Abstract
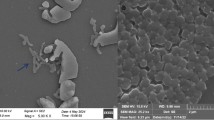
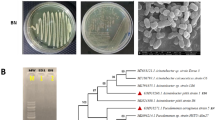
A bacterial strain CMGCZ was isolated from an abandoned oil field soil sample and identified as Rhodococcus sp. by 16S rRNA sequencing. Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ was investigated for the degradation of model polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Iranian light crude oil (ILCO) as a sole carbon source in minimal medium. Biodegradation enhancement was attained by supplementing the minimal medium with yeast extract (YE). Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ was capable to degrade 13.2 % naphthalene (Nap), 13.1 % phenanthrene (Phe), and 99.3 % fluoranthene (Fla) in 1 week and 11 % aliphatic fraction of ILCO in 2 weeks as a sole carbon and energy source. Effect of YE supplementation on degradation potential of Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ depended upon the added hydrocarbon in the medium. YE completely inhibited Nap degradation, slightly enhanced degradation of Phe (14.8 %) and ILCO aliphatics (13.2 %), and promoted a more rapid degradation of Fla (100 %). YE addition promoted rapid degradation of Fla and eliminated delay of 24 h in Fla degradation that was observed in minimal medium. Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ was capable to degrade high concentrations of Fla (1000 mg l−1). Rieske [Fe2-S2] center was amplified in Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ that exhibited homology with Rieske [Fe2-S2] domain protein of Mycobacterium species and pahAC gene of uncultured bacterium clones.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARHDs:
-
Aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases
- Fla:
-
Fluoranthene
- HMW:
-
High molecular weight
- ILCO:
-
Iranian light crude oil
- LB:
-
Luria Bertani
- LMW:
-
Low molecular weight
- MSM:
-
Minimal salt medium
- Nap:
-
Naphthalene
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- PCB:
-
Polychlorinated biphenyl
- Phe:
-
Phenanthrene
- Pyr:
-
Pyrene
- YE:
-
Yeast extract
- YMSM:
-
MSM supplemented with 0.05 % YE
References
Bell, K., Philip, J., Aw, D., & Christofi, N. (1998). The genus Rhodococcus. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 85, 195–210.
Boldrin, B., Thiem, A., & Fritsche, C. (1993). Degradation of phenanthrene, fluorene, fluoranthene, and pyrene by a Mycobacterium sp. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 1927–1930.
Bouchez, M., Blanchet, D., & Vandecasteele, J. P. (1997). An interfacial uptake mechanism for the degradation of pyrene by a Rhodococcus strain. Microbiol, 143, 1087–1093.
Braddock, J. F., Ruth, M. L., Catterall, P. H., Walworth, J. L., & McCarthy, K. A. (1997). Enhancement and inhibition of microbial activity in hydrocarbon contaminated Arctic soils: implications for nutrient amended bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol, 31, 2078–2084.
Brezna, B., Khan, A. A., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2003). Molecular characterization of dioxygenases from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading Mycobacterium spp. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 223, 177–183.
Cerniglia, C. E. (1992). Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodegradation, 3, 351–368.
Chadhain, S. M. N., Norman, R. S., Pesce, K. V., Kukor, J. J., & Zylstra, G. J. (2006). Microbial dioxygenase gene population shifts during polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 4078–4087.
Chang, B. V., Chang, I. T., & Yuan, S. Y. (2008). Biodegradation of phenanthrene and pyrene from mangrove sediment in subtropical Taiwan. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A, 43, 233–238.
de Carvalho, C. C. C. R., & da Fonseca, M. M. R. (2005a). The remarkable Rhodococcus erythropolis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 715–726.
de Carvalho, C. C. C. R., & da Fonseca, M. M. R. (2005b). Degradation of hydrocarbons and alcohols at different temperatures and salinities by Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 51, 389–399.
Dean-Ross, D., & Cerniglia, C. E. (1996). Degradation of pyrene by Mycobacterium flavescens. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 46, 307–312.
Dean-Ross, D., Moody, J., Freeman, J. P., Doerge, D. R., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2001). Metabolism of anthracene by a Rhodococcus species. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 204, 205–211.
Dean-Ross, D., Moody, J., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2002). Utilization of mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria isolated from contaminated sediments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 41, 1–7.
Gariazzo, C., Lamberti, M., Hänninen, O., Silibello, C., Pelliccioni, A., Porta, D., et al. (2015). Assessment of population exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using integrated models and evaluation of uncertainties. Atmosph Environ, 101, 235–245.
Gibson, D. T., & Parales, R. E. (2000). Aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenases in environmental biotechnology. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 11, 236–243.
Hadibarata, T., & Kristanti, A. R. (2015). Biotransformation studies on fluoranthene, a four-ring polycylic aromatic hydrocarbon, by white-rot fungus Armillaria sp. F022. Agriculture and Agricutural Science Procedia, 3, 45–50.
Hall, K., Miller, C. D., Sorensen, D. L., Anderson, A. J., & Sims, R. C. (2005). Development of a catabolically significant genetic probe for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading Mycobacteria in soil. Biodegradation, 16, 475–484.
Hamann, C., Hegemann, J., & Hildebrandt, A. (1999). Detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation genes in different soil bacteria by polymerase chain reaction and DNA hybridization. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 173, 255–263.
Hamme, J. D., Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2003). Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 67, 503–549.
Harayama, S., Kishira, H., Kasai, Y., & Shutsubo, K. (1999). Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1, 63–70.
Heitkamp, M. A., & Cerniglia, C. E. (1988). Mineralization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a bacterium isolated from sediment below an oil field. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 1612–1614.
Herwijnen, V. R., Wattiau, P., Bastiaens, L., Daal, L., Jonker, L., Springael, D., Govers, H. A. J., & Parsons, J. R. (2003). Elucidation of the metabolic pathways of fluorine and cometabolic pathways of phenanthrene, fluoranthene, anthracene and dibenzothiophene by Sphingomonas sp. LB126. Research in Microbiology, 154, 199–206.
Ho, Y., Jackson, M., Yang, Y., Mueller, J. G., & Pritchard, P. H. (2000). Characterization of fluoranthene and pyrene degrading bacteria isolated from PAH-contaminated soils and sediments. J Ind Microbiol Biot, 24, 100–112.
Huang, L., Ma, T., Li, D., Liang, F., Liu, R., & Li, G. (2008). Optimization of nutrient component for diesel oil degradation by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 1714–1718.
Ito, H., Hosokawa, R., Morikaw, M., & Okuyama, H. (2008). A turbine oil-degrading bacterial consortium from soils of oil fields and its characteristics. Int Biodeter Biodeg, 61, 223–232.
Iwabuchi, N., Sunairi, M., Anzai, H., Nakajima, M., & Harayama, S. (2000). Relationship between colony morphotypes and oil tolerance in Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 5073–5077.
Juhasz, A. L., & Naidu, R. (2000). Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. Int Biodeter Biodeg, 45, 57–88.
Kelley, I., & Cerniglia, C. E. (1995). Degradation of mixture of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a Mycobacterium strain PYR-1. J Soil Contam, 4, 77–91.
Kim, T. J., Lee, E. Y., Kim, Y. J., Cho, K. S., & Ryu, H. W. (2003). Degradation of polyaromatics hydrocarbons by Burkholderia cepacia 2A-12. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 411–417.
Kim, J., Kweon, O., Freeman, J. P., Jones, R. C., Adjei, M. D., Jhoo, J., Edmondson, R. D., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2006). Molecular cloning and expression of genes encoding a novel dioxygenase involved in low and high molecular weight polycylic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in Mycobacterium vanbaleenii PYR-1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 1045–1054.
Kiyohara, H., Nagao, K., & Yana, K. (1982). Rapid screen of bacteria degrading water-insoluble, solid hydrocarbons on agar plates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 454–457.
Kulikova, A. K., & Bezborodov, A. M. (2000). Oxidation of organic compounds by propane monooxygenase of Rhodococcus erythropolis 3/89. Appl Biochem Microbiol, 36, 227–230.
Larkin, M. J., Allen, C. C. R., Kulakov, L. A., & Lipscomb, D. A. (1999). Purification and characterization of a novel naphthalene dioxygenase from Rhodococcus sp. strain NCIMB12038. Journal of Bacteriology, 181, 6200–6204.
Larkin, M. J., Kulakov, L. A., & Allen, C. C. R. (2005). Biodegradation and Rhodococcus—masters of catabolic versatility. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 16, 282–290.
Lin, Y., & Cai, L. X. (2008). PAH-degrading microbial consortium and its pyrene-degrading plasmids from mangrove sediment samples in Huian, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57, 703–706.
Lu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Zeng, X., Luo, Q., & Wang, L. (2009). Biodegradation of dimethyl phthalate, diethyl phthalate and di-n-butyl phthalate by Rhodococcus sp. L4 isolated from activated sludge. J Hazard Mater, 168, 938–943.
Maiti, A., Das, S., & Bhattacharyya, N. (2012). Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Bacillus thuringiensis strain NA2. J Sci, 1, 72–75.
Martinkova, L., Uhnakova, B., Patek, M., Nesvera, J., & Kren, V. (2009). Biodegradation potential of the genus Rhodococcus. Environ Int, 35, 162–177.
Mishra, S., Singh, S. N., & Pande, V. (2014). Bacteria induced degradation of fluoranthene in minimal salt medium mediated by catabolic enzymes in vitro condition. Biores Tech, 164, 299–308.
Moser, R., & Stahl, U. (2001). Insights into the genetic diversity of initial dioxygenases from PAH-degrading bacteria. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 55, 609–618.
Mueller, J. G., Chapman, P. J., & Pritchard, P. H. (1989). Action of a fluoranthene utilizing bacterial community on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon components of creosote. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55, 3085–3090.
Mueller, J. G., Chapman, P. J., Blattmann, B. O., & Pritchard, P. H. (1990). Isolation and characterization of a fluoranthene utilizing strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 1079–1086.
Mueller, J. G., Devereux, R., Santavy, D. L., Lantz, S. E., Willis, S. G., & Pritchard, P. H. (1997). Phylogenetic and physiological comparisons of PAH-degrading bacteria from geographically diverse soils. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 71, 329–343.
Neu, T. R. (1996). Significance of bacterial surface active compounds in interaction of bacteria with interfaces. Microbiological Reviews, 60, 151–166.
Pagnout, C., Rast, C., Veber, A., Poupin, P., & Ferard, J. (2006). Ecotoxicological assessment of PAHs and their dead-end metabolites after degradation by Mycobacterium sp. strain SNP11. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 65, 151–158.
Pagnout, C., Frache, G., Poupin, P., Maunit, B., Muller, J., & Ferard, J. (2007). Isolation and characterization of a gene cluster involved in PAH degradation in Mycobacterium sp. strain SNP11: expression in Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155. Research in Microbiology, 158, 175–186.
Parales, R. E., & Resnick, S. M. (2006). Aromatic ring hydroxylating dioxygenases. In J. Ramos & C. Levesque (Eds.), Pseudomonas (Vol. 4, pp. 287–340). Netherlands: Springer.
Peng, R., Xiong, A., Xue, Y., Fu, X., Gao, F., Zhao, W., Tian, Y., & Yao, Q. (2008). Microbial biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 32, 927–955.
Peterson, B. S., Rauh, V. A., Bansal, R., Hao, X., Toth, Z., Nati, G., Walsh, K., Miller, R. L., Arias, F., Semanek, D., & Perera, F. (2015). Effects of prenatal exposure to air pollutants (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) on the development of brain white matter, cognition, and behavior in later childhood. JAMA Psychiatry, 72, 531–540.
Rehmann, K., Hertkorn, N., & Kettrup, A. (2001). Fluoranthene metabolism in Mycobacterium sp. strain KR20: identity of pathway intermediates during degradation and growth. Microbiology, 147, 2783–2794.
Rolling, W. F. M., Milner, M. G., Jones, D. M., Lee, K., Daniel, F., Swannell, R. J. P., & Head, I. M. (2002). Robust hydrocarbon degradation and dynamics of bacterial communities during nutrient enhanced oil spill bioremediation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 5537–5548.
Sepic, E., Bricelj, M., & Leskovse, H. (1998). Degradation of fluoranthene by Pasteurella sp. IFA and Mycobacterium sp. PYR1: isolation and identification of metabolites. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 85, 746–754.
Simarro, R., Gonzalez, N., Bautista, L. F., & Molina, M. C. (2012). Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a wood-degrading consortium at low temperatures. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 83, 438–449.
Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2004). Biodegradation and bioremediation. New York: Springer.
Storey, S., Ashaari, M. M., McCabe, G., Harty, M., Dempsey, R., Doyle, O., Clipson, N., & Doyle, E. (2014). Microbial community structure during fluoranthene degradation in the presence of plants. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 117, 74–84.
Suen, W. C., Haigler, B. E., & Spain, J. C. (1996). 2,4-Dinitrotoluene dioxygenase from Burkholderia sp. strain DNT: similarity to naphthalene dioxygenase. Journal of Bacteriology, 178, 4926–4934.
Ueno, A., Hasanuzzaman, M., Yumoto, I., & Okuyama, H. (2006). Verification of degradation of n-alkanes in diesel oil by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain WatG in soil microcosms. Current Microbiology, 52, 182–185.
Ueno, A., Ito, Y., Yumoto, I., & Okuyama, H. (2007). Isolation and characterization of bacteria from soil contaminated with diesel oil and the possible use of these in autochthonous bioaugmentation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 23, 1739–1745.
Vila, J., Tauler, M., & Grifoll, M. (2015). Bacterial PAH degradation in marine and terrestrial habitats. Curr Opinion Biotechnol, 33, 95–102.
Walter, U., Beyer, M., Klein, J., & Rehm, H. J. (1991). Degradation of pyrene by Rhodococcus sp. UW1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 671–676.
Walworth, J. L., & Reynolds, C. M. (1995). Bioremediation of a petroleum contaminated cryic soil: effects of phosphorus, nitrogen and temperature. J Soil Contam, 4, 299–310.
Warhurst, A. M., & Fewson, C. A. (1994). Biotransformations catalysed by the genus Rhodococcus. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 14, 29–73.
Weißenfels, W. D., Beyer, M., & Klein, J. (1990). Degradation of phenanthrene, fluorene and fluoranthene by pure bacterial cultures. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 32, 479–484.
Whyte, L. G., Hawari, J., Zhou, E., Bourbonniere, L., Inniss, W. E., & Greer, C. W. (1998). Biodegradation of variable-chain-length alkanes at low temperatures by a psychrotrophic Rhodococcus sp. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2578–2584.
Widada, J., Nojiri, H., Kasuga, K., Yoshida, T., Habe, H., & Omori, T. (2002). Molecular detection and diversity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria isolated from geographically diverse sites. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 58, 202–209.
Wong, J. W. C., Lai, K. M., Wan, C. K., Ma, K. K., & Fang, M. (2002). Isolation and optimization of PAH-degradative bacteria from contaminated soil for PAHs bioremediation. Water Air Soil Poll, 139, 1–13.
Wongsa, P., Tanaka, M., Ueno, A., Hasanuzzaman, M., Yumoto, I., & Okuyama, H. (2004). Isolation and characterization of novel strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marces possessing high efficiency to degrade gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil and lubricating oil. Current Microbiology, 49, 415–422.
Xu-Xiang, Z., Shu-Pei, C., Cheng-Jun, Z., & Shi-Lei, S. (2006). Microbial PAH-degradation in soil: degradation pathways and contributing factors. Pedosphere, 16, 555–565.
Yagi, J. M., & Madsen, E. L. (2009). Diversity, abundance and consistency of microbial oxygenase expression and biodegradation in shallow contaminated aquifer. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 6478–6487.
Yam, C. K., van der Geize, R., & Eltis, L. D. (2010). Catabolism of aromatic compounds and steroids by Rhodococcus. In H. M. Alvarez (Ed.), Biology of Rhodococcus (Vol. 16, pp. 133–169). Germany: Springer.
Zhong, Y., Luan, T., Wang, X., Lan, C., & Tam, N. F. Y. (2007). Influence of growth medium on cometabolic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingomonas sp. strain PheB4. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 175–186.
Zhou, Q. X., & Hua, T. (2004). Bioremediation: a review of applications and problems to be resolved. Progr Nat Sci, 14, 937–944.
Zhou, H. W., Luan, T. G., Zou, F., & Tam, N. F. Y. (2008). Different bacterial groups for biodegradation of three-and four-ring PAHs isolated from a Hong Kong mangrove sediment. J Hazard Mater, 152, 1179–1185.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Higher Education Commission, Pakistan, under the program International Research Support Initiative Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, R.Z., Ahmed, N. Isolation of Rhodococcus sp. CMGCZ Capable to Degrade High Concentration of Fluoranthene. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 162 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2857-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2857-4