Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to estimate dietary intakes of trace elements, minerals, and vitamins in hemodialysis patients (HDP) of three centers in one metropolitan and two urban areas of Italy.
Methods
Daily dietary intake was assessed using a 3-day diet diary in 128 HDP.
Results
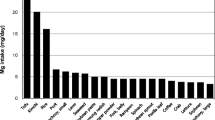
Mean daily intakes of trace elements were as follows: zinc, 7.6 ± 5.4 mg; copper, 14.3 ± 11.8 mg; selenium, 28.3 ± 18.1 μg; and iron, 7.2 ± 4.1 mg (7.8 ± 2.6 mg in women, 6.9 ± 2.4 mg in men). The distribution of patients by daily intakes of trace elements showed most were under the recommended values, with the exception of copper intake, which was much higher. Mean daily intakes of minerals were as follows: magnesium, 174.4 ± 94.3 mg; phosphorus, 842.6 ± 576.8 mg; calcium, 371.8 ± 363.7 mg; potassium, 1,616.2 ± 897.3 mg; and sodium, 1,350 ± 1,281 mg. Mean daily intakes of vitamins were as follows: vitamin A, 486.1 ± 544.6 μg; vitamin B1, 0.86 ± 0.7 mg; vitamin B2, 1.1 ± 0.7 mg; vitamin B3, 13.3 ± 8.1 mg; vitamin C, 47.8 ± 50.3 mg; and vitamin E, 9.5 ± 3.6 mg. The distribution of patients by daily intakes of vitamins showed most were under the recommended values. Daily intakes of trace elements and vitamins were similar among the three centers and did not differ between dialysis and non-dialysis days.
Conclusions
Many HDP have daily dietary intakes of trace elements and vitamins below the recommended values, whereas the intake of copper is much higher.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bossola M, Tazza L, Giungi S, Luciani G (2006) Anorexia in hemodialysis patients: an update. Kidney Int 70:417–422
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD (2003) Trace elements and vitamins in maintenance dialysis patients. Adv Ren Replace Ther 10:170–182
Maruno F, Kamata K, Okubo M (1986) Deranged concentrations of water-soluble vitamins in the blood of undialyzed and dialyzed patients with chronic renal failure. Int J Artif Organs 9:17–24
Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Hemmelgarn B, Klarenbach S, Field C, Manns B, Thadhani R, Gill J, Alberta Kidney Disease Network (2009) Trace elements in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 7:25–30
LARN. Livelli di Assunzione giornalieri raccomandati di energia e nutrienti per la popolazione italiana. www.sinu.it/larn/tab_rias.asp
Fouque D, Vennegoor M, ter Wee P, Wanner C, Basci A, Canaud B, Haage P, Konner K, Kooman J, Martin-Malo A, Pedrini L, Pizzarelli F, Tattersall J, Tordoir J, Vanholder R (2007) EBPG guideline on nutrition. Nephrol Dial Transpl 22(Suppl 2):ii45–ii87
Szpanowska-Wohn A, Kolarzyk E, Chowaniec E (2008) Estimation of intake of zinc, copper and iron in the diet of patients with chronic renal failure treated by haemodialysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 124:97–102
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD, Deepak S, Block D, Block G (2002) Food intake characteristics of hemodialysis patients as obtained by food frequency questionnaire. J Ren Nutr 12:17–31
Komindr S, Puchaiwatananon O, Thirawitayakom J, Domrongkitchaiporn S, Songchitsomboon S (1993) Effects of dietary counseling on vitamin A, B-1, B-2 and zinc status of chronic hemodialysis patients. J Med Assoc Thail 80:724–730
Descombes E, Hanck AB, Fellay G (1993) Water soluble vitamins in chronic hemodialysis patients and need for supplementation. Kidney Int 43:1319–1328
Chen J, Peng H, Zhang K, Xiao L, Yuan Z, Chen J, Wang Z, Wang J, Huang H (2013) The insufficiency intake of dietary micronutrients associated with malnutrition–inflammation score in hemodialysis population. PLoS ONE 8:e66841
Bossola M, Leo A, Viola A, Carlomagno G, Monteburini T, Cenerelli S, Santarelli S, Boggi R, Miggiano G, Vulpio C, Mele C, Tazza L (2013) Dietary intake of macronutrients and fiber in Mediterranean patients on chronic hemodialysis. J Nephrol 26:912–918
Bozalioğlu S, Ozkan Y, Turan M, Simşek B (2005) Prevalence of zinc deficiency and immune response in short-term hemodialysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:243–249
Rodger RS, Sheldon WL, Watson MJ, Dewar JH, Wilkinson R, Ward MK, Kerr DN (1989) Zinc deficiency and hyperprolactinaemia are not reversible causes of sexual dysfunction in uraemia. Nephrol Dial Transpl 4:888–892
Antoniou LD, Shalhoub RJ, Sudhakar T, Smith JC Jr (1977) Reversal of uraemic impotence by zinc. Lancet 2:895–898
Atkin-Thor E, Goddard BW, O’Nion J, Stephen RL, Kolff WJ (1978) Hypogeusia and zinc depletion in chronic dialysis patients. Am J Clin Nutr 31:1948–1951
Roozbeh J, Sharifian M, Ghanizadeh A, Sahraian A, Sagheb MM, Shabani S, Hamidian Jahromi A, Kashfi M, Afshariani R (2011) Association of zinc deficiency and depression in the patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr 21:184–187
Fujishima Y, Ohsawa M, Itai K, Kato K, Tanno K, Turin TC, Onoda T, Endo S, Okayama A, Fujioka T (2011) Serum selenium levels are inversely associated with death risk among hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl 26:3331–3338
Ceballos-Picot I, Witko-Sarsat V, Merad-Boudia M, Nguyen AT, Thévenin M, Jaudon MC, Zingraff J, Verger C, Jungers P, Descamps-Latscha B (1996) Glutathione antioxidant system as a marker of oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. Free Radic Biol Med 21:845–853
Girelli D, Olivieri O, Stanzial AM, Azzini M, Lupo A, Bernich P, Menini C, Gammaro L, Corrocher R (1993) Low platelet glutathione peroxidase activity and serum selenium concentration in patients with chronic renal failure: relations to dialysis treatments, diet and cardiovascular complications. Clin Sci (Lond) 84:611–617
Hampel G, Schaller KH, Rosenmuller M, Oefele C (1985) Selenium-deficiency as contributing factor to anemia and thrombocytopenia in dialysis patients. Life Support Syst 3(Suppl 1):36–40
Cialfa E (1991) Valutazione di sostanze indesiderabili in base a modelli di consumo, Rapporto del Sottoprogetto 4 RAISA, CNR Volterra, pp 733–740
Santaroni GP, Ingrao G, Belloni P, Giambelli L (1992) Livelli di alcuni elementi in traccia in diete italiane. Rapporto del sottoprogetto 4 RAISA CNR, Volterra, vol. II, pp 1087–1088
Testolin G (1992) Presenza di contaminanti nella dieta e loro effetti biologici. Rapporto del Sottoprogetto 4 RAISA CNR Volterra, Vol II, p 1109
Mason KE (1979) A conspectus of research on copper metabolism and requirements of man. J Nutr 1979(109):1979–2066
Anke M, Angelow L (1993) Trace elements on food dietary intake, excretion and requirement: dietary trace element intake and excretion in man. In: Proceedings of the eight international symposium on trace elements in man and animals, pp 180–188
Commission of the European Communities (1993) Nutrient and energy intakes for the European Community, Reports of the Scientific Committee for Food, thirty-first series, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Manzler AD, Schreiner AW (1070) Copper-induced acute haemolytic anaemia. A new complication of hemodialysis. Ann Int Med 73:409–412
Loef M, Walach H (2012) Copper and iron in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and its dietary implications. Br J Nutr 107:7–19
Morris MC, Evans DA, Tangney CC, Bienias JL, Schneider JA, Wilson RS, Scherr PA (2006) Dietary copper and high saturated and trans fat intakes associated with cognitive decline. Arch Neurol 63:1085–1088
Fissell RB, Bragg-Gresham JL, Gillespie BW, Goodkin DA, Bommer J, Saito A, Akiba T, Port FK, Young EW (2004) International variation in vitamin prescription and association with mortality in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am J Kidney Dis 44:293–299
Griffiths A, Russell L, Breslin M, Russell G, Davies S (1999) A comparison of two methods of dietary assessment in peritoneal dialysis patients. J Ren Nutr 9:26–31
Don T, Friedlander S, Wong W (2010) Dietary intakes and biochemical status of B vitamins in a group of children receiving dialysis. J Ren Nutr 20:23–28
Kutner NG, Clow PW, Zhang R, Aviles X (2002) Association of fish intake and survival in a cohort of incident dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 39:1018–1024
As’habi A, Tabibi H, Houshiar Rad A, Nozary Heshmati B, Mahdavi-Mazdeh M, Hedayati M (2011) Dietary assessment of hemodialysis patients in Tehran, Iran. Hemodial Int 15:530–537
Cranenburg EC, Schurgers LJ, Uiterwijk HH, Beulens JW, Dalmeijer GW, Westerhuis R, Magdeleyns EJ, Herfs M, Vermeer C, Laverman GD (2012) Vitamin K intake and status are low in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.191
Bellizzi V, Di Iorio BR, Zamboli P, Terracciano V, Minutolo R, Iodice C, De Nicola L, Conte G (2003) Daily nutrient intake in hemodialysis. G Ital Nefrol 20:592–601
Mafra D, Moraes C, Leal VO, Farage NE, Stockler-Pinto MB, Fouque D (2012) Underreporting of energy intake in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. J Ren Nutr 22:578–583
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bossola, M., Di Stasio, E., Viola, A. et al. Dietary intake of trace elements, minerals, and vitamins of patients on chronic hemodialysis. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 809–815 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0689-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0689-y