Abstract
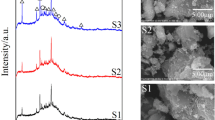
Natural volcanic tuff was used for the synthesis of geopolymer and then for the removal of Zn+2. The characteristics of the natural volcanic tuff and the synthesized geopolymer were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Results referred that the synthesized geopolymer had a higher efficiency uptake of 97.7 % as against 78.5 % for the natural volcanic tuff. The uptake capacity of geopolymer for Zn+2 adsorption increased with increasing temperature in the studied range of 25–45 °C, contact time up to 30 min, pH up to 7, and initial concentration up to 160 ppm, while it decreased with an increase in geopolymer dosage. The isotherm study showed best fit on Langmuir and Radlich-Peterson models. The maximum uptake capacity obtained from Langmuir model increased from 14.7 to 17.63 mg/g as the temperature increased from 25 to 45 °C. The pseudo-second-order model showed the best fitness for the experimental data followed by intraparticle diffusion model. The adsorption process can be characterized as endothermic, homogeneous, spontaneous, irreversible, physical, and a high adhesion of the ions to the geopolymer surface. The results obtained buttressed the feasibility and applicability of producing geopolymer from natural volcanic tuff for the removal of heavy metals.
















Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abdul Kadir, A., Abdullah, A., & Wai, L. K. (2013). Study on ferum (Fe) and zinc (Zn) removal by using rice bran at Sungai Pelepah, Kota Tinggi, Johor. Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(12), 3580–3586.
Abdul Rahim, R. H., Rahmiati, T., Azizli, K. A., Man, Z., Nuruddin, M. F., & Ismail, L. (2014). Comparison of using NaOH and KOH activated fly ash-based geopolymer on the mechanical properties. Materials Science Forum, 803, 179–184.
Abuh, M. A., Akpomie, G. K., Nwagbara, N. K., & Nwafor, E. C. (2013). Equilibrium isotherm studies for the biosorption of Cu (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solution by unmodified lignocellulosic fibrous layer of palm tree trunk—single component system. International Journal of Engineering Science Invention, 2(6), 27–35.
Agarwal, A. K., Mahendra, S., Kadu, C, Pandhurnekar, P., & Muthreja I. L. (2014). Langmuir, Freundlich and BET adsorption, isotherm studies for zinc ions onto coal fly ash. International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management 3(Issue 1).
Agarwal, A. K., Kadu, M. S., Pandhurnekar, C. P., & Muthreja, I. L. (2012). Kinetics and adsorption isotherm study of removal of Zn+2 ions from aqueous solution using thermal power plant fly ash. International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, 3(4), 376–381.
Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2010). A review on the utilization of fly ash. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 36(3), 327–363.
Al Bakri, A. M., Mustafa, H., Kamarudin, M., Bnhussain, I., Khairul Nizar, A., Rafiza, R., & Zarina, Y. (2012). The processing, characterization, and properties of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Review of Advance Science, 30(2012), 90–97.
Al-Harahsheh, M. S., Shawabkeh, R., Batiha, M., Al-Harahsheh, A., & Al-Zboon, K. (2014). Sulfur dioxide removal using natural zeolitic tuff. Fuel Processing Technology, 126, 249–258.
Al-Harahsheh, M. S., Zboon, K. A., Al-Makhadmeh, L., Hararah, M., & Mahasneh, M. (2015). Fly ash based geopolymer for heavy metal removal: a case study on copper removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(3), 1669–1677.
Ali, A. A. & El-Bishtawi, R. (1997) Removal of lead and nickel ions using zeolite tuff. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology 69, (No. 1), 27–34.
Ali Ahmad, M. A.-H., & Marashdeh, L. M. (2014). Removal of aqueous chromium (III) ions using Jordanian natural zeolite tuff in batch and fixed bed modes. Jordan Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 6(2), 45–51.
Al-Jariri, J. S., & Khalili, F. (2010). Adsorption of Zn(II), Pb(II), Cr(III) and Mn(II) from water by Jordanian bentonite. Desalination & Water Treatment, 21(1–3), 308–322.
Almjadleh, M., Alasheh, S., & Raheb, I. (2014). Use of natural and modified Jordanian zeolitic tuff for removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions. Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, 8(3), 332–343.
Al-Shaybe, M., & Khalili, F. (2009). Adsorption of thorium (IV) and uranium (VI) by the Tulul al-Shabba Zeolitic Tuff, Jordan. Jordan Journal of Earth Environmental Science, 2(1), 108–119.
Alvarez-Ayuso, E., Querol, X., Plana, F., Alastuey, A., Moreno, N., Izquierdo, M., Font, O., Moreno, T., Diez, S., Vazquez, E., & Barra, M. (2008). Environmental, physical and structural characterization of geopolymer matrixes synthesized from coal (co-combustion fly ashes). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1–3), 175–183.
Al-Zboon, K. K., & Al-Zou’by, J. (2015). Effect of volcanic tuff on the characteristics of cement mortar. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering. doi:10.1080/19648189.2015.1053151.
Al-zboon, K., Al-Harahsheh, M., & Bani hani, F. (2011). Fly ash based geopolymer for Pb removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 188(1–3), 414–421.
Al-Zou’by Jehad, Y., Kamel, K. A-Z, Al-Tabbal, J. A. (2013). Low-cost treatment of grey water and reuse for irrigation of home garden plants. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal. http://omicron.ch.tuiasi.ro/EEMJ/pdfs/accepted/242_743_Al-Zboon_12.pdf.
Amenaghawon, N. A., Aisien, F. A., & Agho, O. E. Application of recycled rubber from scrap tyres in the adsorption of toluene from aqueous solution. Journal of Applied Science Environment Management 17 (3), 411–417.
Andini, S., Cioffi, R., Colangelo, F., Grieco, T., Montagnaro, F., & Santoro, L. (2008). Coal fly ash for the manufacture of geopolymer-based products. Waste Management, 28(2), 416–423.
Arivoli, S., Marimuthu, V., & Mohamed Jahangir, A. R. (2013). Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study on chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solution using strychnos Nux-Vomica L. Int Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, 3(6), 1321–133.
Armagan, B., & Toprak, F. (2012). Optimum Isotherm parameters for reactive azo dye onto pitstachio nut shells: comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 22(4), 1007–1011.
Astutiningsih S. and Y. Liu, 2005, Geopolymerization of Australian slag with effective dissolution by the alkali. In Geopolymer: green chemistry and sustainable solution, proceeding of Geopolymer congress 2005, edited by Joseph Davidovits, Institute of geopolymer, Paris, pp. 69–73.
Ayawei, N., Inengite, A. K., Wankasi, D., & Dikio, E. D. (2015). Synthesis and sorption studies of lead (II) on Zn/Fe layered double hydroxide. American Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3(3), 124–133.
Baltakys, K., Eisinas, A., Barauskas, I., Prichockiene, E., & Zaleckam, E. (2012). Removal of Zn(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution using gyrolite. Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research, 71(8), 566–572.
Bayat, B. (2002). Combined removal of zinc (II) and cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto high-calcium Turkish fly ash. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 136(1–4), 69–92.
Chafik, D., Bchitou, R., & Bouhaouss, A. (2014). The removal of Zinc in an aqueous solution by the phosphogypsum: modeling and optimizing. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(2), 331–335.
Chaudhary, R., Khale, D., & Badur, S. (2012). Leaching behavior effectiveness of curing days (7 & 28) of solidified/stabilized fly ash based geopolymer of solidified/stabilized fly ash based geopolymer (multi-metal bearing sludge): experimental and modeling study. Journal of Environment Science & Engineering, 54(2), 268–278.
Chawakitchareon, P., & Veesommaia, C. (2013). Geopolymer mortar production using silica waste as raw material. American Transactions on Engineering & Applied Sciences, 2(1), 3–13.
Cheng, T. W., Lee, M. L., Ko, M. S., Ueng, T. H., & Yang, S. F. (2012). The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer. Applied Clay Science, 2012(V56), 90–96.
Chergui, A., Bakhti, M. Z., Chahboub, A., Haddoum, S., Selatnia, A., & Junter, G. A. (2007). Simultaneous biosorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cr6+ from aqueous solution by Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Desalination, 206(1–3), 179–184.
Chong, A. M., Wong, Y. S., & Tam, N. F. (2000). Performance of different micro-algal species in removing nickel and zinc from industrial wastewater. Chemosphere, 41(1–2), 251–257.
Dada, A. O., Olalekan, A. P., Olatunya, A. M., & Dada, O. (2012). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3(1), 38–45.
De Weerdt, K. (2011). Geopolymers—state of the art COIN—Concrete Innovation Centre (COIN) Project report 37. ISBN 978–82–536–1251–5.
Depci, T., Kul, A. R., & Önal, Y. (2012). Competitive adsorption of lead and zinc from aqueous solution on activated carbon prepared from Van apple pulp: study in single- and multisolute systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200–202, 224–236.
Detphan, S., & Chindaprasirt, P. (2009). Preparation of fly ash and rice husk ash geopolymer. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 16(6), 720–726.
Dimitrios, P., Giannopoulou, I. P., & Perraki, T. (2007). Effect of synthesis parameters on the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymers. Colloid and Surface A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 301(1–3), 246–254.
Donat, R., Akdogan, A., Erdem, E., & Cetisli, H. (2005). Thermodynamics of Pb2+ and Ni2+ adsorption onto natural bentonite from aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 286(1), 43–52.
El-Eswed, B., & Yousef, R. I. (2012). The effect of chemical and thermal treatments on the buffering capacity of phillipsite tuff. Jordan Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 4(2), 7–14.
El-Eswed, B., Alshaaer, M., IbrahimYousef, R., Hamadneh, I., & Khalili, F. (2012). Adsorption of Cu(II), Ni(II), Zn(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) onto kaolin/zeolite-based geopolymers. Advances in Materials Physics and Chemistry, 2, 119–125.
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency), 1991. Site characterization for subsurface remediation. EPA/625/4-91/026, Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio
Fan, T., Liu, Y., Feng, B., Zeng, G., Yang, C., Zhou, M., Zhou, H., Tan, Z., & Wang, X. (2008). Biosorption of cadmium (II), zinc (II) and lead (II) by penicillium simplicissimum: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(2–3), 655–661.
Ferone, C., Colangelo, F., Roviello, G., Asprone, D., Menna, C., Balsamo, A., Prota, A., Cioffi, R., & Manfredi, G. (2013). Application-oriented chemical optimization of a Metakaolin based geopolymer. Materials, 2013(6), 1920–1939.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 2–10.
Ghomri, F., Lahsini, A., Laajeb, A., & Addaou, A. (2013). The removal of heavy metal ions (copper, zinc, nickel and cobalt) by natural bentonite. Larhyss Journal, 12, 37–54.
Hardjito, D., Wallah, S. E., Sumajouw, D. M. J., & Rangan, B. V. (2005). Fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Australian Journal of Structural Engineering, 2005(6), 1–9.
Harja, M., Buema, G., Sutiman, D., & Cretescu, I. (2013). Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using low-cost sorbents obtained from ash. Chemical Paper, 67(5), 497–508.
Hasar, H., Cuci, Y., Obek, E., & Dilekoglu, M. F. (2003). Removal of zinc(II) by activated carbon prepared from almond husks under different conditions. Adsorption Science & Technology, 21(9), 799–808.
Izquierdo, M., Querol, X., Davidovits, J., Antenucci, D., Nugteren, H., & Fernández-Pereira, C. (2009). Coal fly ash-slag-based geopolymers: microstructure and metal leachin. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(1), 561–566.
Kaya, A., & Oren, A. H. (2005). Adsorption of zinc from aqueous solutions to bentonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 125(1–3), 183–189.
Kazmi, M., Feroze, N., Javed, H., Zafar, M., & Ramzan, N. (2012). Biosorption of copper (II) on dry fruit by product: characterization, kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan, 34(6), 156–1365.
Khalili Fawwaz, I., Salameh, N. H., & Shaybe, M. M. (2013). Sorption of uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) by Jordanian bentonite. Journal of Chemistry. http://www.hindawi.com/journals/jchem/2013/586136/.
Krol, M., Morawska, J., Mozgawa, W., & Pichor, W. (2014). Low temperature synthesis of zeolite from perlite waste—part I: review of methods and phase compositions of resulting products. Materials Science-Poland, 32(3), 503–513.
Kumar, S., Mishra, A. K., Dhanesh, S., Upadhyay, M., & Sujata, K. (2014). Adsorption studies of fly ash for removing Cu(II) from aqueous solution. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 1(6), 42–52.
Lancellotti, I., Kamseu, E., Barbieri, L., Corradi, A., & Leonelli, C. (2015). Municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash to obtain geopolymers. http://www.srcosmos.gr/srcosmos/showpub.aspx?aa=13176.
Li, L., Wang, S., & Zhu, Z. (2006). Geopolymeric adsorbents from fly ash for dye removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 300(1), 52–9.
Mane, S., & Jadhav, H. S. (2008). Investigation of geopolymer mortar and concrete under high temperature. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, 2(12), 384–390.
Meroufel, B., Benali, O., Benyahia, M., Zenasni, M. A., Merlin, A., & George, B. (2013). Removal of Zn (II) from aqueous solution onto Kaolin by batch design. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2013(5), 669–680.
Mishra, P. C., & Patel, R. K. (2009). Removal of lead and zinc ions from water by low cost adsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(1), 319–25.
Misra, A., Gupta, R., & Gupta, R. C. (2003). Utilization of marble slurry in construction materials, workshop on gainful utilization of marble slurry and other stone waste. Indian School of Mines. available from: http://www.cdosindia.com.
Mon J, Deng, Y., Flury, M., & Harsh, J. B. (2005) Cesium incorporation and diffusion in cancrinite, sodalite, zeolite, and allophane. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 86(1–3) 28, 277–286.
Nikolići, I., Đurović, D., Tadić, M., Blečić, D., & Radmilović, V. (2013). Immobilization of zinc from metallurgical waste and water solutions using geopolymerization technology. Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment, Rome, Italy.
Nriagu, J. (2007) Zinc Toxicity in Humans, elsevier publishing, http://www.extranet.elsevier.com/homepage_about/mrwd/nvrn/Zinc%20Toxicity%20in%20Humans.pdf. Accessed 28 February 2016.
Onisei, S., Pontikes, Y., Van Gervenc, T., Angelopoulos, G. N., Velea, T., Predica, V., & Moldovana, P. (2012). Synthesis of inorganic polymers using fly ash and primary lead slag. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 205–206(2012), 101–110.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Standards). (2015). Occupational Safety and Health Administration; Washington, DC, USA: 200329CFR 1910.1000, Table Z-1.
Ozdemir, G., Ceyhan, N., Ozturk, T., Akirmak, F., & Cosar, T. (2004). Biosorption of chromium(VI), cadmium(II) and copper(II) by Pantoea sp. TEM 18. Chemical Engineering Journal, 102(3), 249–253.
Panias, D., & Giannopoulou, I. P. (2006). Development of inorganic polymeric materials based on fired coal fly ash. Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 12(2006), 321–327.
Plum, L. M., Lothar, R., & Hajo, H. (2010). The essential toxin: impact of zinc on human health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(4), 1342–1365.
Provis, J. L. (2006). Modeling the formation of geopolymer. PhD thesis, University of Melbourne, Australia.
Puranik, P. R., & Paknikar, K. M. (1999). Influence of co-cations on biosorption of lead and zinc—a comparative evaluation in binary and multimetal systems. Bioresource Technology, 70(3), 269–276.
Ramachandran, V., & D’Souza, S. F. (2013). Adsorption of nickel by Indian soils. SF Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 13(1), 165–173.
Rangan, B. V. (2008). Low-calcium fly ash-based geopolymer concrete, chapter 26. In E. G. Nawy (Ed.), Concrete construction engineering handbook (2nd ed., pp. 26.1–26.20). New York: CRC Press.
Rushdi I. Y., Bassam E., Mazen A., Fawwaz K., & Hani K. (2009). The influence of using Jordanian natural zeolite on the adsorption, physical, and mechanical properties of geopolymers products. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165(1), 379–387.
Saeed, A., Akhter, M. W., & Iqbal, M. (2005). Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using papaya wood as a new biosorbent. Separation and Purification Technology, 45, 25–31.
Saha, P., & Chowdhury, S. (2015) Insight into adsorption thermodynamics, chapter 16: edited by Tadashi Mizutani, Intech Open Access Publisher. http://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfswm/13254.pdf.
Salim, R., Al-Subu, M., Abu-Shqair, I., & Braik, H. (2003). Removal of zinc from aqueous solutions by dry plant leaves. Trans I ChemE, 81(Part B), 236–242.
Sampranpiboon, P., Charnkeitkong, P., & Feng, X. (2014). Equilibrium isotherm models for adsorption of zinc (II) ion from aqueous solution on pulp waste. Wseas Transactions on Environment and Development, 10, 35–47.
Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh, S. H., & Babazadeh, H. (2014). Isotherms for the sorption of zinc and copper onto kaolinite: comparison of various error functions. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11(1), 111–118.
Sharmaa, P., Binoy, K., Saikia, B., & Das, M. R. (2014). Removal of methyl green dye molecule from aqueous system using reduced graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic parameters. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical. Eng. Aspects, 457, 125–133.
Shobana, R., Arockia, S. P., Dharmalingam, V., & Soruba, R. (2014). Adsorption study on zinc (II) ions from aqueous solution using chemically activated fruit of Kigelia Pinnata (JACQ) DC carbon. International Research Journal of Environment, 3(9), 65–69.
Sismanoglu, T, Ercag, A., Pura, S., & Ercag, E. (2004). Kinetics and isotherms of dazomet adsorption on natural adsorbents. Journal of Brazilian Chemical Society 15, (5). online, http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0103-50532004000500010.
Solomon Samu, J., Martin Devaprasath, P., & Chandramohan, M. (2012). Removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution by using natural plant material Cynodon dactylon. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 3(2), 304–321.
Srivastava, S., Chaudhary, R., & Khale, D. (2008). Influence of pH, curing time and environmental stress on the immobilization of hazardous waste using activated fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(3), 1103–1109.
Swanepoel, J. C., Strydom, C. A., Swanepoel, J. C., & Strydom, C. A. (2002). Utilization of fly ash in a geopolymeric material. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 1143–1148.
Tahir, S., & Naseem, R. (2007). Removal of Cr(III) from tannery wastewater by adsorption onto bentonite clay. Separation and Purification Technology, 53, 312–321.
van Jaarsveld, J. G., van Deventer, J. S., & Lukey G. (1989) The effect of composition and temperature on the properties of fly ash- and kaolinite-based geopolymers. Chemical Engineering Journal 89 (1–3), 63–73.
Van Jaarsveld, J. G. S., Van Deventer, J. S. J., & Lorenzen, L. (1997). The potential use of geopolymeric materials to immobilise toxic metals: part I. theory and applications. Mineral Engineering, 10(7), 659–669.
Wahi, R., Kanakaraju, D., & Yusuf, N. A. (2010). Preliminary study on zinc removal from aqueous solution by sago wastes. Global Journal of Environmental Research, 4(2), 127–134.
Wang, S., Li, L., & Zhu, Z. H. (2007). Solid-state conversion of fly ash to effective adsorbents for Cu removal from wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 139(2), 254–259.
Wasewar K. L., Atif, M., Prasad, B., & Mishra, I. M. (2009). Batch adsorption of Zn using tea factory waste as an adsorbent. Desalination, 244(1–3), 66–71.
Wasewar, K. L., Mohammad, A., & Prasad, B. (2008). Characterization of factory tea waste as an adsorbent for removal of heavy metals. Jornal of Future Engineering Technonlogy, 3(3), 47–53.
Wu, D., Sui, Y., He, S., Wang, X., Li, C., & Kong, H. (2008). Removal of trivalent chromium from aqueous solution by zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155(3), 415–423.
Xu, H., van Deventer, J. S. J., & Lukey, G. C. (2001). Effect of alkali metals on the preferential geopolymerization of stilbite/kaolinite mixtures. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 40(17), 3749–3756.
Xu, H., Jannie, S. J., & Deventer, V. (2002). Geopolymerisation of multiple minerals. Minerals Engineering, 15(12), 1131–1139.
Yan G., & Viraraghavan T. (2003) Heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution by fungus Mucor rouxii. Water Research, 37(18), 4486–96.
Yun-Guo, L., Ting, F., Guang-ming, Z., Xin, L., Qing, T., Fe, Y., Ming, Z., Wei-hua, X., & Yu-e, H. (2006). Removal of cadmium and zinc ions from aqueous solution by living Aspergillus niger. Transactions of Nonferrous Metal Society China, 16, 681–686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3335-3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Zboon, K.K., Al-smadi, B.M. & Al-Khawaldh, S. Natural Volcanic Tuff-Based Geopolymer for Zn Removal: Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 248 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2937-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2937-5