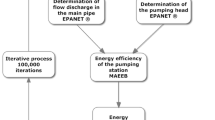
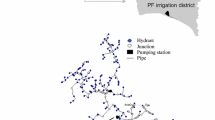
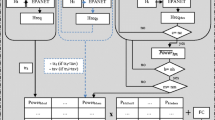
Abstract
Improving energy and hydraulic performance of large-scale pressurized irrigation is now perceived as a very pressing need, after large budgets have been allocated into systems modernization. This paper tackles this priority area by developing a management oriented multi-step methodology, that integrates different existing models, to sector the system according to the pressure requirements of the hydrants, and to regulate the pumping station for i) a fixed and a variable pressure head control, and for ii) an enhanced performance. When applied to an on-demand system in the Sinistra Ofanto irrigation scheme of Foggia (Italy), this integrated approach showed potential for energy saving under the optimal scenario of 49 %, and noticeable improvement in the system performance in terms of hydrant pressure heads, as compared to the actual conditions. The monetary assessment demonstrates that the achieved energy saving amounts to 23,636 Euros per irrigation season, 45 % among which are due to sectoring.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Córcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Carrión PA, Moreno MÁ (2015) Methodology to minimize energy costs in an on-demand irrigation network based on arranged opening of hydrants. Water Resour Manag 29:3697–3710. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-1024-9
Córcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Moreno MA (2016) Pumping station regulation in on-demand irrigation networks using strategic control nodes. Agric Water Manag 163:48–56. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2015.09.001
D’Urso G (2001) Simulation and management of on-demand irrigation systems: a combined agrohydrological and remote sensing approach. Wageningen University
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2009) On-demand pressurized water distribution system impacts on sprinkler network design and performance. Irrig Sci 28:331–339. doi:10.1007/s00271-009-0195-7
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2010) Assessing pressure changes in an on-demand water distribution system on drip irrigation performance-case study in Italy. J Irrig Drain Eng 136(4):261–270. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000170
English MJ, Solomon KH, Hoffman GJ (2002) A paradigm shift in irrigation management. J Irrig Drain Eng 128:267–277
FAO (2011) The state of the world’s land and water resources for food and agriculture (SOLAW) – managing systems at risk. Food and agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Rome and Earthscan, London
FAO (2014) The water-energy-food nexus - a new approach in support of food security and sustainable agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Fernandez Garcia I, Rodriguez Diaz JA, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P (2013) Optimal operation of pressurized irrigation networks with several supply sources. Water Resour Manag 27:2855–2869. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0319-y
González Perea R, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2016) Optimization of irrigation scheduling using soil water balance and genetic algorithms. Water Resour Manag. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1325-7
Jiménez-Bello MA, Martínez Alzamora F, Bou Soler V, Ayala HJB (2010) Methodology for grouping intakes of pressurised irrigation networks into sectors to minimise energy consumption. Biosyst Eng 105:429–438. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.12.014
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2006) A simulation model to generate the demand hydrographs in large-scale irrigation systems. Biosyst Eng 93:335–346. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.12.006
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2010) Development of a decision support system for irrigation systems analysis. Water Resour Manag 24:3279–3297. doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9606-z
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N, Inoubli N (2013) Optimization of on-demand pressurized irrigation networks and on-farm constraints. Procedia Environ Sci 19:942–954. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2013.06.104
Lamaddalena N, Khila S (2011) Energy saving with variable speed pumps in on-demand irrigation systems. Irrig Sci 30:157–166. doi:10.1007/s00271-011-0271-7
Lamaddalena N, Sagardoy JA (2000) Performance analysis of on-demand pressurized irrigation systems. Irrigation and drainage paper no. 59. FAO, Rome, p. 132
Lamaddalena N, Fratino U, Daccache A (2007) On-farm sprinkler irrigation performance as affected by the distribution system. Biosyst Eng 96:99–109. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.09.002
Moreno MA, Carrión PA, Planells P, et al. (2007a) Measurement and improvement of the energy efficiency at pumping stations. Biosyst Eng 98:479–486. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2007.09.005
Moreno MA, Planells P, Ortega JF, Tarjuelo J (2007b) New methodology to evaluate flow rates in on-demand irrigation networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 133:298–306. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:4(298)
Moreno MA, Planells P, Córcoles JI, et al. (2009) Development of a new methodology to obtain the characteristic pump curves that minimize the total cost at pumping stations. Biosyst Eng 102:95–105. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.09.024
Moreno MA, Córcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Ortega JF (2010a) Energy efficiency of pressurised irrigation networks managed on-demand and under a rotation schedule. Biosyst Eng 107:349–363. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2010.09.009
Moreno MA, Ortega JF, Córcoles JI, et al. (2010b) Energy analysis of irrigation delivery systems: monitoring and evaluation of proposed measures for improving energy efficiency. Irrig Sci 28:445–460. doi:10.1007/s00271-010-0206-8
Navarro Navajas JM, Montesinos P, Camacho Poyato E, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2012) Impacts of irrigation network sectoring as an energy saving measure on olive grove production. J Environ Manag 111:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.034
Rodríguez Díaz JA, López Luque R, Carrillo Cobo MT, et al. (2009) Exploring energy saving scenarios for on-demand pressurised irrigation networks. Biosyst Eng 104:552–561. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.09.001
Rodríguez Díaz JA, CamachoPoyato E, BlancoPérez M (2011) Evaluation of water and energy use in pressurized irrigation networks in southern Spain. J Irrig Drain Eng 137:644–650. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000338
Rossman L A (2000) EPANET 2: users manual. US Environ Prot Agency, Washington, D.C. EPA/600/R-00/057, 2000
Acknowledgments
This research was developed in the framework of a master thesis funded by CIHEAM-Mediterranean Agronomic Institute of Bari (MAIB), Italy and conducted in collaboration with the University of Castilla-La Mancha, Spain. The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Division of Land and Water Resources Management at CIHEAM-MAIB, to the University of Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, to the Water Users Organization “Consorzio di bonifca della Capitanata”, which together made this research work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khadra, R., Moreno, M.A., Awada, H. et al. Energy and Hydraulic Performance-Based Management of Large-Scale Pressurized Irrigation Systems. Water Resour Manage 30, 3493–3506 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1365-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1365-z