Abstract
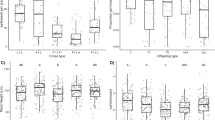
The relative importance of floral versus ecological isolation in preventing introgression remains unclear. This study examines whether ecological isolation can explain the continuing integrity of Silene dioica and S. latifolia where floral isolation is weak and hybrids are fully viable. Eighteen small replicate founder populations of 6 individuals (3 males and 3 females) of either S. latifolia, S. dioica or hybrids were created in woodland and in open sites in southern UK. Survival, reproduction and introgression of these populations were examined over 9 years. S. latifolia and hybrid plants suffered higher mortality than S. dioica in woodland. In open sites, there was extensive introgression, with few or no pure S. latifolia or S. dioica surviving by the end of the experiment. The experiment suggests that the integrity of S. dioica is maintained by its ability to survive in shaded habitats where S. latifolia and hybrids cannot persist. However, how S. latifolia survives as a distinct species in the study area remains a puzzle. Immigration from regions where S. latifolia occurs in isolation (i.e. large-scale ecological isolation) may balance introgression in the study area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker HG (1947) Accounts of Melandrium, M. dioicum and M. album for the biological flora of the British Isles sponsored by the British Ecological Society. J Ecol 35:271–292. doi:10.2307/2256515
Baker HG (1948a) Stages in invasion and replacement demonstrated by species of Melandrium. J Ecol 36:96–119. doi:10.2307/2256649
Baker HG (1948b) The ecotypes of Melandrium dioicum (L. emend.) Coss. & Germ. New Phytol 47:131–145. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1948.tb05096.x
Bleeker W, Hurka H (2001) Introgressive hybridization in Rorippa (Brassicaceae): gene flow and its consequences in natural and anthropogenic habitats. Mol Ecol 10:2013–2022. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01341.x
Buerkle CA, Morris RJ, Asmussen MA, Rieseberg LH (2000) The likelihood of homoploid hybrid speciation. Heredity 84:441–451. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2540.2000.00680.x
Campbell DR (2004) Natural selection in Ipomopsis hybrid zones: implications for ecological speciation. New Phytol 161:8390. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00919.x
Chase VC, Raven PH (1975) Evolutionary and ecological relationships between Aquilegia formosa and A. pubescens (Ranunculaceae), two perennial plants. Evolution 29:474–486. doi:10.2307/2407260
Clapham AR, Tutin TG, Moore DM (1987) Flora of the British Isles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Crie ML (1884) Sur le polymorphisme floral et la pollinisation du Lychnis dioica, L. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences 48:1–2
Darwin C (1876) The effects of cross- and self-fertilization in the animal kingdom. Murray, London, UK
Debussche M, Thompson JD (2003) Habitat differentiation between two closely related Mediterranean plant species, the endemic Cyclamen balearicum and the widespread C. repandum. Acta Oecol 24:35–45. doi:10.1016/S1146-609X(02)00006-1
Goulson D (1994) A model to predict the role of flower constancy in inter-specific competition between insect pollinated flowers. J Theor Biol 168:309–314. doi:10.1006/jtbi.1994.1111
Goulson D, Cory JS (1993) Flower constancy and learning in the foraging behaviour of the green-veined white butterfly, Pieris napi. Ecol Entomol 18:315–320. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2311.1993.tb01107.x
Goulson D, Jerrim K (1997) Maintenance of the species boundary between Silene dioica and S. latifolia (red and white campion). Oikos 78:254–266
Goulson D, Wright NP (1998) Flower constancy in the hoverflies Episyrphus balteatus (Degeer) and Syrphus ribesii (L.) (Syrphidae). Behav Ecol 9:213–219. doi:10.1093/beheco/9.3.213
Goulson D, Stout JC, Hawson SA (1997) Can flower constancy in nectaring butterflies be explained by Darwin’s interference hypothesis? Oecologia 112:225–231. doi:10.1007/s004420050304
Grant V (1952) Isolation and hybridization between Aquilegia formosa and A. pubescens. Aliso 2:341–360
Grant V (1992) Floral isolation between ornithophilous and sphingophilous species of Ipomopsis and Aquilegia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11828–11831. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.24.11828
Grant V (1993a) Effects of hybridisation and selection on floral isolation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:990–993. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.3.990
Grant V (1993b) Origins of floral isolation between ornithophilous and sphingophilous plant species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7729–7733. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.16.7729
Grant V (1994) Modes and origins of mechanical and ethological isolation in angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3–10. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.1.3
Hodges SA, Arnold ML (1994) Floral and ecological isolation between Aquilegia formosa and Aquilegia pubescens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2493–2496. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.7.2493
Hodges SA, Fulton M, Yang YJ, Whittall JB (2004) Verne Grant and evolutionary studies of Aquilegia. New Phytol 161:113–120. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00950.x
James JK, Abbott RJ (2005) Recent, allopatric, homoploid hybrid speciation: the origin of Senecio squalidus (Asteraceae) in the British Isles from a hybrid zone on Mount Etna, Sicily. Evolution 59:2533–2547
Karrenberg S, Favre A (2008) Genetic and ecological differentiation in the hybridizing campions Silene dioica and S. latifolia. Evol Int J Org Evol 62:763–773. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00330.x
Kimball S (2008) Links between floral morphology and floral visitors along an elevational gradient in a Penstemon hybrid zone. Oikos 117:1064–1074. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2008.16573.x
Knuth P (1898) Handbuch der Blütenbiologie, vol II. Wilhelm Engelmann, Liepzig
Lavergne S, Thompson JD, Garnier E, Debussche M (2004) The biology and ecology of narrow endemic and widespread plants: a comparative study of trait variation in 20 congeneric pairs. Oikos 107:505–518. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.13423.x
Lewis AC (1993) Learning and the evolution of resources: pollinators and flower morphology. In: Papaj DR, Lewis AC (eds) Insect learning: ecology and evolutionary perspectives. Chapman and Hall, New York, USA, pp 219–242
Ma XF, Szmidt AE, Wang XR (2006) Genetic structure and evolutionary history of a diploid hybrid pine Pinus densata inferred from the nucleotide variation at seven gene loci. Mol Biol Evol 23:807–816. doi:10.1093/molbev/msj100
Minder AM, Widmer A (2008) A population genomic analysis of species boundaries: neutral processes, adaptive divergence and introgression between two hybridizing plant species. Mol Ecol 17:1552–1563. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03709.x
Minder AM, Rothenbuehler C, Widmer A (2007) Genetic structure of hybrid zones between Silene latifolia and Silene dioica (Caryophyllaceae): evidence for introgressive hybridization. Mol Ecol 16:2504–2516. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03292.x
Nigtevecht GV (1966) Genetic studies in dioecious Melandrium I. Sex-linked and sex influences inheritance in Melandrium album and Melandrium dioicum. Genetica 37:281–306. doi:10.1007/BF01547140
Prentice HC (1979) Numerical analysis of infraspecific variation in European Silene alba and S. dioica (Caryophyllaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 78:181–212. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.1979.tb02193.x
Prentice HC, Malm JU, Hathaway L (2008) Chloroplast DNA variation in the European herb Silene dioica (red campion): postglacial migration and interspecific introgression. Plant Syst Evol 272:23–37. doi:10.1007/s00606-007-0629-8
Ramsey J, Bradshaw HD, Schemske DW (2003) Components of reproductive isolation between the monkeyflowers Mimulus lewisii and M. cardinalis (Phrymaceae). Evolution 57:1520–1534
Rieseberg LH (1997) Hybrid origins of plant species. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:359–389. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.28.1.359
Schluter D (2000) The ecology of adaptive radiation. Oxford University press, Oxford, UK
Taylor DR (1994) Sex ratio in hybrids between Silene alba and Silene dioica: evidence for Y-linked restorers. Heredity 74:518–526. doi:10.1038/hdy.1994.150
van Putten WF, Elzinga JA, Biere A (2007) Host fidelity of the pollinator guilds of Silene dioica and Silene latifolia: possible consequences for sympatric host race differentiation of a vectored plant disease. Int J Plant Sci 168:421–434. doi:10.1086/511050
Willmot A, Moore PD (1973) Adaptation to light intensity in Silene alba and S. dioica. Oikos 24:458–464. doi:10.2307/3543822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulson, D. Evaluating the role of ecological isolation in maintaining the species boundary between Silene dioica and S. latifolia . Plant Ecol 205, 201–211 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9610-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9610-7