Abstract
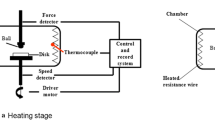
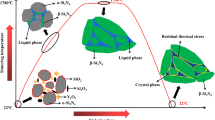
The tribological behavior of self-mated Ti3SiC2 is investigated from ambient temperature to 800 °C at a sliding speed of 0.01 m/s in air. The results show that at the temperatures lower than 300 °C, friction coefficient and wear rates are as high as 0.95 and 10−3 mm3/N m, respectively. With the temperature increasing to 600 °C, both the friction coefficient and wear rates show consecutive decrease. At 700 and 800 °C, friction coefficient and wear rates are 0.5 and 10−6 mm3/N m, respectively. According to the wear mechanism, the tribological behavior of Ti3SiC2 can be divided into three regimes: mechanical wear-dominated regime from ambient temperature to 300 °C characterized by pullout of grains; mixed wear regime (mechanical wear and oxidation wear) from 400 to 600 °C; and tribo-oxidation-dominated wear regime above 700 °C. The tribo-oxides on the worn surfaces involve oxides of Si and Ti. And, species transformation occurs to these two oxides with the increasing temperature. In the competition oxidation of elements Ti and Si, Si is preferably oxidized because of its high active position in the crystal structure. Additionally, plastic flow is another notable characteristic for the tribological behavior of self-mated Ti3SiC2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsoum, M.W.: The M n+1AX n phases: a new class of solids; thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid St. Chem. 28, 201–281 (2000)
Barsoum, M.W., El-Raghy, T.: Synthesis and characterization of a remarkable ceramic: Ti3SiC2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1953–1956 (1996)
Crossley, A., Kisi, E.H., Summers, J.W., Myhra, S.: Ultra-low friction for a layered carbide-derived ceramic, Ti3SiC2, investigated by lateral force microscopy (LFM). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 32, 632–638 (1999)
Sun, Z., Zhou, Y., Li, S.: Tribological behavior Ti3SiC2-based material. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 18, 142 (2002)
Zhai, H., Huang, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Ai, M.: Oxidation layer in sliding friction surface of high-purity Ti3SiC2. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 6635–6637 (2004)
Souchet, A., Fontaine, J., Belin, M., Mogne, T.L., Loubet, J.-L., Barsoum, M.W.: Tribological duality of Ti3SiC2. Tribol. Lett. 18 (2005)
Sarkar, D., Kumar, B.V., Basu, B.: Understanding the fretting wear of Ti3SiC2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2441–2452 (2006)
Hibi, Y., Miyake, K., Murakami, T., Sasaki, S.: Tribological behavior of SiC-reinforced Ti3SiC2-based composites under dry condition and under lubricated condition with water and ethanol. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 2983–2985 (2006)
Huang, Z., Zhai, H., Guan, M., Liu, X., Ai, M., Zhou, Y.: Oxide-film-dependent tribological behaviors of Ti3SiC2. Wear 262, 1079–1085 (2007)
Gupta, S., Barsoum, M.W.: On the tribology of the MAX phases and their composites during dry sliding: a review. Wear 271, 1878–1894 (2011)
Ren, S., Meng, J., Lu, J., Yang, S.: Tribological behavior of Ti3SiC2 sliding against Ni-based alloys. Tribol. Lett. 31, 129–137 (2008)
Peterson M. B.: Design considerations for effective wear control. In: Peterson, M.B., Winer, W.O. (eds.) Wear Controll Handbook, p. 451. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York (1980)
Gupta, S., Filimonov, D., Zaitsev, V., Palanisamy, T., Barsouma, M.W.: Ambient and 550 °C tribological behavior of select MAX phases against Ni-based superalloys. Wear 264, 270–278 (2008)
Gupta, S., Filimonov, D., Palanisamy, T., Barsoum, M.W.: Tribological behavior of select MAX phases against Al2O3 at elevated temperatures. Wear 265, 560–565 (2008)
Woydt, M., Skopp, A., Hantsche, H.: Ceramic wear track characterisation by advanced X-ray diffraction. The Rigaku Journal 9, 9–16 (1992)
Skopp, A., Woydt, M.: Ceramic and ceramic composite materials with improved friction and wear properties. Tribol. Trans. 38(2), 233–242 (1995)
Zhou, Y., Sun, Z.: Electronic structure and bonding properties in layered ternary carbide Ti3SiC2. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 457–462 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51075382) and the Hundred Talent Program (Junhu Meng) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hai, W., Ren, S., Meng, J. et al. Tribo-oxidation of Self-mated Ti3SiC2 at Elevated Temperatures and Low Speed. Tribol Lett 48, 425–432 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-0036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-0036-3