koricheva, J., Gurevitch, J., & Mengersen, K. (2013). Handbook of meta-analysis in ecology and evolution. Princeton University Press.
LeBauer, D. S., & Treseder, K. K. (2008). Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed. Ecology, 89, 371–379.
Li, J., Yang, Y., Li, B., Li, W., Wang, G., & Knops, J. M. (2014). Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on soil carbon fractions in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. PloS One, 9, e103266.
Li, Y., Niu, S., & Yu, G. (2016). Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biology, 22, 934–943.
Liu, L., & Greaver, T. L. (2010). A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecology Letters, 13, 819–828.
Liu, A., Hamel, C., Spedding, T., Zhang, T. Q., Mongeau, R., Lamarre, G. R., & Tremblay, G. (2008). Soil microbial carbon and phosphorus as influenced by phosphorus fertilization and tillage in a maize-soybean rotation in south-western Quebec. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 88, 21–30.
Liu, L., Gundersen, P., Zhang, T., & Mo, J. (2012). Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 44, 31–38.
Loladze, I. (2014). Hidden shift of the ionome of plants exposed to elevated CO2 depletes minerals at the base of human nutrition. eLife, 3, e02245.
Lu, M., Yang, Y., Luo, Y., Fang, C., Zhou, X., Chen, J., Yang, X., & Li, B. (2011a). Responses of ecosystem nitrogen cycle to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 189, 1040–1050.
Lu, M., Zhou, X., Luo, Y., Yang, Y., Fang, C., Chen, J., & Li, B. (2011b). Minor stimulation of soil carbon storage by nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 140, 234–244.
Lu, M., Zhou, X., Yang, Q., Li, H., Luo, Y., Fang, C., Chen, J., Yang, X., & Li, B. (2013). Responses of ecosystem carbon cycle to experimental warming: A meta-analysis. Ecology, 94, 726–738.
Mao, R., Zeng, D. H., Zhang, X. H., & Song, C. C. (2015). Responses of plant nutrient resorption to phosphorus addition in freshwater marsh of Northeast China. Scientific Reports, 5, 8097.
Mao, R., Chen, H. M., Zhang, X. H., Shi, F. X., & Song, C. C. (2016). Effects of P addition on plant C: N: P stoichiometry in an N-limited temperate wetland of Northeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 559, 1–6.
Marschner, P. (2011). Mineral nutrition of higher plants London. Academic Press.
Peñuelas, J., Poulter, B., Sardans, J., Ciais, P., van der Velde, M., Bopp, L., Boucher, O., Godderis, Y., Hinsinger, P., Llusia, J., Nardin, E., Vicca, S., Obersteiner, M., & Janssens, I. A. (2013). Human-induced nitrogen–phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nature Communications, 4, 2934.
Rejmánková, E., & Snyder, J. M. (2008). Emergent macrophytes in phosphorus limited marshes: Do phosphorus usage strategies change after nutrient addition? Plant and Soil, 313, 141–153.
Rosenberg, M. S., Adams, D. C., & Gurevitch, J. (2000). MetaWin: Statistical software for meta-analysis, version 2. Sinauer Associates Sunderland: Massachusetts.
Schachtman, D. P., Reid, R. J., & Ayling, S. M. (1998). Phosphorus uptake by plants: From soil to cell. Plant Physiology, 116, 447–453.
Soudzilovskaia, N., Onipchenko, V., Cornelissen, J., & Aerts, R. (2005). Biomass production, N: P ratio and nutrient limitation in a Caucasian alpine tundra plant community. Journal of Vegetation Science, 16, 399–406.
Townsend, A. R. & Asner, G. P. (2013). Multiple dimensions of resource limitation in tropical forests. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 110, 4864–4865.
Valkama, E., Uusitalo, R., Ylivainio, K., Virkajärvi, P., & Turtola, E. (2009). Phosphorus fertilization: A meta-analysis of 80 years of research in Finland. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 130, 75–85.
Vilà, M., Espinar, J. L., Hejda, M., Hulme, P. E., Jarošík, V., Maron, J. L., Pergl, J., Schaffner, U., Sun, Y., & Pyšek, P. (2011). Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: A meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702–708.
Vitousek, P. M., Porder, S., Houlton, B. Z., & Chadwick, O. A. (2010). Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen–phosphorus interactions. Ecological Applications, 20, 5–15.
Yuan, Z., & Chen, H. Y. (2015). Negative effects of fertilization on plant nutrient resorption. Ecology, 96, 373–380.
Yue, K., Peng, Y., Peng, C., Yang, W., Peng, X., & Wu, F. (2016). Stimulation of terrestrial ecosystem carbon storage by nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Scientific Reports, 6, 19895.
Yue, K., Fornara, D. A., Yang, W., Peng, Y., Li, Z., Wu, F., & Peng, C. (2017a). Effects of three global change drivers on terrestrial C: N: P stoichiometry: A global synthesis. Global Change Biology, 23, 2450–2463.
Yue, K., Fornara, D. A., Yang, W., Peng, Y., Peng, C., Liu, Z., & Wu, F. (2017b). Influence of multiple global change drivers on terrestrial carbon storage: Additive effects are common. Ecology Letters, 20, 663–672.
Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S., Keiblinger, K. M., Mooshammer, M., PENuelas, J., Richter, A., Sardans, J., & Wanek, W. (2015). The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecological Monographs, 85, 133–155.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the scientists whose work was used in this meta-analysis. Kai Yue acknowledges the China Scholarship Council for supporting a joint Ph.D. program grant (201506910002). This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40202036, 40572163, and 41172277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2790 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Peng, Y., Yue, K. et al. Different Responses of Terrestrial C, N, and P Pools and C/N/P Ratios to P, NP, and NPK Addition: a Meta-Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 197 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3383-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3383-8