Abstract
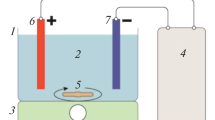
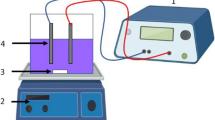
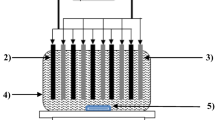
In the present investigation, treatment of metal cutting wastewater (MCW) using electrocoagulation (EC) process is designed and analyzed using response surface methodology (RSM). RSM is applied to optimize the operating variables viz. initial pH, current density, and operating time on the treatment of MCW in a batch mode by EC process using iron and aluminum electrodes. Quadratic models are developed for the responses such as chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC), and turbidity, and operating cost is calculated with respect to energy, electrode, and chemical consumptions. The actual COD, TOC, and turbidity removal efficiencies at optimized conditions are found to be 93.0%, 83.0%, and 99.8% for Fe electrode and 93.5%, 85.2%, and 99.9% for Al electrode, respectively, which agree well with the predicted response. The proposed model fits very well with the experimental data with R 2 adjusted correlation coefficients of 0.927 for COD, 0.924 for TOC, and 0.968 for turbidity removal for Al and 0.904 for COD, 0.976 for TOC, and 0.989 for turbidity removal for Fe electrodes, respectively. This study clearly shows that RSM is one of the suitable methods to optimize the operating conditions and maximize the COD, TOC, and turbidity removal efficiencies for both electrodes while keeping the operating costs to minimal (0.371 €/m3 for Fe and 0.337 €/m3 for Al electrodes).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. E., Kim, B. R., Mueller, S. A., & Lofton, T. V. (2003). Composition and analysis of mineral oils and other compounds in metalworking and hydraulic fluids. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 73–109.
Arslan-Alaton, I., Kabdaşlı, I., Hanbaba, D., & Kuybu, E. (2008). Electrocoagulation of a real reactive dyebath effluent using aluminum and stainless steel electrodes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150, 166–173.
Barrera-Diaz, C., Roa-Morales, G., Avila-Cordoba, L., Pavon-Silva, T., & Bilyeu, B. (2006). Electrochemical treatment applied to food-processing industrial wastewater. Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research, 45, 34–38.
Bensadok, K., Benammar, S., Lapicque, F., & Nezzal, G. (2008). Electrocoagulation of cutting oil emulsions using aluminium plate electrodes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 423–430.
Bergmann, H., Rittel, A., Iourtchouk, T., Schoeps, K., & Bouzek, K. (2003). Electrochemical treatment of cooling lubricants. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 42, 105–119.
Byers, J. P. (2006). Metalworking fluids. New York: CRC.
Can, O. T., Bayramoglu, M., & Kobya, M. (2003). Decolorization of reactive dye solutions by electrocoagulation using aluminum electrodes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 42, 3391–3396.
Canizares, P., Martinez, F., Jimenez, C., Saez, C., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2008). Coagulation and electrocoagulation of oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151, 44–51.
Canizares, P., Martinez, F., Lobato, J., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2007). Break-up of oil-in-water emulsions by electrochemical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 145, 233–240.
Chen, G. (2004). Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 38, 11–41.
Cheng, C., Phipps, D., & Alkhaddar, R. M. (2006). Thermophilic aerobic wastewater treatment of waste metalworking fluids. Water and Environment Journal, 20, 227–232.
Cleceri, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., & Eaton, A. D. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association.
Greeley, M., & Rajagopalan, N. (2004). Impact of environmental contaminants on machining properties of metal working fluids. Tribology International, 37, 327–332.
Hilal, N., Busca, G., Hankins, N., & Mohammad, A. (2004). The use of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes in the treatment of metal-working fluids. Desalination, 167, 227–238.
Kabdasli, I., Arslan, T., Ölmez-Hanci, T., Arslan-Alaton, I., & Tünay, O. (2009). Complexing agent and heavy metal removals from metal plating effluent by electrocoagulation with stainless steel electrodes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 838–845.
Khemis, M., Tanguy, G., Leclerc, J. P., Valentin, G., & Lapicque, F. (2005). Electrocoagulation for the treatment of oil suspensions. Trans IChemE, Part B, Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 83, 50–57.
Kobya, M., Ciftci, C., Bayramoglu, M., & Sensoy, M. T. (2008). Study on the treatment of waste metal cutting fluids using electrocoagulation. Separation and Purification Technology, 60, 285–291.
Kobya, M., & Delipinar, S. (2008). Treatment of the baker’s yeast wastewater by electrocoagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 1133–1140.
Kobya, M., Demirbas, E., & Akyol, A. (2009). Electrochemical treatment and operating cost analysis of textile wastewater using sacrificial iron electrodes. Water Science and Technology, 60, 2261–2270.
Kobya, M., Demirbas, E., Dedeli, A., & Sensoy, M. T. (2010). Treatment of rinse water from zinc phosphate coating by batch and continuous electrocoagulation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 326–334.
Kobya, M., Hiz, H., Senturk, E., Aydiner, C., & Demirbas, E. (2006b). Treatment of potato chips manufacturing wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination, 190, 201–211.
Kobya, M., Senturk, E., & Bayramoglu, M. (2006a). Treatment of poultry slaughterhouse wastewaters by electrocoagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 133, 172–176.
Korbahti, B. K., Aktas, N., & Tanyolac, A. (2007). Optimization of electrochemical treatment of industrial paint wastewater with response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 83–90.
Mollah, M. Y. A., Schennach, R., Parga, J. P., & Cocke, D. L. (2001). Electrocoagulation (EC)—science and applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 84, 29–41.
Myers, R. H., & Montgomery, D. C. (2002). Response surface methodology: Process and product optimization using designed experiments (2nd ed.). USA: Wiley.
Olmez, T. (2009). The optimization of Cr(VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162, 1371–1378.
Ponselvan, F. I. A., Kumar, M., Malviya, J. R., Srivastava, V. C., & Mall, I. D. (2009). Electrocoagulation studies on treatment of biodigester effluent using aluminum electrodes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 199, 371–379.
Prasad, R. K., Kumar, R. R., & Srivastava, S. N. (2008). Design of optimum response surface experiments for electro-coagulation of distillery spent wash. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 191, 5–13.
Rios, S., Pazos, C., & Coca, J. (1998). Destabilization of cutting oil emulsions using inorganic salts as coagulants. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 138, 383–389.
Sanchez-Calvo, L., Leclerc, J.-P., Tanguy, G., Cames, M. C., Paternotte, G., Valentin, G. (2003). An electrocoagulation unit for the purification of soluble oil wastes of high COD. Environmental Progress, 22, 57–65.
Saravanathamizhan, R., Mohan, N., Balasubramanian, N., Ramamurthi, V., & Basha, C. A. (2007). Evaluation of electro-oxidation of textile effluent using response surface methods. Clean, 35, 355–361.
Tir, M., & Moulai-Mostefa, N. (2008). Optimization of oil removal from oily wastewater by electrocoagulation using response surface method. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 158, 107–115.
Xu, X., & Zho, X. (2004). Treatment of refectory oily wastewater by electrocoagulation process. Chemosphere, 56, 889–894.
Acknowledgements
This research work is a part of TUBITAK project. The authors thank TUBITAK for their financial support of this work under contract TUBITAK-CAYDAG-104Y267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobya, M., Demirbas, E., Bayramoglu, M. et al. Optimization of Electrocoagulation Process for the Treatment of Metal Cutting Wastewaters with Response Surface Methodology. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 399–410 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0486-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0486-x