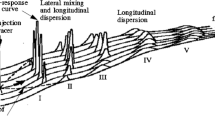
Abstract
Modeling river mixing mechanism in terms of pollution transmission in rivers is an important subject in environmental studies. Dispersion coefficient is an important parameter in river mixing problem. In this study, to model and predict the longitudinal dispersion coefficient (D L ) in natural streams, two soft computing techniques including multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) as a new approach to study hydrologic phenomena and multi-layer perceptron neural network as a common type of neural network model were prepared. To this end, related dataset were collected from literature and used for developing them. Performance of MARS model was compared with MLP and the empirical formula was proposed to calculate D L . To define the most effective parameters on D L structure of obtained formula from MARS model and more accurate formula was evaluated. Calculation of error indices including coefficient of determination (R2) and root mean square error (RMSE) for the results of MARS model showed that MARS model with R2 = 0.98 and RMSE = 0.89 in testing stage has suitable performance for modeling D L . Comparing the performance of empirical formulas, ANN and MARS showed that MARS model is more accurate compared to others. Attention to the structure of developed MARS and the most accurate empirical formulas model showed that flow velocity, depth of flow (H) and shear velocity are the most influential parameters on D L .










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson T, Davis P (2000) Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels: l. Experimental results from the River Severn, UK. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 4:345–353
Azamathulla H, Ghani A (2011) Genetic programming for predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficients in streams. Water Resour Manage 25:1537–1544. doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9759-9
Azamathulla HM, Wu F-C (2011) Support vector machine approach for longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural streams. Appl Soft Comput 11:2902–2905. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2010.11.026
Boyd CE (2015) Water quality: an introduction. Springer International Publishing
Bozorg-Haddad O, Zarezadeh-Mehrizi M, Abdi-Dehkordi M, Loáiciga HA, Mariño MA (2016) A self-tuning ANN model for simulation and forecasting of surface flows. Water Resour Manage 30:2907–2929. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1301-2
Davis P, Atkinson T (2000) Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels: 3. An aggregated dead zone model applied to the River Severn, UK. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 4:373–381
Davis P, Atkinson T, Wigley T (2000) Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels: 2. The roles of shear flow dispersion and dead zones in the River Severn, UK. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 4:355–371
Dehghani M, Saghafian B, Nasiri Saleh F, Farokhnia A, Noori R (2014) Uncertainty analysis of streamflow drought forecast using artificial neural networks and Monte-Carlo simulation. Int J Climatol 34:1169–1180. doi:10.1002/joc.3754
Elder JW (1959) The dispersion of a marked fluid in turbulent shear flow. J Fluid Mech 5(4):544–560
Emamgolizadeh S, Bateni SM, Shahsavani D, Ashrafi T, Ghorbani H (2015) Estimation of soil cation exchange capacity using Genetic Expression Programming (GEP) and Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS). J Hydrol 529(Part 3):1590–1600. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.08.025
Etemad-Shahidi A, Taghipour M (2012) Predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural streams using M5′ model tree. J Hydraul Eng 138:542–554. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000550
Fisher BH (1967) The mechanics of dispersion in natural streams. J Hydraul Div, Am Soc Civil Eng 93(6):187–216
Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann Stat 1–67
Iwasa Y, Aya S (1991) Predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in open channel flows. In: Proceedings of international symposium on environmental hydraulics, Hong Kong, (pp. 505–510)
Jiang T, Zhong M, Cao Y-j, Zou L-j, Lin B, Zhu A-p (2016) Simulation of water quality under different reservoir regulation scenarios in the tidal river. Water Resour Manage 30:3593–3607. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1375-x
Kashefipour SM, Falconer RA (2002) Longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural channels. Water Res 36:1596–1608. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00351-7
Kashefipur SM, Falconer A (2002) Longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural channels. In: Proceedings of the fifth international hydro informatics conference, 1–5 July, Cardiff University. (pp. 95–102)
Kisi O (2015) Pan evaporation modeling using least square support vector machine, multivariate adaptive regression splines and M5 model tree. J Hydrol 528:312–320. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.052
Koussis AD, Rodriguez-Mirasol J (1998) Hydraulic estimation of dispersion coefficient for streams. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 124:317–320
Leta O, Shrestha N, de Fraine B, van Griensven A, Bauwens W (2014) Integrated water quality modelling of the river Zenne (Belgium) using OpenMI. In: Gourbesville P, Cunge J, Caignaert G (eds) Advances in hydroinformatics, Springer hydrogeology. Springer, Singapore, pp 259–274. doi:10.1007/978-981-4451-42-0_22
Li ZH, Huang J, Li J (1998) Preliminary study on longitudinal dispersion coefficient for the gorges reservoir. In Proceedings of the seventh international symposium environmental hydraulics, 16–18 December, Hong Kong, China
Liu H (1977) Predicting dispersion coefficient of stream. J Environ Eng Div 103(1):59–69
McQuivey RS, Keefer TN (1974) Simple method for predicting dispersion in streams. J Environ Eng Div, Am Soc Civil Eng 100(4):997–1011
Najafzadeh M, Sattar AA (2015) Neuro-fuzzy GMDH approach to predict longitudinal dispersion in water networks. Water Resour Manage 29:2205–2219. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-0936-8
Najafzadeh M, Tafarojnoruz A (2016) Evaluation of neuro-fuzzy GMDH-based particle swarm optimization to predict longitudinal dispersion coefficient in rivers. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–12. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4877-6
Naseri Maleki M, Kashefipour SM (2012) Application of numerical modeling for solution of flow equations and estimation of water quality pollutants in rivers (Case Study: Karkheh River). Civil Environ Eng 42(3):51–60
Noori R, Hooshyaripor F (2014) Effective prediction of scour downstream of ski-jump buckets using artificial neural networks. Water Resour 41:8–18. doi:10.1134/s0097807814010096
Noori R, Khakpour A, Omidvar B, Farokhnia A (2010) Comparison of ANN and principal component analysis-multivariate linear regression models for predicting the river flow based on developed discrepancy ratio statistic. Expert Syst Appl 37:5856–5862. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.02.020
Noori R, Karbassi AR, Mehdizadeh H, Vesali-Naseh M, Sabahi MS (2011) A framework development for predicting the longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural streams using an artificial neural network. Environ Prog Sustainable Energy 30:439–449. doi:10.1002/ep.10478
Noori R, Deng Z, Kiaghadi A, Kachoosangi FT (2015) How reliable are ANN, ANFIS, and SVM techniques for predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural rivers? J Hydraul Eng 0:04015039. doi:10.1061/(asce)hy.1943-7900.0001062
Palancar MC, Aragón JM, Sánchez F, Gil R (2003) The determination of longitudinal dispersion coefficients in rivers. Water Environ Res 324–335
Parsaie A, Haghiabi A (2015a) The effect of predicting discharge coefficient by neural network on increasing the numerical modeling accuracy of flow over side weir. Water Resour Manage 29:973–985. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0827-4
Parsaie A, Haghiabi A (2015b) Predicting the longitudinal dispersion coefficient by radial basis function neural network. Model Earth Syst Environ 1:1–8. doi:10.1007/s40808-015-0037-y
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH (2015c) Computational modeling of pollution transmission in rivers. Appl Water Sci 1–10. doi:10.1007/s13201-015-0319-6
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH, Saneie M, Torabi H (2016) Prediction of energy dissipation on the stepped spillway using the multivariate adaptive regression splines ISH. J Hydraul Eng 1–12. doi:10.1080/09715010.2016.1201782
Rajeev RS, Dutta S (2009) Prediction of longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural rivers using genetic algorithm. Hydrol Res 40(6):544–552
Riahi-Madvar H, Ayyoubzadeh SA, Khadangi E, Ebadzadeh MM (2009) An expert system for predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural streams by using ANFIS. Expert Syst Appl 36:8589–8596. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.10.043
Sahay R (2011) Prediction of longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural rivers using artificial neural network. Environ Fluid Mech 11:247–261. doi:10.1007/s10652-010-9175-y
Sahin S (2014) An empirical approach for determining longitudinal dispersion coefficients in rivers. Environ Process 1:277–285. doi:10.1007/s40710-014-0018-6
Samadi M, Jabbari E, Azamathulla H, Mojallal M (2015) Estimation of scour depth below free overfall spillways using multivariate adaptive regression Splines and artificial neural networks. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 1–10
Sattar AMA, Gharabaghi B (2015) Gene expression models for prediction of longitudinal dispersion coefficient in streams. J Hydrol 524:587–596. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.016
Seo I, Baek K (2004) Estimation of the longitudinal dispersion coefficient using the velocity profile in natural streams. J Hydraul Eng 130:227–236. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2004)130:3(227)
Seo I, Cheong T (1998) Predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural streams. J Hydraul Eng 124:25–32. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1998)124:1(25)
Sharda V, Prasher S, Patel R, Ojasvi P, Prakash C (2008) Performance of Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS) in predicting runoff in mid-Himalayan micro-watersheds with limited data/Performances de régressions par splines multiples et adaptives (MARS) pour la prévision d’écoulement au sein de micro-bassins versants Himalayens d’altitudes intermédiaires avec peu de données. Hydrol Sci J 53:1165–1175
Tavakollizadeh A, Kashefipur SM (2007) Effects of dispersion coefficient on quality modeling of surface waters. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium river engineering, 16–18 October, Ahwaz, Iran, pp 67–78
Wang Z-Y, Lee JW, Melching C (2015) Water quality management. In: River dynamics and integrated river management. Springer, Berlin, p 555–631. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-25652-3_10
Zeng Y, Huai W (2014) Estimation of longitudinal dispersion coefficient in rivers. J Hydro Environ Res 8:2–8. doi:10.1016/j.jher.2013.02.005
Zhang W, Goh ATC (2014) Multivariate adaptive regression splines and neural network models for prediction of pile drivability. Geosci Front. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2014.10.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghiabi, A.H. Modeling River Mixing Mechanism Using Data Driven Model. Water Resour Manage 31, 811–824 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1475-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1475-7