Abstract
Objectives
To investigate bladder function in a model of nonbacterial prostatitis (NBP) induced in castrated rats by 17β-estradiol injection.
Methods
Ten-month-old male Wistar rats were divided into two groups, sham and NBP (both N = 8). NBP was induced by castration followed by daily subcutaneous injection of 17β-estradiol for 30 days. On the 31st day after surgery, we investigated (1) voiding behavior, (2) bladder blood flow (BBF), (3) prostate and bladder weight, and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and CXCL1) levels and (4) bladder contractile responses to electrical field stimulation (EFS), carbachol and KCl.
Results
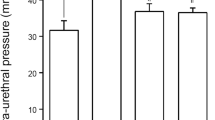
(1) Voiding behavior (average micturition volume, total urine volume and number of micturitions) and (2) BBF were not significantly different between the sham and NBP groups. (3) NBP led to a significant decrease in prostatic weight and increase in proinflammatory cytokine levels in the prostate, but NBP did not cause a significant change in bladder weight or proinflammatory cytokine levels in the bladder. (4) Bladder contractile forces in response to EFS, carbachol and KCl were not significantly affected by NBP.
Conclusions
In this rat model, NBP did not cause a significant change in the level of proinflammatory cytokines in the bladder and affect bladder function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nickel JC, Roehrborn CG, O’Leary MP, Bostwick DG, Somerville MC, Rittmaster RS (2008) The relationship between prostate inflammation and lower urinary tract symptoms: examination of baseline data from the REDUCE trial. Eur Urol 54:1379–1384
Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr, Nickel JC (1999) NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA 282:236–237
Gonzalez RR, Te AE (2006) Is there a role for urodynamics in chronic nonbacterial prostatitis? Curr Urol Rep 7:335–338
Bernoulli J, Yatkin E, Talvitie EM, Santti R, Streng T (2007) Urodynamic changes in a Noble rat model for nonbacterial prostatic inflammation. Prostate 67:888–899
Funahashi Y, Takahashi R, Gotoh M, Yoshimura N (2012) Bladder overactivity induced by prostate-to-bladder afferent cross-sensitization in rats with prostatic inflammation. J Urol 187:e442. In: Abstract no. 1090. Poster presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association, May 21, 2012, Atlanta, GA, USA
Naslund MJ, Strandberg JD, Coffey DS (1988) The role of androgens and estrogens in the pathogenesis of experimental nonbacterial prostatitis. J Urol 140:1049–1053
Kawai Y, Oka M, Kyotani J, Oyama T, Matsumoto S, Kakizaki H (2012) Effect of the phytotherapeutic agent eviprostat on the bladder in a rat model of bladder overdistension/emptying. Neurourol Urodyn. doi:10.1002/nau.22350
Oka M, Fukui T, Ueda M, Tagaya M, Oyama T, Tanaka M (2009) Suppression of bladder oxidative stress and inflammation by a phytotherapeutic agent in a rat model of partial bladder outlet obstruction. J Urol 182:382–390
Oka M, Ueda M, Oyama T, Kyotani J, Tanaka M (2009) Effect of the phytotherapeutic agent Eviprostat® on 17β-estradiol-induced nonbacterial inflammation in the rat prostate. Prostate 69(13):1404–1410
Sugimoto M, Oka M, Tsunemori H, Yamashita M, Kakehi Y (2011) Effect of a phytotherapeutic agent, Eviprostat®, on prostatic and urinary cytokines/chemokines in a rat model of nonbacterial prostatitis. Prostate 71:438–444
Shabsigh A, Chang DT, Heitjan DF, Kiss A, Olsson CA, Puchner PJ, Buttyan R (1998) Rapid reduction in blood flow to the rat ventral prostate gland after castration: preliminary evidence that androgens influence prostate size by regulating blood flow to the prostate gland and prostatic endothelial cell survival. Prostate 36:201–206
Robinette CL (1988) Sex-hormone-induced inflammation and fibromuscular proliferation in the rat lateral prostate. Prostate 12:271–286
Kamijo T, Sato S, Kitamura T (2001) Effect of cernitin pollen-extract on experimental nonbacterial prostatitis in rats. Prostate 49:122–131
Ishigooka M, Zermann DH, Doggweiler R, Schmidt RA (2000) Similarity of distributions of spinal c-Fos and plasma extravasation after acute chemical irritation of the bladder and the prostate. J Urol 164:1751–1756
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, S., Kawai, Y., Oka, M. et al. Bladder function in 17β-estradiol-induced nonbacterial prostatitis model in Wister rat. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 749–754 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0442-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0442-y