Abstract
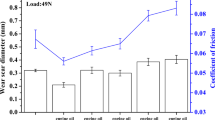
The neutralization reaction mechanism of acetic acid by fully formulated lubricant oil is discussed in this paper. The video analysis of acetic-acid droplets in oil phase indicates that neutralization exists simultaneously on the oil–acid interface and bulk oil phase during the droplet shrinkage. This behavior is different from the one exhibited by sulfuric acid, which is insoluble in base oil and its neutralization by overbased lubricant occurs exclusively at the oil–acid interface. Besides, FTIR and NMR analyses show the neutralization of acetic acid as an instantaneous process, and almost all of the dissolved acetic acids in the bulk are eventually neutralized. Therefore, a two-mode-mechanism, including both interfacial and bulk reaction, is proposed for the neutralization of acetic acid by overbased nanoparticles. At the end, tribological behavior of sulfuric acid and acetic-acid neutralization products is discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galsworthy, J., Hammond, S., Hone, D.: Oil-soluble colloidal additives. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface 5(5), 274–279 (2000)
Mitsutake, S., Ono, S., Maekawa, K., Takahashi, F., Deguchi, A.: Lubrication of cylinder liners and piston rings of low-speed marine diesel engines. Mitsubishi Tech. Rev. 24(2), 87–93 (1987)
Wilbur, C.T., Wight, D.: Pounder’s Marine Diesel Engines and Gas Turbines. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2013)
Hone, D.C., Robinson, B.H., Steytler, D.C., Glyde, R.W., Galsworthy, J.R.: Mechanism of acid neutralization by overbased colloidal additives in hydrocarbon media. Langmuir 16(2), 340–346 (2000)
Hudson, L., Eastoe, J., Dowding, P.: Nanotechnology in action: Overbased nanodetergents as lubricant oil additives. Adv. Colloid Interface 123, 425–431 (2006)
Wu, R.C., Papadopoulos, K.D., Campbell, C.B.: Visualization test for neutralization of acids by marine cylinder lubricants. AIChE J. 45(9), 2011–2017 (1999)
Fu, J., Papadopoulos, K.D., Lu, Y., Campbell, C.B.: Ostwald ripening: a decisive cause of cylinder corrosive wear. Tribol. Lett. 27(1), 21–24 (2007)
Akiyama, K., Masunaga, K., Kado, K., Yoshioka, T.: Cylinder wear mechanism in an EGR-equipped diesel engine and wear protection by the engine oil. SAE Technical Paper 872158 (1987)
Sudarshan, T., Bhaduri, S.: Wear in cylinder liners. Wear 91(3), 269–279 (1983)
Jones, B., Mead, G., Steevens, P.: The effects of E20 on plastic automotive fuel system components. Minnesota Center Automotive Research Minnesota at State University, 11 (2008)
Hanson, N., Devens, T., Rohde, C., Larson, A., Mead, G., Steevens, P., Jones, B.: The effects of E20 on automotive fuel pumps and sending units. Minnesota Center Automotive Research Minnesota at State University, 12 (2008)
Renewable Fuels Association.: Accelerating idustry innovation: 2012 e Industry outlook. Renewable Fuels Association, Washington, DC (2012)
Kawamura, K., Kaplan, I.R.: Motor exhaust emissions as a primary source for dicarboxylic acids in Los Angeles ambient air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21(1), 105–110 (1987)
Souza, S.R., Vasconcellos, P.C., Carvalho, L.R.: Low molecular weight carboxylic acids in an urban atmosphere: winter measurements in Sao Paulo City Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 33(16), 2563–2574 (1999)
Chebbi, A., Carlier, P.: Carboxylic acids in the troposphere, occurrence, sources, and sinks: a review. Atmos. Environ. 30(24), 4233–4249 (1996)
Agarwal, A.K.: Biofuels (alcohols and biodiesel) applications as fuels for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energ. Combust. 33(3), 233–271 (2007)
Corradi, M., Bomparola, R.: A lubricating oil composition comprising a corrosion inhibitor. Patent No. EP 2692839 A1 (2014)
Intermediate-level ethanol blends engine durability study. Coordinating Research Council (2012)
Mansot, J., Hallouis, M., Martin, J.: Colloidal antiwear additives 1. structural study of overbased calcium alkylbenzene sulfonate micelles. Colloid Surf. A 71(2), 123–134 (1993)
Fu, J., Lu, Y., Campbell, C.B., Papadopoulos, K.D.: Acid neutralization by marine cylinder lubricants inside a heating capillary: strong/weak-stick collision mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45(16), 5619–5627 (2006)
Costello, M., Riff, I.: Study of hydroforming lubricants with overbased sulfonates and friction modifiers. Tribol. Lett. 20(3–4), 201–208 (2005)
Griffiths, J., Heyes, D.: Atomistic simulation of overbased detergent inverse micelles. Langmuir 12(10), 2418–2424 (1996)
Cunningham, I.D., Courtois, J.-P., Danks, T.N., Heyes, D.M., Moreton, D.J., Taylor, S.E.: Synthesis and characterisation of calixarene-stabilised calcium carbonate overbased detergents. Colloid Surf. A 229(1), 137–147 (2003)
Bearchell, C., Heyes, D.M., Moreton, D., Taylor, S.: Overbased detergent particles: experimental and molecular modelling studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3(21), 4774–4783 (2001)
Adams, C.J., Dowding, P.J.: Overbased metal sulphonate detergent. Patent No. US 8,105,991 B2 (2012)
Brown, J.R., Adams, P.E., Carrick, V.A., Dohner, B.R., Abraham, W.D., Vilardo, J.S., Lange, R.M., Mosier, P.E.: Titanium compounds and complexes as additives in lubricants. Patent No. US 8,268,759 B2 (2012)
Wu, R.C., Campbell, C.B., Papadopoulos, K.D.: Acid-neutralizing of marine cylinder lubricants: effects of nonionic surfactants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39(10), 3926–3931 (2000)
Duan, Y., Rausa, R., Fiaschi, P., Papadopoulos, K.D.: Neutralization of acetic acid by automobile motor oil. Tribol. Int. 98, 94–99 (2016)
Griffiths, P.R., De Haseth, J.A.: Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, vol. 171. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Silverstein, R.M., Webster, F.X., Kiemle, D.J., Bryce, D.L.: Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds. Wiley, (2014)
Erhan, S.Z., Asadauskas, S.: Lubricant basestocks from vegetable oils. Ind. Crop. Prod 11(2–3), 277–282 (2000)
Papay, A.G., Zaweski, E.F.: Lubricating oil composition. Patent No. US 4,178,258 A (1979)
Mortier, R.M., Orszulik, S.T., Fox, M.F.: Chemistry and Technology of Lubricants. Springer, London (1992)
Duncan, P.B., Needham, D.: Microdroplet dissolution into a second-phase solvent using a micropipet technique: test of the Epstein–Plesset model for an aniline-water system. Langmuir 22(9), 4190–4197 (2006)
Duncan, P.B., Needham, D.: Test of the Epstein–Plesset model for gas microparticle dissolution in aqueous media: effect of surface tension and gas undersaturation in solution. Langmuir 20(7), 2567–2578 (2004)
Zhu, P., Harris, T.V., Driver, M.S., Campbell, C.B., Pratt, L.R., Papadopoulos, K.D.: Dissolution Kinetics of [Hmim][BF4] Ionic Liquid Droplets in 1-pentanol. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(37), 16458–16463 (2009)
Garcia-Bermudes, M., Rausa, R., Papadopoulos, K.: Formation of colloidal shells on acidic droplets undergoing neutralization in marine diesel engine cylinder oils. Tribol. Lett. 51(1), 85–92 (2013)
Lide, D.R.: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Buhaug, Ø.: Deposit formation on cylinder liner surface in medium-speed engines. Dissertation, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (2003)
Buhaug, Ø., Almås, T.: Characterisation of diesel engine cylinder liner deposits by surface measurements. Tribotest 10(3), 207–223 (2004)
Sautermeister, F.A., Priest, M.: Physical and chemical impact of sulphuric acid on cylinder lubrication for large 2-stroke marine diesel engines. Tribol. Lett. 47(2), 261–271 (2012)
Sautermeister, F., Priest, M., Lee, P., Fox, M.: Impact of sulphuric acid on cylinder lubrication for large 2-stroke marine diesel engines: contact angle, interfacial tension and chemical interaction. Tribol. Int. 59, 47–56 (2013)
Hsu, C.-P.S.: Infrared spectroscopy. In: Handbook of Instrumental Techniques for Analytical Chemistry, p. 248 (1997)
Musumeci, A.W., Frost, R.L., Waclawik, E.R.: A spectroscopic study of the mineral paceite (calcium acetate). Spectrochim. Acta A 67(3), 649–661 (2007)
Papke, B.L.: Neutralization of basic oil-soluble calcium sulfonates by carboxylic acids. Tribol T 31(4), 420–426 (1988)
Jerome, P.: Stabilized suspensions of calcium acetate in oil. Patent No. US 2,989,464 A (1961)
Tobias, D.J., Klein, M.L.: Molecular dynamics simulations of a calcium carbonate/calcium sulfonate reverse micelle. J. Phys. Chem.-US 100(16), 6637–6648 (1996)
Mansot, J., Hallouis, M., Martin, J.: Colloidal antiwear additives 2. Tribological behaviour of colloidal additives in mild wear regime. Colloid Surf. A 75, 25–31 (1993)
Najman, M., Kasrai, M., Bancroft, G.M., Davidson, R.: Combination of ashless antiwear additives with metallic detergents: interactions with neutral and overbased calcium sulfonates. Tribol. Int. 39(4), 342–355 (2006)
Stott, F., Macdonald, A.: The influence of acid strength on the corrosive wear of grey cast irons in oil-sulphuric acid mixtures. Wear 122(3), 343–361 (1988)
Erdemir, A.: Review of engineered tribological interfaces for improved boundary lubrication. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 249–256 (2005)
Priest, M., Taylor, C.: Automobile engine tribology-approaching the surface. Wear 241(2), 193–203 (2000)
Wu, R.C., Papadopoulos, K.D., Campbell, C.B.: Acid-neutralizing of marine cylinder lubricants: measurements and effects of dispersants. AIChE J. 46(7), 1471–1477 (2000)
Detweiler, W.K.: Calcium mixed-salt lubricant stabilized. Patent No. US 3,125,521 A (1964)
Morway, A.J.: Oil dispersions of calcium acetate hydrates. Patent No. US 2,927,892 A (1960)
James, N.: Calcium acetate lubricant. Patent No. US 3,310,490 A (1967)
Coant, P.M., De, M.F.G.A.: Lubricant and additives therefor. Patent No. US 3,259,577 A (1966)
Jesse, M.A., John, B.A.: Finely divided calcium acetate particles and lubricating compositions thereof. Patent No. US 3,231,495 A (1966)
Davis, R.H.: Lubricating oil compositions containing calcium acetate and lubricating solids. Patent No. US 3,194,760 A (1965)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Marco Lattuada, of Eni S.p.A., for the preparation of the fully formulated oil sample and for the helpful discussions. Support from Eni S.p.A. and Tulane’s Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering made this work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (AVI 5232 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (AVI 7726 kb)
Supplementary material 4 (AVI 10428 kb)
Supplementary material 5 (AVI 19002 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Y., Rausa, R., Zhao, Q. et al. Neutralization Mechanism of Acetic Acid by Overbased Colloidal Nanoparticles. Tribol Lett 64, 8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0742-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0742-3