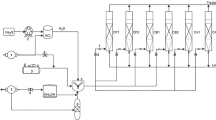
Abstract
Low elimination capacities (less than 10 gm−3day−1) were observed for the odorant dimethyl sulphide (Me2S) when either wood bark or compost was used as the carrier material in a laboratory-scale biofilter. Enrichment experiments were set up by incubation of garden soil samples during 4 weeks with 100 ppm (v/v) headspace concentrations of both Me2S and dimethyl disulphide (Me2S2). After transfer to a mineral medium, Me2S- and Me2S2-degrading enrichment cultures were obtained for all five soil samples tested, both compounds being converted stoichiometrically to sulphuric acid. Upon inoculation of the laboratory-scale biofilter with one of these enrichment cultures (± 120 g cell dry weight m−3 reactor), the elimination capacity for Me2S increased in a 3-week period to 35 gm−3 day−1 and 680 gm−3 day−1 when wood bark and compost were used as the respective carrier materials. Both inoculated biofilters were able to degrade Me2S2, however the elimination capacities obtained for Me2S2 were lower (e.g. 24 g m−3 day−1 for the wood bark filter) compared to those for Me2S. For both inoculated biofilters, a gradual decrease of the elimination capacity for the methyl sulphides was observed as a result of acidification of the carrier material, suggesting that pH regulation is necessary if long-term biofiltration experiments are to be performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1980) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 15th edn American Public Health Association, Washington, p1134
Bendinger B (1992) Microbiology of biofilters for the treatment of animal-rendering plant emissions: occurrence, identification and properties of isolated Coryneform bacteria. PhD Thesis, University of Osnabruck, Germany
De Zwart JMM, Kuenen JG (1992) C1-cycle of sulfur compounds. Biodegradation 3: 37–59
Gellens V, Boelens J. Verstraete W (1995) Source separation, selective collection and in reactor digestion of biowaste. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 67: 79 89
Kelly DP, Smith NA (1990) Organic sulfur compounds in the environment. Adv Microb Ecol 11: 345–385
Leson G, Winer AM (1991) Biofiltration: an innovative air pollution control technology for VOC emissions. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 41: 1045–1054
Pauwels JM, Van Ranst E, Verloo M, Mvondo ZA (1992) Manuel de laboratoire de pedologie. Administration Générale de la Coopération au Développement, Bruxelles, p265
Phae CG, Shoda M (1991) A new fungus which degrades hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide. Biotechnol Lett 13: 375–380
Pol A, Op den Camp HJM, Mees SGM, Kersten MASH, Van der Drift C (1994) Isolation of a dimethylsulfide-utilizing Hyphomicrobium species and its application in biofiltration of polluted air. Biodegradation 5: 105–112
Schoene K, Steinhanses J (1989) Generating vapour mixtures for calibration purposes. II. Dynamic diffusive system. Fresenius Z Anal Chem 355: 557–561
Van Groenestijn JW, Hesselink PGM (1993) Biotechniques for air pollution control. Biodegradation 4: 283–301
Van Langenhove H, Bendinger B, Oberthiir R, Schamp N (1991) Organic sulfur compounds: persistent odourants in the biological treatment of complex waste gases. In: Dragt AJ, Van Ham J (eds) Biotechniques for air pollution abatement and odour control policies. Proceedings of an International Symposium, Maastricht, the Netherlands 27–29 October. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 177–182
Zhang L, Kuniyoshi I, Hirai M, Shoda M (1991) Oxidation of dimethyl sulfide by Pseudomonas acidovorans DMR-11 isolated from peat biofilter. Biotechnol Lett 13: 223–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smet, E., Chasaya, G., Van Langenhove, H. et al. The effect of inoculation and the type of carrier material used on the biofiltration of methyl sulphides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45, 293–298 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050686
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050686