Abstract
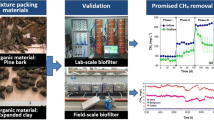
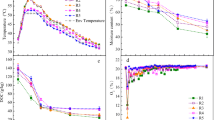
Robust and cheap, biofiltration is one of the most used methods for the biological treatment of industrial gaseous odours and VOCs emissions. The chemical, physical and microbial properties, as well as the economical impact of 11 organic and inorganic packing materials potentially suitable for biofiltration, have been investigated in order to select the most relevant for the treatment of rendering gaseous emissions. Fibrous materials such as peat and coconut fibres are predisposed to compaction. Moreover, according to their low expected running period, their implementation remains expensive, such as activated carbon which induce overweening costs (>100,000€ an−1 for the treatment of 40,000 m3 h−1 with a 60-s empty bed gas residence time). Considering economical aspects, physico-chemical and biological properties, pines barks, composted wood mulch and expanded schist seem fit for this application. The performance of these materials was therefore investigated in a pilot-scale study conducted on a rendering site. According to its appropriate pH (8.62) and water-holding capacity (1.41 g g−1) and its highest nutrients content and colonization at the biofilter start-up (93 g of ATP m−3, 29.1013 CFU m−3), composted would mulch show the best odour removal efficiency during the 134 days of operation. Performances ranged between 75 and 93 % for the treatment of odourous inlet load between 1.16 and 10.10 · 106 ouE m−3 h−1 with an empty bed gas residence time of 47 s. However, the pressure drop of the compost bed decreased, suggesting structural changes which may impact the performances in the long term.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M. E., Villanueva, C., Cárdenas, B., Christen, P., & Revah, S. (2002). The effect of nutrient concentration on biofilm formation on peat and gas phase toluene biodegradation under biofiltration conditions. Process Biochemistry, 38(1), 7–13.
AFNOR. (1998). Sols: Reconnaissance et essais—Détermination de la teneur pondérale en matières organiques d'un matériau—Méthode par calcination. France: AFNOR. XP P94-047.
Aizpuru, A., Khammar, N., Malhautier, L., & Fanlo, J. L. (2003). Biofiltration for the treatment of complex mixtures of VOC—influence of the packing material. Acta Biotechnologica, 23(2–3), 211–226.
Akdeniz, N., Janni, K. A., & Salnikov, I. A. (2011). Biofilter performance of pine nuggets and lava rock as media. Bioresource Technology, 102(8), 4974–4980.
Álvarez-Hornos, F. J., Gabaldón, C., Martínez-Soria, V., Martín, M., Marzal, P., & Penya-roja, J. M. (2008). Biofiltration of ethylbenzene vapours: influence of the packing material. Bioresource Technology, 99(2), 269–276.
Anet, B., Couriol, C., Lendormi, T., Amrane, A., Le Cloirec, P., Cogny, G. & Fillières, R. 2012a. Characterization of gaseous effluent and packing material autopsy of a biofilter operating in the rendering industry. Internationnal Conference on Control of Industrial Gaseous Emissions. 9-10th February 2012, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, India
Anet, B., Couriol, C., Lendormi, T., Amrane, A., Le Cloirec, P., Cogny, G., & Fillières, R. (2012b). Packing material evolutions and odorous abatement of peat and heather biofilters operating in rendering industry. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 30, 61–66.
Chou, M. S., & Shiu, W. Z. (1997). Bioconversion of methylamine in biofilters. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 47(1), 58–65.
Delhoménie, M.-C., Bibeau, L., Roy, S., Brzezinski, R., & Heitz, M. (2001). Influence of nitrogen on the degradation of toluene in a compost-based biofilter. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 76(9), 997–1006.
Dorado, A., Lafuente, F., Gabriel, D., & Gamisans, X. (2010). A comparative study based on physical characteristics of suitable packing materials in biofiltration. Environmental Technology, 31(2), 193–204.
Dumont, E., & Andrès, Y. (2009). Evaluation of innovative packing materials for the biodegradation of H2S: a comparative study. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85(3), 434.
Dumont, E., Andrès, Y., Le Cloirec, P., & Gaudin, F. (2008). Evaluation of a new packing material for H2S removed by biofiltration. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 42(2), 120–127.
Dumont, E., Ayala Guzman, L. M., Rodríguez Susa, M. S., & Andrès, Y. (2012). H2S biofiltration using expanded schist as packing material: performance evaluation and packed-bed tortuosity assessment. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 87(6), 725–731.
Elias, A., Barona, A., Arreguy, A., Rios, J., Aranguiz, I., & Peñas, J. (2002). Evaluation of a packing material for the biodegradation of H2S and product analysis. Process Biochemistry, 37(8), 813–820.
Gabriel, D., Maestre, J. P., Martín, L., Gamisans, X., & Lafuente, J. (2007). Characterisation and performance of coconut fibre as packing material in the removal of ammonia in gas-phase biofilters. Biosystems Engineering, 97(4), 481–490.
Gaudin, F., Andres, Y., & Le Cloirec, P. (2008). Packing material formulation for odorous emission biofiltration. Chemosphere, 70(6), 958–966.
Hartikainen, T., Martikainen, P. J., Olkkonen, M., & Ruuskanen, J. (2002). Peat biofilters in long-term experiments for removing odorous sulphur compounds. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 133(1), 335–348.
ITERG. (2001). Caractérisation des odeurs émises par l’agro-industrie et détermination des traitements appropriés. ITERG, 72.
Jin-Ying, X., Hong-Ying, H., Hong-Bo, Z., & Yi, Q. (2005). Effects of adding inert spheres into the filter bed on the performance of biofilters for gaseous toluene removal. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 23(2), 123–130.
Jorio, H., & Heitz, M. (1999). Traitement de l’air par biofiltration. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: National Research Council of Canada.
Kennes, C., & Thalasso, F. (1998). Review: waste gas biotreatment technology. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 72(4), 303–319.
Kennes, C., Rene, E. R., & Veiga, M. C. (2009). Bioprocesses for air pollution control. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 84(10), 1419–1436.
Khammar, N., Malhautier, L., Degrange, V., Lensi, R., & Fanlo, J.-L. (2004). Evaluation of dispersion methods for enumeration of microorganisms from peat and activated carbon biofilters treating volatile organic compounds. Chemosphere, 54(3), 243–254.
Le Cloirec, P., Humeau, P., & Ramirez-Lopez, E. (2001). Biotreatments of odours: control and performances of a biofilter and a bioscrubber. Water Science and Technology, 44(9), 219–226.
Legrand, P. (2011). Traitement de composés soufrés organiques récalcitrants par biofiltration : optimisation des conditions opératoires pour une application industrielle. Université de Montpellier 2. Alès, Ecole des Mines d’Alès: 195.
Luo, J., & Agnew, M. P. (2001). Gas characteristics before and after biofiltration treating odorous emissions from animal rendering processes. Environmental Technology, 22(9), 1091–1103.
Luo, J., & Lindsey, S. (2006). The use of pine bark and natural zeolite as biofilter media to remove animal rendering process odours. Bioresource Technology, 97(13), 1461–1469.
Luo, J., & Van Oostrom, A. J. (1997) Biofilters for controlling animal rendering odour - a pilot scale study. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 69, 2403–2410.
Maestre, J. P., Gamisans, X., Gabriel, D., & Lafuente, J. (2007). Fungal biofilters for toluene biofiltration: evaluation of the performance with four packing materials under different operating conditions. Chemosphere, 67(4), 684–692.
Malhautier, L., Gracian, C., Roux, J.-C., Fanlo, J.-L., & Le Cloirec, P. (2003). Biological treatment process of air loaded with an ammonia and hydrogen sulfide mixture. Chemosphere, 50(1), 145–153.
Malhautier, L., Khammar, N., Bayle, S., & Fanlo, J.-L. (2005). Biofiltration of volatile organic compounds. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68(1), 16–22.
McNevin, D., & Barford, J. (2000). Biofiltration as an odour abatement strategy. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 5(3), 231–242.
Morgan-Sagastume, J. M., & Noyola, A. (2006). Hydrogen sulfide removal by compost biofiltration: effect of mixing the filter media on operational factors. Bioresource Technology, 97(13), 1546–1553.
Morgan-Sagastume, J. M., Noyola, A., Revah, S., & Ergas, S. J. (2003). Changes in physical properties of a compost biofilter treating hydrogen sulfide. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 53(8), 1011–1021.
Mudliar, S., Giri, B., Padoley, K., Satpute, D., Dixit, R., Bhatt, P., Pandey, R., Juwarkar, A., & Vaidya, A. (2010). Bioreactors for treatment of VOCs and odours—a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 91(5), 1039–1054.
Oh, D. I., Song, J., Hwang, S. J., & Kim, J. Y. (2009). Effects of adsorptive properties of biofilter packing materials on toluene removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(1), 144–150.
Oyarzún, P., Arancibia, F., Canales, C., & Aroca, G. E. (2003). Biofiltration of high concentration of hydrogen sulphide using Thiobacillus thioparus. Process Biochemistry, 39(2), 165–170.
Prado, Ó. J., Gabriel, D., & Lafuente, J. (2009). Economical assessment of the design, construction and operation of open-bed biofilters for waste gas treatment. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8), 2515–2523.
SIFCO (2013). Syndicat des industries françaises des sous-produits animaux. Retrieved 05/05/2013, from http://www.sifco.fr/.
Sironi, S., Capelli, L., Céntola, P., Del Rosso, R., & Grande, M. I. (2007). Odour emission factors for assessment and prediction of Italian rendering plants odour impact. Chemical Engineering Journal, 131(1–3), 225–231.
Smet, E., Chasaya, G., Van Langenhove, H., & Verstraete, W. (1996a). The effect of inoculation and the type of carrier material used on the biofiltration of methyl sulphides. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 45(1), 293–298.
Smet, E., Langenhove, H. V., & Verstraete, W. (1996b). Long-term stability of a biofilter treating dimethyl sulphide. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 46(2), 191–196.
Tampion, J. & Tampion, M. D. 1987. Immobilized cells: principles and applications, Cambridge Univ Pr
Vincent, A. & Hobson, J. 1998. CIWEM monographs on best practice no. 2. Chartered Institution of Water and Environmental Management, 31.
Wani, A. H., Branion, R. M. R., & Lau, A. K. (1998). Effects of periods of starvation and fluctuating hydrogen sulfide concentration on biofilter dynamics and performance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 60(3), 287–303.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Atemax Ouest Company. The authors acknowledge the “Centre de Microscopie Électronique à Balayage et microAnalyse” of the Rennes 1 University for the scanning electron microscope observations. The authors also acknowledge the GEPEA department of the “Ecole des Mines De Nantes” for the mercury porosimeter measurements and the elemental analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anet, B., Couriol, C., Lendormi, T. et al. Characterization and Selection of Packing Materials for Biofiltration of Rendering Odourous Emissions. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1622 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1622-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1622-1