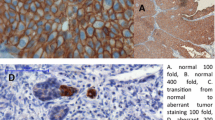
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the relationship between the expression of E-cadherin (E-CD) and tumor recurrence and progression in patients with high-grade stage T1 urothelial carcinoma of bladder.
Methods
Fifty-two patients who had primary high-grade stage T1 urothelial carcinoma were enrolled to the study. The pathologic specimens of patients were evaluated and staged as T1a and T1b according to muscularis mucosae involvement by the tumor. The immunohistochemical demonstration of E-CD was accomplished by using immunoperoxidase method and all the specimens were examined under light microscope for E-CD level.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 64.0 ± 7.7 (range 36–81) years. The mean follow-up period was 56.4 ± 19.4 (range 14–84) months. Among 52 patients, 27 (52%) of them were stage T1b and 25 (48%) were T1a tumors. The recurrence rates for T1a and T1b groups were 52% (n = 13) and 92.6% (n = 25), respectively (P < 0.05). The expression of E-CD was homogenous in 52% of pT1a and 14.8% of T1b tumors (P < 0.05). In T1a group with recurrence, homogeneous E-CD staining ratio was 30.7% (n = 4/13), but it was 75% (n = 9/12) in T1a patients without recurrence (P < 0.05). In T1b group with recurrence, the homogenous expression of E-CD was 12% (n = 3/25) and the expression of E-CD was heterogenous in 88% (n = 22/25) of them (P < 0.05). In T1a group, progression of the disease was detected in 28% (n = 7/25) of the patients, but disease progression was seen in 55.5% (n = 15/27) of T1b group patients (P < 0.05). In T1a group with progression, heterogeneous E-CD staining ratio was 85.7% (n = 6/7), but it was 80% (n = 12/15) in T1b patients with progression. The effects of tumor number, tumor size and carcinoma in situ presence on recurrence were evaluated within each group. It was determined that parameters such as tumor number and tumor size had no significant effect on recurrence of the groups. The mean survival rates were statistically different between the groups. On multivariate analysis only E-cadherin expression (P = 0.012, odds ratio 6.291, 95% confidence interval for odds ratio 1.303–4.72) and tumor stage (P = 0.003, odds ratio 11.58, 95% confidence interval for odds ratio 2.446–8.542) remained independently significant as predictors of recurrence.
Conclusion
E-CD expression was decreased in pathologic specimens of bladder tumor patients with muscularis mucosae involvement and this condition correlated well with tumor recurrence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Syrigos KN, Harrington KJ, Pignatelli M (1999) Role of adhesion molecules in bladder cancer an important part of the jigsaw. Urology 53:428–434
Gunlusoy B, Degirmenci T, Arslan M, Nergiz N, Minareci S, Ayder AR (2005) Recurrence and progression of T1G3 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder treated with intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Urol Int 75:107–113
Sozen S, Akbal C, Sokmensuer C, Ekici S, Ozen H (2002) Microstaging of pT1 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Does it really differentiate two populations with different prognoses? (pT1 subcategory). Urol Int 69:200–206
Durkan GC, Brotherick L, Mellon JK (1999) The impact of transurethral resection of bladder tumour on serum levels of soluble E-cadherin. BJU Int 83:424–428
Otto T, Birchmeier W, Schmidt U (1994) Inverse relation of E-cadherin and autocrine motility factor receptor expression as a prognostic factor in patients with bladder carcinomas. Cancer Res 54:3120–3123
Imao T, Koshida K, Endo Y (1999) Dominant role of E-cadherin in the progression of bladder cancer. J Urol 161:692–698
Sobin DH, Witteking Ch (eds) (2002) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 6th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Angulo C, Lopez JI, Grignon DJ, Sanchez-Chapado M (1995) Muscularis mucosae differentiates two populations with different prognosis in stage T1 bladder cancer. Urology 45:47–53
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA (eds) (2004) World Health Organization classification of tumors. Tumors of the urinary system and genital organs. Pathology and Genetics. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 90–109
Holzbeierlein JM, Smith JA (1999) Management of superficial Ta/T1/T1S bladder cancer. Comprehensive textbook of genitourinary oncology. 2nd edn. Vogelzang NJ, Scardino PT, Shipley WU, Coffey DS ed, pp 384–394
Hasui Y, Osada Y, Kıtada S (1994) Signifıcance of invasion to the muscularis mucosaee on the progression of superficial bladder cancer. Urology 43:782–786
Holmang S, Hedelin H, Anderstrom C (1997) The importance of the depth of invasion in stage T1 bladder carcinoma: a prospectıve cohort study. J Urol 157:800–804
Dixon JS, Gosling JA (1983) Histology and fine structure of the muscularis mucosae of the human urinary bladder. J Anat 136:265–271
Raghaven D, Shipley WU, Garnick MB (1990) Biology and management of bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 322:1129–1138
Esrig D, Spruck CH, Nıchols PW (1993) P53 nuclear protein accumulation correlates with mutations in the p53 gene, tumor grade, and stage in bladder cancer. Am J Pathol 143:1389–1397
Shimazui T, Schalken JA, Giroldi LA (1996) Prognostic value of cadherin-associated molecules (α-, β-,and γ-catenins and p120cas) in bladder tumors. Cancer Res 56:4154–4158
Ross JS, Rosario AD, Figge HL (1995) E-cadherin expression in papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Hum Pathol 26:940–944
Popov Z, Medina SGD, Belda MAL (2000) Low E-cadherin expression in bladder cancer at the transcriptional and protein level provides prognostic information. Br J Cancer 83:209–214
Bringuier PP, Umbas R, Schaafsma HE (1993) Decreased E-cadherin immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with bladder tumors. Cancer Res 53:3241–3245
Kinsella AR, Green B, Lepts GC (1993) The role of the cell–cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin in large bowel tumour cell invasion and metastasis. Br J Cancer 67:904–949
Matsuura K, Kawanishi J, Fuji S (1992) Altered expression of E-cadherin in gastric cancer tissues and carcinomatous fluid. Br J Cancer 66:1122–1130
Umbas R, Isaacs WB, Bringuier PP (1994) Decreased E-cadherin expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer Res 54:3929–3933
Rebel JMJ, Thijsenn CDEM, Vermey M (1994) E-cadherin expression determines the mode of replacement of normal urothelium by human bladder carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 54:5488–5492
Nakopoulou L, Zervas A, Gakiopoulou H (2000) Prognostic value of E-cadherin, β-catenin, P120ctn in patients with transitional cell bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 20:4571–4578
Otto T, Bex A, Schmidt U (1997) Improved prognosis assessment for patients with bladder carcinoma. J Pathol 150:1919–1923
Sun W, Herrera GA (2004) E-cadherin expression in invasive urothelial carcinoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 8:17–22
Byrne RR, Shariat SF, Brown R, Kattan MW, Morton RA Jr, Wheeler TM, Lerner SP (2001) E-cadherin immunostaining of bladder transitional cell carcinoma, carcinoma in situ and lymph node metastases with long-term followup. J Urol 165:1473–1479
Smits G, Schaafsma E, Kiemeney L, Caris C, Debruyne F, Witjes JA (1998) Microstaging of pT1 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: identification of subgroups with distinct risks of progression. Urology 52:1009–1014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdemir, F., Ozcan, F., Kılıcaslan, I. et al. The relationship between the expression of E-cadherin and tumor recurrence and progression in high-grade stage T1 bladder urothelial carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 39, 1031–1037 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-006-9159-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-006-9159-5