Abstract
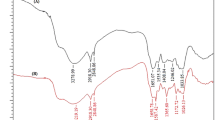
The batch sorption experiments were carried out using a novel adsorbent, freshwater macrophyte alligator weed, for the removal of basic dye malachite green from aqueous solution. Effects of process parameters such as initial solution pH, contact time, adsorbent concentration, particle size, and ion strength were investigated. The adsorbent was characterized by FT-IR. The adsorption of malachite green by alligator weed was solution pH dependent. The adsorption reached equilibrium at 240 min for two particle size fractions. The pseudo-first-order equation, Ritchie second-order equation, and intraparticle diffusion models were tested. The results showed that adsorption of malachite green onto alligator weed followed the Ritchie second-order equation very well and the intraparticle diffusion played important roles in the adsorption process. The Langmuir and Freundlich equations were applied to the data related to the adsorption isotherms and the observed maximum adsorption capacity (q max) was 185.54 mg g−1 at 20°C according to the Langmuir model. The effects of particle size, adsorbent concentration, and ionic strength on the malachite green adsorption were very marked. The alligator weed could serve as low-cost adsorbents for removing malachite green from aqueous solution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekçi, Z., Özveri, C., Seki, Y., & Yurdakoç, K. (2008). Sorption of malachite green on chitosan bead. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 254–261. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.021.
Bekçi, Z., Seki, Y., & Cavas, L. (2009). Removal of malachite green by using an invasive marine alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 1454–1460.
Cengiz, S., & Cavas, L. (2008). Removal of methylene blue by invasive marine seaweed. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2357–2363. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.05.011.
Chuah, T. G., Jumasiah, A., Azni, I., Katayon, S., & Thomas Choong, S. Y. (2005). Rice husk as a potentially low-cost biosorbent for heavy metal and dye removal: an overview. Desalination, 175, 305–316. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2004.10.014.
Daneshvar, N., Ayazloo, M., Khataee, A. R., & Pourhassan, M. (2007). Biological decolorization of dye solution containing malachite green by microalgae Cosmarium sp. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1176–1182. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.025.
Freundlich, H. (1907). Udber die adsorption in Loesungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Garg, V. K., Gupta, R., Yadav, A. B., & Kumar, R. (2003). Dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on treated sawdust. Bioresource Technology, 89, 121–124. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00058-0.
Gómez, V., Larrechi, M. S., & Callao, M. P. (2007). Kinetic and adsorption study of acid dye removal using activated carbon. Chemosphere, 69, 1151–1158. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.076.
Guo, Y., Yang, S., Fu, W., Qi, J., Li, R., Wang, Z., et al. (2003). Adsorption of malachite green on micro- and mesoporous rice husk-based active carbon. Dyes and Pigments, 56, 219–229. doi:10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00160-2.
Hamdaoui, O., Saoudi, F., Chiha, M., & Naffrechoux, E. (2008). Sorption of malachite green by a novel sorbent, dead leaves of plane tree: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143, 73-84.
Hameed, B. H., & EI-Khaiary, M. I. (2008a). Malachite green adsorption by rattan sawdust: isotherm, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 159, 574–579. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.054.
Hameed, B. H., & EI-Khaiary, M. I. (2008b). Kinetics and equilibrium studies of malachite green adsorption on rice straw-derived char. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 701–708. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.019.
Huang, C. P., & Smith, E. H. (1981). Removal of Cd (II) from plating wastewater by an activated carbon process. In W. J. Cooper (Ed.), Chemistry in water reuse. Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Science Publishers.
Isik, M., & Sponza, D. T. (2008). Anaerobic/aerobic treatment of a simulated textile wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 60, 64–72. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.07.043.
Khadhraoui, M., Trabelsi, H., Ksibi, M., Bouguerra, S., & Elleuch, B. (2009). Discoloration and detoxification of Congo red dye solution by means of ozone treatment for possible water reuse. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 974–981.
Khattri, S. D., & Singh, M. K. (1999). Color removal from dye wastewater using sugar cane dust as an adsorbent. Adsorption Science and Technology, 17, 269–282.
Khattri, S. D., & Singh, M. K. (2000). Color removal from synthetic dye wastewater using a bioadsorbent. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 120, 283–294. doi:10.1023/A:1005207803041.
Kim, D. S., & Park, Y. S. (2008). Comparison study of dyestuff wastewater treatment by the coupled photocatalytic oxidation and biofilm process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 139, 256–263. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2007.07.095.
Lagergren, S. (1898). Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403. doi:10.1021/ja02242a004.
Mahmoud, A. S., Ghaly, A. E., & Brooks, M. S. (2007). Removal of dye from textile wastewater using plant oils under different pH and temperature conditions. American Journal of Environmental Science, 3, 205–218.
Nemr, A. E., Abdelwahab, O., EI-Sikaily, A., & Khaled, A. (2009). Removal of direct blue-86 from aqueous solution by new activated carbon developed from orange peel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(1), 102–110.
Pavan, F. A., Mazzocato, A. C., & Gushikem, Y. (2008). Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption using yellow passion fruit peel as adsorbent. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3162–3165. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.05.067.
Ritchie, A. G. (1977). Alternative to the Elovich equation for the kinetics of adsorption of gases on solids. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 73, 1650–1653. doi:10.1039/f19777301650.
Sirés, I., Guivarch, E., Oturan, N., & Oturan, M. A. (2008). Efficient removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous medium by in situ electrogenerated Fenton’s reagent at carbon-felt cathode. Chemosphere, 72, 592–600. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.010.
Sirianuntapiboon, S., Sadahiro, O., & Salee, P. (2007). Some properties of a granular activated carbon-sequencing batch reactor (GAC-SBR) system for treatment of textile wastewater containing direct dyes. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 162–170. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.09.001.
Sleiman, M., Vildozo, D., Ferronato, C., & Chovelon, J. M. (2007). Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye metanil yellow: optimization and kinetic modeling using a chemometric approach. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 77, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.06.015.
Valderrama, C., Cortina, J. L., Farran, A., Gamisans, X., & de las Heras, F. X. (2008). Evaluation of hyper-cross-linked polymeric sorbents (Macronet MN200 and MN300) on dye (Acid red 14) removal process. Reactive and Functional Polymer, 68, 679–691.
Wang, X. S., & Qin, Y. (2006). Removal of Ni (II), Zn (II) and Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by Alternanthera philoxeroides biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B138, 582–588. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.091.
Weber, W. J., Jr., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Environmental Engineering Division, 89, 31–59.
Zidane, F., Drogui, P., Lekhlif, B., Bensaid, J., Blais, J. F., Belcadi, S., et al. (2008). Decolourization of dye-containing effluent using mineral coagulants produced by electrocoagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155, 153–163. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.S. Invasive Freshwater Macrophyte Alligator Weed: Novel Adsorbent for Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 206, 215–223 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0097-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0097-6