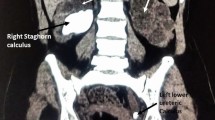
Abstract
Aim
We aimed to study the clinical profile, prognostic factors, and the 6-month outcome of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN)
Methods
All patients admitted with a diagnosis of emphysematous pyelonephritis between January 2001 and July 2007 were included.
Results
Overall 19 cases were diagnosed to have emphysematous pyelonephritis. There were 16 females and three males. Fourteen cases had type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fourteen cases had unilateral involvement and five had bilateral involvement. Eleven cases were classified as having class 1 or 2 disease and eight cases had class 3 and 4 disease. E. coli was the most common organism cultured (68.4%). Five cases underwent percutaneous drainage of the collecting system and three cases had nephrectomy of which 10.5% (two with advanced disease) expired. Shock at admission (p = 0.03), serum creatinine >5.0 mg/dl (p = 0.035) and DIC (p = 0.017) were independent poor prognostic factors. There was no difference in the prognosis between patients who had ≥2 or <2 poor prognostic factors (p = 0.16). However, prognosis was not related to disease class, unilateral vs. bilateral involvement, sepsis or the age of the patient. At 6 months, two patients were on maintenance hemodialysis.
Conclusions
In cases of EPN, shock, serum creatinine >5.0 mg/dl and DIC at admission are poor prognostic factors. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang JJ, Tseng CC (2000) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med 27:797–805. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.6.797
Tang HJ, Li CM, Yen MY et al (2001) Clinical characteristics of emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 34:125–130
Modi P, Goel R, Dodia S (2007) Scrotal extension of emphysematous pyelonephritis 2007. Int Urol Nephrol 40:405–407. doi:10.1007/s11255-006-9018-4
Baliga KV, Narula AS, Sharma A et al (2007) Successful medical treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis in a renal allograft recipient. Ren Fail 29:755–758. doi:10.1080/08860220701460434
Chuang YW, Chen CH, Cheng CH et al (2007) Severe emphysematous pyelonephritis in a renal allograft: successful treatment with percutaneous drainage and antibiotics. Clin Nephrol 68:42–46
Fujita S, Watanabe J, Reed AI et al (2005) Case of emphysematous pyelonephritis in a renal allograft. Clin Transplant 19:559–562. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0012.2005.00264.x
Kalra OP, Malik N, Minz M et al (1993) Emphysematous pyelonephritis and cystitis in a renal transplant recipient-computed tomographic appearance. Int J Artif Organs 16:41–44
Schultz EH, Klorfein EH (1962) Emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol 87:762–766
Kamaliah MD, Bhajan MA, Dzarr GA (2005) Emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by Candida infection. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 36:725–727
Hildebrand TS, Nibbe L, Frei U et al (1999) Bilateral emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by Candida infection. Am J Kidney Dis 33:E10. doi:10.1016/S0272-6386(99)70331-8
Sultana SR, McNeill SA, Phillips G et al (1998) Candidal urinary tract infection as a cause of pneumaturia. J R Coll Surg Edinb 43:198–199
Seidenfeld SM, Lemaistre CF, Setiawan H et al (1982) Emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by Candida tropicalis. J Infect Dis 146:569
Wu VC, Fang CC, Li WY et al (2004) Candida tropicalis-associated bilateral renal papillary necrosis and emphysematous pyelonephritis. Clin Nephrol 62:473–475
Wan YL, Lo SK, Bullard MJ et al (1998) Predictors of outcome in Emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol 159:369–373. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)63919-3
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Kapur A et al (2001) High prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India: National Urban Diabetes Survey. Diabetologia 44:1094–1101. doi:10.1007/s001250100627
Dutta P, Bhansali A, Singh SK et al (2007) Presentation and outcome of emphysematous renal tract disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Urol Int 78:13–22. doi:10.1159/000096929
Shokeir AA, El-Azab M, Mohsen T et al (1997) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 15-year experience with 20 cases. Urology 49:343–346. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(96)00501-8
Ahlering TE, Boyd SD, Hamilton CL et al (1985) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 5-year experience with 13 patients. J Urol 134:1086–1088
Soo Park B, Lee SJ, Wha Kim Y et al (2006) Outcome of nephrectomy and kidney-preserving procedures for the treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 40:332–338
Arun N, Hussain A, Kapoor MM et al (2007) Bilateral emphysematous pyelonephritis and emphysematous cystitis with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease: is conservative management justified? Med Princ Pract 16:155–157. doi:10.1159/000098371
Shimizu H, Hariu K, Kamiyama Y et al (1999) Bilateral emphysematous pyelonephritis with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease successfully treated by conservative method. Urol Int 63:252–254. doi:10.1159/000030462
Somani BK, Nabi G, Thorpe P et al (2008) ABACUS Research Group is percutaneous drainage the new gold standard in the management of emphysematous pyelonephritis? Evidence from a systematic review. J Urol 179:1844–1849. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2008.01.019
Liao HW, Chen TH, Lin KH et al (2005) Emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by Bacteroides fragilis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2575–2577. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi146
Tolwani AJ, Wheeler TS, Wille KM (2007) Sustained low-efficiency dialysis. Contrib Nephrol 156:320–324. doi:10.1159/000102122
Edwards SJ, Clarke MJ, Wordsworth S et al (2008) Carbapenems versus other beta-lactams in treating severe infections in intensive care: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27:531–543. doi:10.1007/s10096-008-0472-z
Baldwin CM, Lyseng-Williamson KA, Keam SJ (2008) Meropenem: a review of its use in the treatment of serious bacterial infections. Drugs 68:803–838. doi:10.2165/00003495-200868060-00006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaira, A., Gupta, A., Rana, D.S. et al. Retrospective analysis of clinical profile prognostic factors and outcomes of 19 patients of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol 41, 959–966 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9552-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9552-y