Abstract
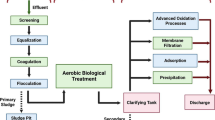
This research work evaluates the use of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of cyanide from coking wastewater deriving from the washing of gases in coal combustion furnace. The effect of the presence or absence of suspended solids and organic micropollutants on the efficiency of the treatment is analyzed. Various dosages of hydrogen peroxide (6.5–200 mg/L) were added to both aqueous solution (at pH 10.5) and industrial wastewater (at pH 10.3) samples. The influence of suspended solids in coking wastewater was analyzed by applying a coagulation–flocculation–decantation process before the hydrogen peroxide treatment. The preliminary cyanide removal treatment in aqueous solution showed that the maximum cyanide removal did not exceed 14 % using a mass ratio of hydrogen peroxide to cyanide of 11.6. The maximum cyanide removal obtained in coking wastewater was 47 % with a mass ratio of hydrogen peroxide to cyanide of 12.2 provided that a coagulation–flocculation–decantation pretreatment was applied to remove the suspended solids composed mainly of coal, calcium carbonate, and magnesium carbonate. On the other hand, the cyanide removal treatment in coking wastewater with hydrogen peroxide showed promising results in the removing of different organic micropollutants formed mainly by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and quinolines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boening, D. W., & Chew, C. M. (1999). A critical review: general toxicity and environmental fate of three aqueous cyanide ions and associated ligands. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 109(1), 67–79.
Centi, G., Pinelli, D., & Trifiro, F. (1989). Heterogeneous catalytic ammoxidation of o-xylene to phthalimide: analysis of the reaction network. Gazzetta Chimica Italiana, 119, 133–137.
Chang, E. E., Hsing, H. J., Chiang, P. C., Chen, M. Y., & Shyng, J. Y. (2008). The chemical and biological characteristics of coke-oven wastewater by ozonation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156(1–3), 560–567.
Chen, F., Zhao, X., Liu, H., & Qu, J. (2014). Reaction of Cu(CN)3 2− with H2O2 in water under alkaline conditions: cyanide oxidation, Cu+/Cu2+ catalysis and H2O2 decomposition. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 158–159, 85–90.
Chu, L., Wang, J., Dong, J., Liu, H., & Sun, X. (2012). Treatment of coking wastewater by an advanced Fenton oxidation process using iron powder and hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere, 86(4), 409–414.
Dash, R. R., Gaur, A., & Balomajumder, C. (2009). Cyanide in industrial wastewaters and its removal: a review on biotreatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(1), 1–11.
Directive 2010/75/EU of 24 of November of 2010 laid down industrial emissions (integrated pollution prevention and control). Official Journal of the European Union L 334:17 of December of 2010.
Eaton, A. D., Clesceri, L. S., Rice, E. W., Greenberg, A. E., & Franson, M. A. H. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington: American Public Health Association.
Eisler, R. (2000). Handbook of chemical risk assessment: health hazards to humans, plants and animals. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
EPA Method 625 (1984). Methods for organic chemical analysis of municipal and industrial wastewater–base/neutrals and acids.
Esplugas, S., Gimenez, J., Contreras, S., Pascual, E., & Rodriguez, M. (2002). Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for phenol degradation. Water Research, 36(4), 1034–1042.
Georgi, A., & Kopinke, F. (2005). Interaction of adsorption and catalytic reactions in water decontamination processes Part I. Oxidation of organic contaminants with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by activated carbon. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 58(1–2), 9–18.
Gottschalk, C., Libra, J. A., & Saupe, A. (2000). Ozonation of water and waste water: a practical guide to understanding ozone and its applications. Germany: Wiley-VCH.
Griffiths, S. R., Donato, D. B., Coulson, G., & Lumsden, L. F. (2014). High levels of activity of bats at gold mining water bodies: implications for compliance with the International Cyanide Management Code. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(12), 7263–7275.
Hartinger, L. (1994). Handbook of effluent treatment and recycling for the metal finishing industry. Warrington: Finishing Publications.
Huang, H., Lu, M., Chen, J., & Lee, C. (2003). Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and 4-chlorophenol in the presence of modified activated carbons. Chemosphere, 51(9), 935–943.
Jin, X., Li, E., Lu, S., Qiu, Z., & Sui, Q. (2013). Coking wastewater treatment for industrial reuse purpose: combining biological processes with ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(8), 1565–1574.
Kepa, U., Stanczyk-Mazanek, E., & Stepniak, L. (2008). The use of the advanced oxidation process in the ozone + hydrogen peroxide system for the removal of cyanide from water. Desalination, 223(1–3), 187–193.
Khorramfar, S., Mahmoodi, N., Arami, M., & Bahrami, H. (2011). Oxidation of dyes from colored wastewater using activated carbon/hydrogen peroxide. Desalination, 279(1–3), 183–189.
Kim, Y. J., Qureshi, T. I., & Min, K. S. (2003). Application of advanced oxidation processes for the treatment of cyanide containing effluent. Environmental Technology, 24(10), 1269–1276.
Kitis, M., Akcil, A., Karakaya, E., & Yigit, N. O. (2005a). Destruction of cyanide by hydrogen peroxide in tailings slurries from low bearing sulphidic gold ores. Minerals Engineering, 18(3), 353–362.
Kitis, M., Karakaya, E., Yigit, N. O., Civelekoglu, G., & Akcil, A. (2005b). Heterogeneous catalytic degradation of cyanide using copper-impregnated pumice and hydrogen peroxide. Water Research, 39(8), 1652–1662.
Kjeldsen, P. (1999). Behaviour of cyanides in soil and groundwater: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 115(1), 279–307.
Knorre, H., & Griffiths, A. (1984). Cyanide detoxification with hydrogen peroxide using the Degussa process. Tucson: Proceedings of the Cyanide and the Environment Conference.
Ku, Y., Tu, Y. H., & Ma, C. M. (2005). Effect of hydrogen peroxide on the decomposition of monochlorophenols by sonolysis in aqueous solution. Water Research, 39(6), 1093–1098.
Kuyucak, N., & Akcil, A. (2013). Cyanide and removal options from effluents in gold mining and metallurgical processes. Minerals Engineering, 50–51, 13–29.
Lee, T., Kwon, Y., & Kim, D. (2004). Oxidative treatment of cyanide in wastewater using hydrogen peroxide and homogeneous catalyst. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 39(3), 787–801.
Liao, C. H., & Gurol, M. D. (1995). Chemical oxidation by photolytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Environmental Science and Technology, 29(12), 3007–3014.
Marañón, E., Vázquez, I., Rodríguez, J., Castrillón, L., & Fernández, Y. (2008). Coke wastewater treatment by a three-step activated sludge system. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 192(1), 155–164.
Monteagudo, J. M., Rodríguez, L., & Villaseñor, J. (2004). Advanced oxidation processes for destruction of cyanide from thermoelectric power station waste waters. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 79(2), 117–125.
Mudder, T., Botz, M., & Smith, A. (2001). Chemistry and treatment of cyanidation wastes. London: Mining Journal Books Ltd.
Mudliar, R., Umare, S. S., Ramteke, D. S., & Wate, S. R. (2009). Energy efficient—advanced oxidation process for treatment of cyanide containing automobile industry wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2–3), 1474–1479.
Nekrasov, L. N., Peregudova, S. M., Yur’eva, L. P., Kravtsov, D. N., Uralets, I. A., & Zaitseva, N. N. (1989). Study of redox reactions of bis(arene)chromium complexes by use of the rotating disk and the rotating ring-disk electrodes: V. Cathodic processes involving nitriles; cyano derivatives of benzene and dibenzenechromium. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 365(3), 269–284.
Nelieu, S., Kerhoas, L., & Einhorn, J. (2000). Degradation of atrazine into ammeline by combined ozone/hydrogen peroxide treatment in water. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(3), 430–437.
Pak, D., & Chang, W. (1997). Oxidation of aqueous cyanide solution using hydrogen peroxide in the presence of heterogeneous catalyst. Environmental Technology, 18(5), 557–561.
Park, D., Kim, Y. M., Lee, D. S., & Park, J. M. (2008). Chemical treatment for treating cyanides-containing effluent from biological cokes wastewater treatment process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143(1–3), 141–146.
Royal Decree 817/2015 of 11 of September of 2015, laid down the criteria for monitoring and evaluating the status of continental surface waters and the Environmental Quality Standards. Bulletin Official of State, 219 (I), 12.
Sarla, M., Pandit, M., Tyagi, D. K., & Kapoor, J. C. (2004). Oxidation of cyanide in aqueous solution by chemical and photochemical process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 116(1–2), 49–56.
Van-Leeuwen, J., Badriyha, B., & Vaczi, S. (2003). Investigation into ozonation of coal coking processing wastewater for cyanide, thiocyanate and organic removal. Ozone Science and Engineering, 25(4), 273–283.
Wei, X., Zhang, Z., Fan, Q., Yuan, X., & Guo, D. (2012). The effect of treatment stages on the coking wastewater hazardous compounds and their toxicity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 239–240, 135–141.
Wild, S. R., Rudd, T., & Neller, A. (1994). Fate and effects of cyanide during wastewater treatment processes. Science of the Total Environment, 56(2), 93–107.
Wu, Z., & Zhu, L. (2012). Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phenols from coking wastewater by simultaneously synthesized organobentonite in a one-step process. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(2), 248–253.
Xu, S., & Ning, P. (2002). Analysis of organic pollutants from the wastewater of coking plant by GC/MS. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 29(5), 32–34.
Yan, F., Guo, C., Zhang, X., & Yuan, G. (2012). Hydrogen peroxide as a crystal growth modifier of CaCO3. CrystEngComm, 14(6), 2046–2052.
Yazici, E.Y., Deveci, H., Alp, Í., Uslu, T., & Celep, O. (2006). Factors affecting decomposition of cyanide by hydrogen peroxide. Proceedings of the 23rd International Mineral Processing Congress, Istanbul.
Yazici, E. Y., Deveci, H., & Alp, Í. (2009). Treatment of cyanide effluents by oxidation and adsorption in batch and column studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 1362–1366.
Yeddou, A. R., Nadjemi, B., Halet, F., Ould-Dris, A., & Capart, R. (2010). Removal of cyanide in aqueous solution by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in presence of activated carbon prepared from olive stones. Minerals Engineering, 23(1), 32–39.
Yeddou, A. R., Nadjemi, B., Halet, F., Ould-Dris, A., & Belkouch, J. (2011). Removal of cyanide in aqueous solution by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in presence of copper-impregnated carbon. Minerals Engineering, 24(8), 788–793.
Young, C.A., & Jordan, T.S. (1995). Cyanide remediation: current and past technologies. Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Hazardous Waste Research, Kansas.
Zhang, W., Liu, W., Lv, Y., Li, B., & Ying, W. (2010). Enhanced carbon adsorption treatment for removing cyanide from coking plant effluent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184(1–3), 135–140.
Zhang, W., Wei, C., Chai, X., He, J., Cai, Y., Ren, M., Yan, B., Peng, P., & Fu, J. (2012). The behaviors and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a coking wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere, 88(2), 174–182.
Zhang, W., Wei, C., Yan, B., Feng, C., Zhao, G., Lin, C., Yuan, M., Wu, C., Ren, Y., & Hu, Y. (2013). Identification and removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wastewater treatment processes from coke production plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(9), 6418–6432.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the DGA-FSE Research Team T33 and the University of Zaragoza (Project JIUZ2014-TEC-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pueyo, N., Rodríguez-Chueca, J., Ovelleiro, J.L. et al. Limitations of the Removal of Cyanide from Coking Wastewater by Treatment with Hydrogen Peroxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 222 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2915-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2915-y