Abstract
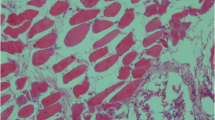
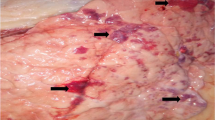
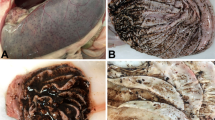
Panting syndrome and respiratory infection have been recorded in complicated cases of foot and mouth disease (FMD) in cattle. However, investigations on the causative agents of respiratory disease in such cases are scarce. In this study, 30 animals (13 buffalo and 17 cattle) suffering from respiratory distress associated with signs of FMD were examined. Serum samples were collected and FMD infection was confirmed. Bacteriological examination of lungs from eight necropitized cases revealed the presence of C. perfringens. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR) was performed on the positive samples followed by sequencing analysis. The alpha toxin gene (plc) of C. perfringens was identified in six cases. The present investigation highlights the role of clostridial infection as a complication of FMD in cattle and buffalo. This is the first report identifying the C. perfringens toxins from lung of animals with respiratory distress associated with FMD infection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandersen, S., Zhang, Z., Donaldson, A., Garland, A., 2003. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. Journal of Comparative Cathology, 129, 1–36.
Beveridge, T.J., 2001. Use of the Gram stain in microbiology. Biotechnic and Histochemistry, 76, 111–118.
Brett, M., 1994. Outbreaks of food-poisoning associated with lecithinase-negative Clostridium perfringens. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 41, 405–407.
Chandranaik, B.M., Hegde, R., Shivashankar, B.P., Giridhar, P., Muniyellappa, H.K., Kalge, R., Sumathi, B.R., Nithinprabhu, K., Chandrashekara, N., Manjunatha, V., 2015. Serotyping of foot and mouth disease virus and Pasteurella multocida from Indian gaurs (Bos gaurus), concurrently infected with foot and mouth disease and haemorrhagic septicaemia. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 47, 933–937.
Chen, C.-H., Ho, S.-Y., Lin, K.-H., 2011. Necrotizing Pneumonia Associated with Septicemia Caused by Clostridium perfringens: A Case Report. Internal Medicine, 22, 287–291.
Chhabra, R., Sharma, R., Kakker, N.K., 2004. Comparative immunogenecity of foot and mouth disease virus antigens in FMD-haemorrhagic septicaemia combined vaccine and FMD vaccine alone in buffalo calves. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 42, 259–264.
Constable, P.D., Hinchcliff, K.W., Done, S.H., Grünberg, W., 2016. Veterinary medicine-e-book: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs and goats. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Craven, C., 1989. Fatal Clostridium perfringens septicemia associated with gastrointestinal arteriovenous malformations (vascular ectasias). Archives of pathology and laboratory Medicine, 113, 534–535.
De Diego, M., Brocchi, E., Mackay, D., De Simone, F., 1997. The non-structural polyprotein 3ABC of foot-and-mouth disease virus as a diagnostic antigen in ELISA to differentiate infected from vaccinated cattle. Archives of Virology, 142, 2021–2033.
Díaz-San Segundo, F., Rodríguez-Calvo, T., de Avila, A., Sevilla, N., 2009. Immunosuppression during acute infection with foot-and-mouth disease virus in swine is mediated by IL-10. PLoS One, 4, e5659.
Fernandez-Miyakawa, M.E., Sayeed, S., Fisher, D.J., Poon, R., Adams, V., Rood, J.I., McClane, B.A., Saputo, J., Uzal, F.A., 2007. Development and application of an oral challenge mouse model for studying Clostridium perfringens type D infection. Infection and Immunity, 75, 4282–4288.
Francoz, D., Buczinski, S., Bélanger, A., Forté, G., Labrecque, O., Tremblay, D., Wellemans, V., Dubuc, J., 2015. Respiratory pathogens in Quebec dairy calves and their relationship with clinical status, lung consolidation, and average daily gain. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 29, 381–387.
Freedman, J.C., Theoret, J.R., Wisniewski, J.A., Uzal, F.A., Rood, J.I., McClane, B.A., 2015. Clostridium perfringens type A-E toxin plasmids. Research in Microbiology, 166, 264–279.
Grubman, M.J., Baxt, B., 2004. Foot-and-mouth disease. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 17, 465–493.
Gurjar, A., Hegde, N., Love, B., Jayarao, B., 2008. Real-time multiplex PCR assay for rapid detection and toxintyping of Clostridium perfringens toxin producing strains in feces of dairy cattle. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 22, 90–95.
Hatheway, C.L., 1990. Toxigenic clostridia. Clinical microbiology reviews 3, 66–98.
Howard, B.G., 2007. Alimentary system. In: Pathologic basis of veterinary medicine. McGavin MD, Zachary JF, (ed.). (4thedn), Mosby Elsevier, USA 30.
Karasawa, T., Wang, X., Maegawa, T., Michiwa, Y., Kita, H., Miwa, K., Nakamura, S., 2003. Clostridium sordellii phospholipase C: gene cloning and comparison of enzymatic and biological activities with those of Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium bifermentans phospholipase C. Infection and Immunity, 71, 641–646.
Katayama, S., Matsushita, O., Minami, J., Mizobuchi, S., Okabe, A., 1993. Comparison of the alpha-toxin genes of Clostridium perfringens type A and C strains: evidence for extragenic regulation of transcription. Infection and Immunity 61, 457–463.
Knowles, N.J., Wadsworth, J., Reid, S.M., Swabey, K.G., El-Kholy, A.A., El-Rahman, A.O.A., Soliman, H.M., Ebert, K., Ferris, N.P., Hutchings, G.H., 2007. Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype A in Egypt. Emerging Infectious Diseases 13, 1593.
Koneman, E., Allen, S., Janda, W., Schreckenberger, P., Winn, W., 1992. Diagnostic Microbiology, 4. baski. J В Lippincott Co, Philadelphia, USA.
Lee, H.-S., Lee, N.-H., Seo, M.-G., Ko, Y.-J., Kim, B., Lee, J.-B., Kim, J.-S., Park, S., Shin, Y.-K., 2013. Serological responses after vaccination of growing pigs with foot-and-mouth disease trivalent (type O, A and Asia1) vaccine. Veterinary Microbiology, 164, 239–245.
Lorenz, T.C., 2012. Polymerase chain reaction: basic protocol plus troubleshooting and optimization strategies. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 22, e3998.
Lyons, N.A., Alexander, N., Strk, K.D., Dulu, T.D., Rushton, J., Fine, P.E., 2015. Impact of foot-and-mouth disease on mastitis and culling on a large-scale dairy farm in Kenya. Veterinary Research, 46, 015–0173.
Moustafa, A.M., Ali, S.N., Bennett, M.D., Hyndman, T.H., Robertson, I.D., Edwards, J., 2017. A Case-control Study of Haemorrhagic Septicaemia in Buffaloes and Cattle in Karachi, Pakistan, in 2012. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 64, 520–527.
Nakamura, s., Kimura, i., Kamakawa, k., Nishida, S., 1983. Taxonomic relationships among Clostridium novyi types A and B, Clostridium haemolyticum and Clostridium botulinum type C. Microbiology, 129, 1473–1479.
Palmacci, C., Antocicco, M., Bonomo, L., Maggi, F., Cocchi, A., Onder, G., 2009. Necrotizing pneumonia and sepsis due to Clostridium perfringens: a case report. Cases Journal, 2, 50.
Rweyemamu, M., Roeder, P., Mackay, D., Sumption, K., Brownlie, J., Leforban, Y., Valarcher, J.F., Knowles, N., Saraiva, V., 2008. Epidemiological patterns of foot-and-mouth disease worldwide. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 55, 57–72.
Sasani, F., Marzban, H., Javanbakht, J., Moosakhani, F., Imanparast, M., 2013. The Relationship between Microscopic Lesions and Different Types of Clostridium perfringens and their Related Toxins by Sandwich ELISA in Cattle. Journal of Microbial and Biochemical Technology, 5, 034–038.
Sievers, F., Higgins, D.G. 2014. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences, In: Multiple Sequence Alignment Methods,. Springer, 105–116.
Siqueira, F.F., Almeida, M.O., Barroca, T.M., Horta, C.C., Carmo, A.O., Silva, R.O., Pires, P.S., Lobato, F.C., Kalapothakis, E., 2012. Characterization of polymorphisms and isoforms of the Clostridium perfringens phospholipase C gene (plc) reveals high genetic diversity. Veterinary Microbiology, 159, 397–405.
Sutmoller, P., Barteling, S.S., Olascoaga, R.C., Sumption, K.J., 2003. Control and eradication of foot-and-mouth disease. VirusResearch, 91, 101–144.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., Kumar, S., 2013. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Tanabe, K., Jones, W., Barie, P., 1989. Clostridial sepsis and malignant disease. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics, 169, 423–428.
Tsutsui, K., Minami, J., Matsushita, O., Katayama, S., Taniguchi, Y., Nakamura, S., Nishioka, M., Okabe, A., 1995. Phylogenetic analysis of phospholipase C genes from Clostridium perfringens types A to E and Clostridium novyi. Journal of Bacteriology, 177, 7164–7170.
Uzal, F., Kelly, W., Morris, W., Assis, R., 2002. Effects of intravenous injection of Clostridium perfringens type D epsilon toxin in calves. Journal of Comparative pathology, 126, 71–75.
Venkataramanan, R., Bandyopadhyay, S., Oberoi, M., 2005. Present status and strategies for the control of transboundary and other economically important animal diseases in India: a review. The Indian Journal of Animal Sciences, 75.
Verma, S.C., Mahajan, N.K., Malik, G., Dahiya, J.P., 2004. An Epidemiological Study On Bovine Haemorrhagic Septicaemia In Haryana. Indian Journal of Animal Research, 38, 14–19.
Yoo, H.S., Lee, S.U., Park, K.Y., Park, Y.H., 1997. Molecular typing and epidemiological survey of prevalence of Clostridium perfringens types by multiplex PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 35, 228–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical disclosure
Farm owners approved and signed the informed consent forms for the study. All animal procedures implemented in this study complied with institutional guidlines obtained from ethics committee in Mansoura University, Egypt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgioushy, M., Rizk, M.A., El-Adl, M. et al. The first molecular detection of Clostridium perfringens from pneumonic cases associated with foot and mouth disease in cattle and buffalo in Egypt. Trop Anim Health Prod 51, 847–852 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-1763-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-1763-8