Abstract
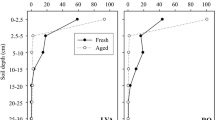
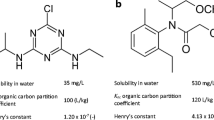
Although degradation data for herbicides are essential in understanding their potential to be contaminants and are indispensable inputs in computer-based modeling of their fate in environment, most available data only concern surface soils. Soil samples, collected at two depths from four representative sites of a 31.4-ha field located in Blue Earth County, MN, USA, were used to determine acetochlor dissipation under laboratory conditions. A field study was also carried out within a 16-ha watershed in Dakota County, MN, USA, where 38 locations were sampled to obtain sample representative of the full range of soil properties found within the watershed. Acetochlor DT50 values ranged from 6.51 to 13.9 days for surface soils and from 20.3 to 26.7 days for subsurface soils. DT90 values were a factor of four times longer than for DT50 values. Field DT50 values for acetochlor dissipation were not significantly different for the 2 years, 5.7 ± 2.5 and 7.7 ± 4.5 days. Dissipation was slightly faster in the field as compared to the laboratory; however, the difference seems insignificant in view of the wide range in soil properties in Minnesota. In both studies, acetochlor would be classified as slightly persistent. For acetochlor, laboratory dissipation studies can be considered representative of field dissipation for the soils and climatic conditions in this study. Inclusion of subsoil degradation data in mathematical models used for ground water risk assessment may improve their capability of predicting potential movement of acetochlor to groundwater.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accinelli, C., Dinelli, G., Vicari, A., & Catizone, P. (2001). Atrazine and metolachlor degradation in subsoils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 33, 495–500.
Aktar, W., Paramasivam, M., & Sengupta, D. (2009). Persistence of benthiocarb in soil: influence of ultraviolet and sunlight. International Journal of Environmental Research, 3, 349–352.
Albuquerque, M. A., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Foloni, J. M., Ker, J. C., & Fontes, L. E. F. (2001). Mineralisation and sorption of atrazine in an oxisol under conventional and no-tillage cropping. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 25, 179–188.
Baran, N., Mouvet, C., Dagnac, T., & Jeannot, R. (2004). Infiltration of acetochlor and two of its metabolites in two contrasting soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 241–249.
Barbash, J. E., Thelin, G. P., Kolpin, D. W., & Gilliom, R. J. (2001). Major herbicides in ground water: results from the national water-quality assessment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 831–845.
Battaglin, W. A., Furlong, E. T., Burkhardt, M. R., & Peter, C. J. (2000). Occurrence of sulfonylurea, sulfonamide, imidazolinone, and other herbicides in rivers, reservoirs and ground water in the Midwestern United States, 1998. Science of the Total Environment, 248, 123–133.
Bending, G. D., & Rodriguez-Cruz, M. S. (2007). Microbial aspects of the interaction between soil depth and biodegradation of the herbicide isoproturon. Chemosphere, 66, 664–671.
Boyd, R. A. (2000). Herbicides and herbicide degradates in shallow groundwater and the Cedar River near a municipal well field, Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Science of the Total Environment, 248, 241–253.
Bundt, M., Widmer, F., Pesaro, M., Zeyer, J., & Blaser, P. (2001). Preferential flow paths: biological 'hot spots' in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 729–738.
Cai, X., Sheng, G., & Liu, W. (2007). Degradation and detoxification of acetochlor in soils treated by organic and thiosulfate amendments. Chemosphere, 66, 286–292.
Costa, M. A., Monteiro, R. T. R., & Tornisiello, V. L. (2000). Degradation of ametryn in a sandy soil after addition of root soil from sugarcane. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 24, 43–48.
Dagnac, T., García-Chao, M., Fernández-Álvarez, M., Castro-Insua, J., García-Pomar, M. I., & Llompart, M. (2012). Study of the presence of priority pesticides in surface water of river basins located in two areas of intensive dairy farming in the NW Spain (Galicia). International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 92, 995–1011.
Dictor, M. C., Baran, N., Gautier, A., & Mouvet, C. (2008). Acetochlor mineralization and fate of its two major metabolites in two soils under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere, 71, 663–670.
Díez, C., & Barrado, E. (2010). Soil-dissipation kinetics of twelve herbicides used on a rain-fed barley crop in Spain. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 397, 1617–1626.
Fan, Z. J., Hu, J. Y., Ai, Y. W., Qian, C. F., Yu, W. Q., & Li, Z. M. (2004). Residue analysis and dissipation of monosulfuron in soils and wheat. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 16, 717–721.
Ferri, M. V. W., & Vidal, R. A. (2002). Acetochlor persistence in soil under no-tillage and conventional systems. Planta Daninha, 20, 133–139.
Flury, M. (1996). Experimental evidence of transport of pesticides through field soils - a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 25–45.
Gaynor, J. D., Tan, C. S., Ng, H. Y. F., Drury, C. F., Welacky, T. W., & vanWesenbeeck, I. J. (2000). Tillage and controlled drainage-subirrigated management effects on soil persistence of atrazine, metolachlor, and metribuzin in corn. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 936–947.
Graff, C. D. (2003). Influence of soil property variability and terrain attributes on the spatial distribution in the field dissipation of the herbicides: acetochlor and isoxaflutole. University of Minnesota, ProQuest, UMI Dissertations Publishing, 3109352 230p
Inoue, M. H., Oliveira, R. S., Jr., Constantin, J., Alonso, D. G., & Tormena, C. A. (2009). Bioavailability of diuron, imazapic and isoxaflutole in soils of contrasting textures. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, 44, 757–763.
Kalkhoff, S. J., Vecchia, A. V., Capel, P. D., & Meyer, M. T. (2012). Eleven-year trend in acetanilide pesticide degradates in the Iowa River, Iowa. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41, 1566–1579.
Khakural, B. R., Robert, P. C., Mulla, D. J., Oliveira Jr., R. S., Johnson, G. A., & Koskinen, W. C. (1998). Site-specific herbicide management for preserving water quality. In P. C. Robert, R. H. Rust & W. E. Larson (Eds.), Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Precision Agriculture (pp. 1719–1731). St. Paul, MN.
Koskinen, W. C., Jarvis, L. J., Dowdy, R. H., Wyse, D. L., & Buhler, D. D. (1991). Automation of atrazine and alachlor extraction from soil using a laboratory robotic system. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 55, 561–562.
Laabs, V., Amelung, W., Pinto, A., Altstaedt, A., & Zech, W. (2000). Leaching and degradation of corn and soybean pesticides in an Oxisol of the Brazilian Cerrados. Chemosphere, 41, 1441–1449.
Linden, D. R., Larson, W. E., Dowdy, R. H., & Clapp, C. E. (1995). Agricultural utilization of sewage sludge. A twenty year study at the Rosemount Agricultural Experiment Station. Station Bulletin 605–1995. St. Paul: Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Minnesota.
Loor-Vela, S. X., Simmons, J. J. C., Simmons, F. W., & Raskin, L. (2003). Dissipation of [(14)C]acetochlor herbicide under anaerobic aquatic conditions in flooded soil microcosms. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51, 6767–6773.
Ma, Q., Rahman, A., Holland, P. T., James, T. K., & McNaughton, D. E. (2004). Field dissipation of acetochlor in two New Zealand soils at two application rates. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 930–938.
Mallawatantri, A. P., McConkey, B. G., & Mulla, D. J. (1996). Characterization of pesticide sorption and degradation in macropore linings and soil horizons of Thatuna silt loam. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 227–235.
Mills, M. S., Hill, I. R., Newcombe, A. C., Simmons, N. D., Vaughan, P. C., & Verity, A. A. (2001). Quantification of acetochlor degradation in the unsaturated zone using two novel in situ field techniques: comparisons with laboratory generated data and implications for groundwater risk assessments. Pest Management Science, 57, 351–359.
Mulla, D. J., Perillo, C. A., & Cogger, C. G. (1996). A site-specific farm-scale GIS approach for reducing groundwater contamination by pesticides. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 419–425.
Nemeth-Konda, L., Füleky, G., Morovjan, G., & Csokan, P. (2002). Sorption behavior of acetochlor, atrazine, carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere, 48, 545–552.
Paraíba, L. C., Cerdeira, A. L., Silva, E. F., Martins, J. S., & Coutinho, H. L. C. (2003). Evaluation of soil temperature effect on herbicide leaching potential into groundwater in the Brazilian Cerrado. Chemosphere, 53, 1087–1095.
Petersen, B. B., Shea, P. J., & Wicks, G. A. (1988). Acetanilide activity and dissipation as influenced by formulation and wheat stubble. Weed Science, 36, 243–249.
Poppell, C. A., Hayes, R. M., & Mueller, T. C. (2002). Dissipation of nicosulfuron and rimsulfuron in surface soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50, 4581–4585.
Postle, J. K., Rheineck, B. D., Allen, P. E., Baldock, J. O., Cook, C. J., Zogbaum, R., et al. (2004). Chloroacetanilide herbicide metabolites in Wisconsin groundwater: 2001 survey results. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5339–5343.
Roberts, T. R. (1996). Assessing the environmental fate of agrochemicals. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, 31, 325–335.
Santos, J. B., Ferreira, E. A., Fialho, C. M. T., Santos, E. A., Galon, L. V., Concenço, G., et al. (2009). Biodegradation of glyphosate in rhizospheric soil cultivated with Glycine max, Canavalia ensiformis and Stizolobium aterrimum. Planta Daninha, 27, 781–787.
Senseman, S. A. (2007). Herbicide handbook (9th ed.). Lawrence: Weed Science Society of America.
Shaner, D., & Henry, W. B. (2007). Field history and dissipation of atrazine and metolachlor in Colorado. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 128–134.
Shipitalo, M. J., & Owens, L. B. (2006). Tillage system, application rate, and extreme event effects on herbicide losses in surface runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 2186–2194.
Spokas, K. A., Koskinen, W. C., Baker, J. M., & Reiocosky, D. C. (2009). Impacts of woodchip biochar additions on greenhouse gas production and sorption/degradation of two herbicides in a Minnesota soil. Chemosphere, 77, 574–581.
Taylor, J. P., Mills, M. S., & Burns, R. G. (2005). Dissipation of acetochlor and its distribution in surface and sub-surface soil fractions during laboratory incubations. Pest Management Science, 61, 539–548.
Terzyk, A. P. (2004). The effect of carbon surface chemical composition on the adsorption of acetanilide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 272, 59–75.
USGS – United States Geological Suvey. (2013). National Water-Quality Assessment (NAWQA) Program, Pesticide National Synthesis Project. http://water.usgs.gov/nawqa/pnsp/usage/maps. Accessed 20 May 2012.
Vanni, A., Anfossi, L., Cignetti, A., Baglieri, A., & Gennari, M. (2006). Degradation of pyrimethanyl in soil: influence of light, oxygen and microbial activity. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part B: Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 41, 67–80.
Vecchia, A. V., Gilliom, R. J., Sullivan, D. J., Lorenz, D. L., & Martin, J. D. (2009). Trends in concentrations and use of agricultural herbicides for Corn Belt rivers, 1996–2006. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 9096–9102.
Wauchope, R. D., Yeh, S., Linders, J. B. H. J., Kloskowski, R., Tanaka, K., Rubin, B., et al. (2002). Pesticide soil sorption parameters: theory, measurement, uses, limitations and reliability. Pest Management Science, 58, 419–445.
Ye, C. (2003). Environmental behavior of the herbicide acetochlor in soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicolocy, 71, 919–923.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CAPES, CNPq (Brazil), and the Center of Agricultural Impacts on Water Quality, University of Minnesota for partial financial support and Brian Barber for his technical support in GC analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, R.S., Koskinen, W.C., Graff, C.D. et al. Acetochlor Persistence in Surface and Subsurface Soil Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1747 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1747-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1747-2