Abstract
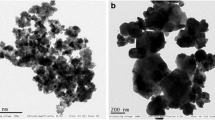
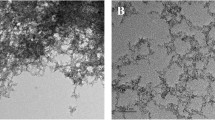
In this study, the effects of exposure to engineered nickel oxide (NiO 40–60 nm) and cobalt oxide (CoO <100 nm) nanoparticles (NP) were investigated on Artemia salina. Aggregation and stability of the aqueous NP suspensions were characterized by DLS and TEM. Acute exposure was conducted on nauplii (larvae) in seawater in a concentration range from 0.2 to 50 mg/L NPs for 24 h (short term) and 96 h (long term). The hydrodynamic diameters of NiO and CoO NPs in exposure medium were larger than those estimated by TEM. Accumulation rate of NiO NPs were found to be four times higher than that of CoO NPs under the same experimental conditions. Examinations under phase contrast microscope showed that the nanoparticles accumulated in the intestine of Artemia, which increased with increasing exposure concentration. Differences were observed in the extent of dissolution of the NPs in the seawater. The CoO NPs dissolved significantly while NiO NPs were relatively more stable. Oxidative stress induced by the NP suspensions was measured by malondialdehyde assay. Suspensions of NiO NPs caused higher oxidative stress on nauplii than those of CoO NPs. The results imply that CoO and NiO NPs exhibit toxicity on Artemia (e.g., zooplankton) that is an important source of food in aquatic food chain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, L. K., Lyon, D. Y., & Alvarez, P. J. J. (2006). Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Research, 40, 3527–3532.
Ahamed, M., Ali, D., Alhadlaq, H. A., & Akhtar, M. J. (2013). Nickel oxide nanoparticles exert cytotoxicity via oxidative stress and induce apoptotic response in human liver cells (HepG2). Chemosphere, 93, 2514–2522.
Arslan, Z., Ates, M., McDuffy, W., Agachan, M. S., Farah, I. O., Yu, W. W., & Bednar, A. J. (2011). Probing metabolic stability of CdSe nanoparticles: alkaline extraction of free cadmium from liver and kidney samples of rats exposed to CdSe nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 192–199.
Aruoja, V., Dubourguier, H. C., Kasemets, K., & Kahru, A. (2009). Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 1461–8.
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z., & Farah, I. O. (2013a). Uptake and toxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles to brine shrimp (Artemia salina). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 3339–3348.
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z., Farah, I. O., & Félix-Rivera, H. (2013b). Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on Brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 15, 225–233.
Ates M, Demir V, Adiguzel R, Arslan Z. (2013c). Bioaccumulation, subacute toxicity, and tissue distribution of engineered titanium dioxide nanoparticles in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Journal of Nanomaterials, doi.org/10.1155/2013/460518.
Ates, M., Demir, V., Arslan, Z., Daniels, J., Farah, I. O., & Bogatu, C. (2015a). Evaluation of alpha and gamma aluminum oxide nanoparticle accumulation, toxicity and depuration in Artemia salina larvae. Environmental Toxicology, 30, 109–118.
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z., & Farah, I. O. (2015b). Comparative study of accumulation, toxicity and trophic transfer of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environmental Toxicology, 30, 119–128.
Baker, T. J., Tyler, C. R., & Galloway, T. S. (2014). Impacts of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on marine organisms. Environmental Pollution, 186, 257–271.
Chattopadhyay, S., Dash, S. K., Tripathy, S., Das, B., Mandal, D., Pramanik, P., & Roy, S. (2015). Toxicity of cobalt oxide nanoparticles to normal cells; an in vitro and in vivo study. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 226, 58–71.
Clogston, J. D., & Patri, A. K. (2011). Zeta potential measurement. Methods in Molecular Biology, 697, 63–70.
Fairbairn, E. A., Keller, A. A., Madler, L., Zhou, D., Pokhrel, S., & Cherr, G. N. (2011). Metal oxide nanomaterials in seawater: linking physicochemical characteristics with biological response in sea urchin development. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 1565–1571.
Gong, N., Shao, K., Feng, W., Lin, Z., Liang, C., & Sun, Y. (2011). Biotoxicity of nickel oxide nanoparticles and bio-remediation by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris.
Huber, D. (2005). Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small, 1, 482–501.
Kovrižnych, J. A., Sotníková, R., Zeljenková, D., Rollerová, E., Szabová, E., & Wimmerová, S. (2013). Acute toxicity of 31 diff erent nanoparticles to zebrafish (Danio rerio) tested in adulthood and in early life stages—comparative study. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 6, 67–73.
Kovrižnych, J. A., Sotníková, R., Zeljenková, D., Rollerová, E., & Szabová, E. (2014). Long-term (30 days) toxicity of NiO nanoparticles for adult zebrafish Danio rerio. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7(1), 23–26.
Liu, X., Qiu, G., & Li, X. (2005). Shape-controlled synthesis and properties of uniform spinel cobalt oxide nanotubes. Nanotechnology, 16, 3035–3040.
Miller, R. J., Lenihan, H. S., Muller, E. B., Tseng, N., Hanna, S. K., & Keller, A. A. (2010). Impacts of metal oxide nanoparticles on marine phytoplankton. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 7329–7334.
OECD. (2004). Guideline for testing of chemicals—Daphnia sp. acute immobilisation test 202.
Oukarroum, A., Barhoumi, L., Samadani, M., & Dewez, D. (2015). Toxic effects of nickel oxide bulk and nanoparticles on the aquatic plant Lemna gibba L. BioMed Research International, 2015, 1–7. doi:10.1155/2015/501326.
Oyabu, T., Ogami, A., Morimoto, Y., Shimada, M., Lenggoro, W., Okuyama, K., & Tanaka, I. (2007). Biopersistence of inhaled nickel oxide nanoparticles in rat lung. Inhalation Toxicology, 19(Suppl 1), 55–58.
Papis, E., Rossi, F., Raspanti, M., Dalle-Donne, I., Colombo, G., Milzani, A., Bernardini, G., & Gornati, R. (2009). Engineered cobalt oxide nanoparticles readily enter cells. Toxicology Letters, 189, 253–259.
Rao, K. V., & Sunandana, C. S. (2008). Effect of fuel to oxidizer ratio on the structure, micro structure and EPR of combustion synthesized NiO nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoscience & Nanotechnology, 8, 4247–4253.
Rebello, V., Shaikh, S., & Desa, P. V. (2010). Toxicity of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Applications (ICEEA 2010) (pp. 195–199).
Salimi, A., Sharifi, E., Noorbakhsh, A., & Soltanian, S. (2007). Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalytic activity of catalase immobilized onto electrodeposited nanoscale islands of nickel oxide. Biophysical Chemistry, 125, 540–548.
Weber, C. I. (1993). Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms (4th ed., p. 167). Cincinnati, OH: EPA/600/4-90/027F. Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory.
Wiesner, M. R., Lowry, G. V., Alvarez, P., Dionysiou, D., & Biswas, P. (2006). Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 4336–4345.
Zhao, Y., Meng, H., Chen, Z., Feng, Z., & Chai, Z. (2007). Dependence of nanotoxicity on nanoscale characteristics and strategies for reducing and eliminating nanotoxicity. In Y. Zhao & N. H. Singh (Eds.), Nanotoxicology (pp. 265–280). Valencia, CA, USA: American Scientific Publisher.
Acknowledgments
This project is funded in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI) Program (Grant No: G12RR013459) and the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) through the Engineer, Research and Development Center (Vicksburg, MS); (Contract #W912HZ-10-2-0045). The views expressed herein are those of authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies, and any of their sub-agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ates, M., Demir, V., Arslan, Z. et al. Toxicity of Engineered Nickel Oxide and Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Artemia salina in Seawater. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 70 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2771-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2771-9