Abstract
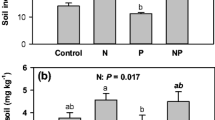
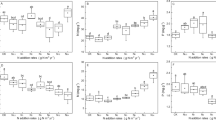
Increased nitrogen (N) availability induced by fertilizer use, rapid urbanization, and livestock cultivation has important effects on the biogeochemical cycles of plant N and phosphorus (P). Knowledge of the long-term N enrichment effects on the biogeochemical cycling of N and P via plant ecological stoichiometry and nutrient resorption remains limited. Nutrient resorption plays an important role in the plant nutrient economy and nutrient cycling. A three-year field experiment was performed to test the effects of N addition on leaf nutrient resorption of two dominant grass species (Leymus tiansecalinus and Festuca ovina) from an 11-year grassland experiment involving four N levels (0, 30, 90, and 150 kg N ha−1 year−1) in an alpine grassland of Tianshan Mountains in northwestern China. Nitrogen addition significantly increased aboveground biomass (AGB) and soil N availability. The N concentrations and N:P ratio in mature and senesced leaves consistently increased with increasing N across all three years. The P concentrations in mature and senesced leaves notably decreased with increasing N. The N addition resulted in decreased N resorption efficiency (NRE) and increased P resorption efficiency (PRE). The divergent responses of plant N and P resorption and N:P ratios resulted in the decoupling of the plant internal nutrient cycles for both grass species, attributed to increased soil N availability and nonsignificant effects on soil available P caused by N addition. In addition, the N:P resorption ratios were negatively correlated with increasing N levels, suggesting different sensitivities of plant N and P to N addition. The aboveground production of both grass species was positively correlated with PRE and negatively correlated with NRE. Under the background of the currently high and steadily increasing atmospheric N deposition, the imbalance of plant nutrient cycling will likely alter plant community compositions and subsequent litter decomposition, ultimately affecting ecosystem stability and function.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågren GI, Wetterstedt JAM, Billberger MFK (2012) Nutrient limitation on terrestrial plant growth-modeling the interaction between nitrogen and phosphorus. New Phytol 194:953–960
Bai YF, Wu JG, Clark CO, Naeem S, Pan QM, Huang JH, Zhang LX, Han XG (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from inner Mongolia Grasslands. Glob Chang Biol 16:358–372
Brant AN, Chen HYH (2015) Patterns and Mechanisms of Nutrient Resorption in Plants. Crit Rev plant Sci 34:471–486
Chen FS, Niklas KJ, Liu Y, Fang XM, Wan SZ, Wang HM (2015) Nitrogen and phosphorus additions alter nutrient dynamics but not resorption efficiencies of Chinese fir leaves and twigs differing in age. Tree Physiol 35:1106–1117
Chen H, Sayer SJ, Li ZA, Mo QF, Li YW, Ding YZ, Wang J, Lu XK, Tang JW, Wang FM (2016) Nutrient limitation of woody debris decomposition in a tropical forest: contrasting effects of N and P addition. Funct Ecol 30:295–304
Eckstein RL, Karlsson PS, Weih M (1999) Leaf life span and nutrient resorption as determinants of plant nutrient conservation in temperate-arctic regions. New Phytol 143:177–189
Fujita Y, Robroek BJM, De Ruiter PC, Heil GW, Wassen MJ (2010) Increased N affects P uptake of eight grassland species: the role of root surface phosphatase activity. Oikos 119:1665–1673
Fornara DA, Tilman D (2012) Soil carbon sequestration in prairie grasslands increased by chronic nitrogen addition. Ecology 93(9):2030–2036
Güsewell S (2005) Nutrient resorption of wetland graminoids is related to the type of nutrient limitation. Funct Ecol 19:344–354
Güsewell S, Gessner MO (2009) N: P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct Ecol 23:211–219
Han X, Sistla SA, Zhang YH, Lü XT, Han XG (2014) Hierarchical responses of plant stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition and mowing in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 382:175–187
Hao TX, Song L, Goulding K, Zhang FS, Liu XJ (2018) Cumulative and partially recoverable impacts of nitrogen addition on a temperate steppe. Ecol Appl 28:237–248
Hou SL, Yin JX, Yang JJ, Wei HW, Yang GJ, Hu YY, Han XG, Lü XT (2017) Consistent responses of litter stoichiometry to N addition across different biological organization levels in a semi-arid grassland. Plant Soil 421:191–202
Huang G, Su YG, Mu XH, Li Y (2018) Foliar nutrient resorption responses of three life-form plants to water and nitrogen additions in a temperate desert. Plant Soil 424:479–489
Huang JY, Zhu XG, Yuan ZY, Song SH, Li X, Li LH (2008) Changes in nitrogen resorption traits of six temperate grassland species along a multi-level N addition gradient. Plant Soil 306:149–158
Killingbeck KT (1996) Nutrients in senesced leaves: keys to the search for potential resorption and resorption proficiency. Ecology 77:1716–1727
Kozovits AR, Bustamante MMC, Garofalo CR, Buccl S, Franco AC, Goldstein G, Meinzer FC (2007) Nutrient resorption and patterns of litter production and decomposition in a Neotropical Savanna. Funct Ecol 21:1034–1043
Li KH, Gong YM, Song W, Lv JL, Chang YH, Hu YK, Tian CY, Christie P, Liu XJ (2012) No significant nitrous oxide emissions during spring thaw under grazing and nitrogen addition in an alpine grassland. Global Change Biol 18:2546–2554
Li KH, Liu XJ, Song L, Gong YM, Lu CF, Yue P, Tian CY, Zhang FS (2015) Response of alpine grassland to elevated nitrogen deposition and water supply in China. Oecologia 177:65–72
Li L, Gao XP, Li XY, Lin LS, Zeng FJ, Gui DW, Lu Y (2016a) Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) resorption of two dominant alpine perennial grass species in response to contrasting N and P availability. Environ Exp Bot 127:37–44
Li Y, Niu SL, Yu GR (2016b) Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: a meta-analysis. Global Change Biol 22:934–943
Liu XJ, Duan L, MO JM, Du EZ, Shen JL, Lu XK, Zhang Y, Zhou XB, He CN, Zhang FS, (2011) Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in china: An overview. Environ Pollut 159:2251–2264
Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Han WX, Tang AH, Shen JL, Cui ZL, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang FS (2013) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462
Lu XK, Mao QG, Gilliam F, Luo YQ, Mo JM (2014) Nitrogen deposition contributes to soil acidification in tropical ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 20:3790–3801
Lü XT, Han XG (2010) Nutrient resorption responses to water and nitrogen amendment in semi-arid grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. Plant Soil 327:481–491
Lü XT, Cui Q, Wang QB, Han XG (2011) Nutrient resorption response to fire and nitrogen addition in a semi-arid grassland. Ecol Eng 37:534–538
Lü XT, Reed S, Yu Q, He NP, Wang ZW, Han XG (2013) Convergent responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption to nitrogen inputs in a semiarid grassland. Glob Chang Biol 19:2775–2784
Lü XT, Reed SC, Yu Q, Han XG (2016) Nutrient resorption helps drive intra-specific coupling of foliar nitrogen and phosphorus under nutrient-enriched conditions. Plant Soil 398:111–120
Ma FF, Song B, Quan Q, Zhang FY, Wang JS, Zhou QP, Niu SL (2020) Light competition and biodiversity loss cause saturation response of aboveground net primary productivity to nitrogen enrichment. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 123:3308–3319
Mao R, Song CC, Zhang XH, Wang XW, Zhang ZH (2012) Response of leaf, sheath and stem nutrient resorption to 7 years of N addition in freshwater wetland of Northeast China. Plant Soil 364:385–394
Menge DNL, Field CB (2007) Simulated global changes alter phosphorus demand in annual grassland. Glob Chang Biolo 13:582–2591
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA circular 939. United states Government Printing Office, DC, Washington
Peng YF, Li F, Zhou GY, Fang K, Zhang DY, Li CB, Yang GB, Wang GQ, Wang J, Yang YH (2017) Linkages of plant stoichiometry to ecosystem production and carbon fluxes with increasing nitrogen inputs in an alpine steppe. Glob Chang Biol 23:5249–5259
Penuelas J, Sardans J, Rivas-Ubach A, Janssens, (2012) The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth’s life system. Glob Chang Biol 18:3–6
Reichmann LG, Sala OE, Peters DPC (2013) Water controls on nitrogen transformations and stocks in an arid ecosystem. Ecosphere 4:1–11
Richardson SJ, Allen RB, Doherty JE (2008) Shifts in leaf N: P ratio during resorption reflect soil P in temperate rainforest. Funct Ecol 22:738–745
Sardans J, Alonso R, Janssens IA, Carnicer J, Vereseglou S, Rillig MC, Fernández-Martínez M, Sanders TGM, Penuelas J (2016) Foliar and soil concentrations and stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorous across European Pinus sylvestris forests: relationships with climate, N deposition and tree growth. Funct Ecol 30:676–689
Soudzilovskaia NA, Onipchenko VG, Cornelissen JHC, Aerts R (2007) Effects of fertilisation and irrigation on ‘foliar afterlife’ in alpine tundra. J Veg Sci 18:755–766
Van Heerwaarden LM, Toet S, Aerts R (2003) Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption efficiency and proficiency in six sub-arctic bog species after 4 years of nitrogen fertilization. J Ecol 91:1060–1070
Vergutz L, Manzonl S, Porporato A, Novals RF, Jackson RB (2012) Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol Monogr 82:205–220
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15
Wang M, Murphy MT, Moore TR (2014) Nutrient resorption of two evergreen shrubs in response to long-term fertilization in a bog. Oecologia 174:365–377
Wang HY, Wang ZW, Ding R, Hou SL, Yang GJ, Lü XT, Han XG (2018) The impacts of nitrogen deposition on community N: P stoichiometry do not depend on phosphorus availability in a temperate meadow steppe. Environ Pollut 242:82–89
Xia JY, Wan SQ (2008) Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol 179:428–439
Xia MX, Talhelm AF, Pregitzer KS (2017) Chronic nitrogen deposition influences the chemical dynamics of leaf litter and fine roots during decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 112:24–34
You CM, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, Xu ZF, Tan B, Zhang L, Yue K, Ni XY, Li H, Chang CH, Fu CK (2018a) Does foliar nutrient resorption regulate the coupled relationship between nitrogen and phosphorus in plant leaves in response to nitrogen deposition? Sci Total Environ 645:733–742
You CM, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, Xu ZF, Tan B, Yue K, Ni XY (2018b) Nutrient-limited conditions determine the responses of foliar nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry to nitrogen addition: A global meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 241:740–749
Yu GR, Jia YL, He NP, Zhu JX, Chen Z, Wang QW, Piao SL, Liu XJ, He H, Guo XB, Wen Z, Li P, Ding GA, Goulding K (2019) Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decades. Nat Geosci 12:424–429
Yu Q, Chen QS, Elser JJ, He NP, Wu HH, Zhang GM, Wu JG, Bai YF, Han XG (2010) Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability. Ecol Lett 13:1390–1399
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2015a) Decoupling of nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial plants associated with global changes. Nat clim change 5:465–469
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2015b) Negative effects of fertilization on plant nutrient resorption. Ecology 96:373–380
Zhan SX, Wang Y, Zhu ZC, Li WH, Bai YF (2017) Nitrogen enrichment alters plant N: P stoichiometry and intensifies phosphorus limitation in a steppe ecosystem. Environ Exp Bot 134:21–32
Zhang DY, Peng YF, Li f, Yang GB, Wang J, Yu JC, Zhou GY, Yang YH, (2019) Trait identity and functional diversity co-drive response of ecosystem productivity to nitrogen enrichment. J Ecol 107:2402–2414
Zhang JJ, Yan XB, Su FL, Li Z, Wang Y, Wei YA, Ji YG, Yang Y, Zhou XH, Guo H, Hu SJ (2018) Long-term N and P additions alter the scaling of plant nitrogen to phosphorus in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Sci Total Environ 625:440–448
Zheng J, She WW, Zhang YQ, Bai YX, Qin SG, Wu B (2018) Nitrogen enrichment alters nutrient resorption and exacerbates phosphorus limitation in the desert shrub Artemisia ordosica. Ecol evol 8:9998–10007
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the staff of the Bayanbulak Grassland Ecosystem Research Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences, who helped with the fieldwork. The present study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41673079, 41425007) and the "Light of West China" Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Han W.X.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Dafeng Hui.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Ma, X., Le, J. et al. Decoupling of nitrogen and phosphorus in dominant grass species in response to long-term nitrogen addition in an Alpine Grassland in Central Asia. Plant Ecol 222, 261–274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-020-01103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-020-01103-3