Abstract
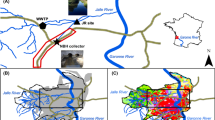
Road runoff waters are able to convey a number of organic and inorganic pollutants originated by different non-point sources and by the road surface itself. Such pollutants can enter aquatic systems, thus contributing to water and soil contamination. This study was aimed at evaluating the pollutant content in first flush runoff waters from a highway located in Central Italy. A water sampling apparatus was devised able to collect only the first 10 L of runoff water. Water samples were analyzed by atomic absorption spectroscopy, ion chromatography, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in order to determine metals, ions, and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, respectively. Soil samples were collected as well for metal and hydrocarbon determination. Results obtained in a field experiment carried out in two different seasons and in two different sites along the highway are reported. The study was extended to water samples collected in a strip of the same road not yet in use.
Results obtained showed a temporal and a spatial variability due to the different period rainfall and to sites features, respectively. Within such a variability, a substantial agreement, in terms of order of magnitude, with other studies carried out in European sites was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, E., Jenksb, R. and Aubourgb, D.: 1998, ‘An assessment of the availability of pollutant constituents on road surfaces’, Sci. Total Environ. 209, 243–254.
Bauske, B. and Goetz, D.: 1993, ‘Effects of de-icing salts on heavy metal mobility’, Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 21, 38–42.
Bertrand-Krajewski, J. L., Chebbo, G. and Saget, A.: 1998, ‘Distribution of pollutant mass vs. volume in stormwater discharges and the first flush phenomenon’, Wat. Res. 32/8, 2341–2356.
Boxall, A. B. A. and Maltby L.: 1995, ‘The characterization and toxicity of sediment contaminated with road runoff’,Wat. Res. 29/9, 2043–2050.
Brezonik, P. L. and Stadelmann, T. H.: 2002, ‘Analysis and predictive models of storm water runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA’, Wat. Res. 36, 1743–1757.
Deletic, A.: 1998, ‘The first flush load of urban surface runoff’, Wat. Res. 32/8, 2462–2470.
Hoornaert, S., Van Malderen, H. and Van Grieken, R.: 1996, ‘Gypsum and other calcium-rich aerosol particles above the North Sea’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1515–1520.
Koeleman, M., Janssen vd Laak, W. and Ietswaart, H.: 1999, ‘Dispersion of PAH and heavy metals along motorways in the Netherlands—An overview’, Sci. Total Environ. 235, 347–349.
Krein, A. and Schorer, M.: 2000, ‘Road runoff pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its contribution to river sediments’, Wat. Res. 34/16, 4110–4115.
Legret, M. and Pagotto, C.: 1999, ‘Evaluation of pollutant loadings in the runoff waters from a major rural highway’, Sci. Total Environ. 235, 143–150.
Leitão T. E., Lobo Ferriera J. P., Smets S. and Diamantino C.: ‘A Poluição Ambiental causada por estradas. O Projecto POLMIT’ Proceedings of the 1st ASEM Workshop on Water Management Issues, Changsha, China 10–13 June, 2002, available at http://www.dha.lnec.pt/nas/textos/novidades/Estradas2000_POLMIT_pp.pdf.
Lindgren, Å.: 1996, ‘Asphalt wear and pollution transport’, Sci. Total Environ. 189/190, 281–286.
Maltby, L., Forrow, D. M., Boxall, A. B. A., Calow, P. and Betton, C. I.: 1995a, ‘The effects of mororway runoff on freshwater ecosystems: 1. Field Study’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14/6, 1079–1092.
Maltby, L., Boxall, A. B. A., Forrow, D. M., Calow, P. and Betton, C. I.: 1995b, ‘The effects of mororway runoff on freshwater ecosystems: 2. Identifying major toxicants’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14/6, 1093–1101.
Perdikaki, K. and Mason, C. F.: 1999, ‘Impact of road run-off on receiving streams in eastern England’, Wat. Res. 33/7, 1627–1633.
Sansalone, J. J. and Buchberger, S. G.: 1997, ‘Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water’, J. Environ. Eng. 123(2), 134–143.
Stahre, P. and Urbonas, B.: 1990, Storm-Water Detention for Drainage, Water Quality and CSO Management, Prentice Hall, Engelwood Cliffs, NJ, U.S.A., p. 338.
Thornton, R. C. and Saul, A. J.: 1987, ‘Temporal variation of pollutants in two combined sewer systems’, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Urban Storm Drainage, Lausanne, Switzerland, pp. 51–52.
Wanielista, M. and Yousel, Y.: 1993, Stormwater Management. Wiley, NY, U.S.A., p. 579.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangani, G., Berloni, A., Bellucci, F. et al. Evaluation of the Pollutant Content in Road Runoff First Flush Waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 160, 213–228 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-2887-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-2887-9