Abstract
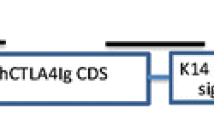
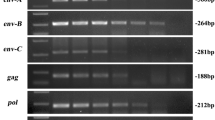
Pigs seem to be the answer to worldwide organ donor shortage. Porcine skin may also be applied as a dressing for severe burns. Genetic modifications of donor animals enable reduction of immune response, which prolongs xenograft survival as temporary biological dressing and allows achieving resistance against xenograft rejection. The risk posed by porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) cannot be eliminated by breeding animals under specific-pathogen-free conditions and so all recipients of porcine graft will be exposed to PERVs. Therefore our study has been focused on the assessment of PERV DNA and mRNA level in skin samples of transgenic pigs generated for xenotransplantation. Porcine skin fragments were obtained from 3- to 6-month-old non-transgenic and transgenic Polish Landrace pigs. Transgenic pigs were produced by pronuclear DNA microinjection and were developed to express the human α-galactosidase and the human α-1,2-fucosyltransferase gene. The copy numbers of PERV DNA and RNA were evaluated using real-time Q-PCR and QRT-PCR. Comparative analysis of all PERV subtypes revealed that PERV-A is the main subtype of PERVs in analyzed skin samples. There was no significantly different copy number of PERV-A, PERV-B and PERV-C between non-transgenic pigs, pigs with the human α-galactosidase and pigs expressing the human α-1,2-fucosyltransferase gene, except of PERV-C DNA. It brings the conclusion, that transgenesis process exerts no influence on PERVs transinfection. That is another step forward in the development of pig skin xenografts as burn wounds dressing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albritton A, Leonard DA, Barone AL, Keegan J, Mallard C, Sachs DH, Kurtz JM, Cetrulo CL Jr (2014) Lack of cross-sensitization between α-1,3-galactosyltransferase knockout porcine and allogeneic skin grafts permits serial grafting. Transplantation 97:1209–1215
Bae EH, Jung YT (2014a) A comparison of the effects of retroviral restriction factors involved in resistance to porcine endogenous retrovirus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(4):577–583
Bae EH, Jung YT (2014b) Tetherins of various species inhibit the release of porcine endogenous retrovirus from human cells. Acta Virol 58(1):53–60
Bernhardt AM, Reichenspurner H (2014) High-risk donors: extending our criteria in times of organ shortage. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 19(5):494–499
Bittmann I, Mihica D, Plesker R, Denner J (2012) Expression of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV) in different organs of a pig. Virology 433(2):329–336
Bösch S, Arnauld C, Jestin A (2000) Study of full-length porcine endogenous retrovirus genomes with envelope gene polymorphism in a specific-pathogen-free Large White swine herd. J Virol 74:8575–8581
Chiarini A, Dal Pra I, Armato U (2007) In vitro and in vivo characteristics of frozen/thawed neonatal pig split-skin strips: a novel biologically active dressing for areas of severe, acute or chronic skin loss. Int J Mol Med 19(2):245–255
Cyganek-Niemiec A, Strzalka-Mrozik B, Pawlus-Lachecka L, Wszolek J, Adamska J, Kudrjavtseva J, Zhuravleva I, Kimsa M, Okla H, Kimsa M, Gudek A, Mazurek U (2012) Degradation effect of diepoxide fixation on porcine endogenous retrovirus DNA in heart valves: molecular aspects. Int J Artif Organs 35(1):25–33
Denner J (2008) Recombinant porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV-A/C): a new risk for xenotransplantation? Arch Virol 153:1421–1426
Denner J, Tönjes RR (2012) Infection barriers to successful xenotransplantation focusing on porcine endogenous retroviruses. Clin Microbiol Rev 25:318–343
Denner J, Schuurman HJ, Patience C (2009) The International Xenotransplantation Association consensus statement on conditions for undertaking clinical trials of porcine islet products in type 1 diabetes—chapter 5: strategies to prevent transmission of porcine endogenous retroviruses. Xenotransplantation 16(4):239–248
Di Nicuolo G, D’Alessandro A, Andria B, Scuderi V, Scognamiglio M, Tammaro A, Chamuleau RA (2010) Long-term absence of porcine endogenous retrovirus infection in chronically immunosuppressed patients after treatment with the porcine cell–based Academic Medical Center bioartificial liver. Xenotransplantation 17(6):431–439
Dieckhoff B, Petersen B, Kues WA, Kurth R, Niemann H, Denner J (2008) Knockdown of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) expression by PERV-specific shRNA in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 15(1):36–45
Dieckhoff B, Kessler B, Jobst D, Kues W, Petersen B, Pfeifer A, Kurth R, Niemann H, Wolf E, Denner J (2009) Distribution and expression of porcine endogenous retroviruses in multi-transgenic pigs generated for xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 16(2):64–73
Fang J, Walters A, Hara H, Long C, Yeh P, Ayares D, Cooper DK, Bianchi J (2012) Anti-gal antibodies in α1,3-galactosyltransferase gene-knockout pigs. Xenotransplantation 19:305–310
Garkavenko O, Dieckhoff B, Wynyard S, Denner J, Elliott RB, Tan PL, Croxson MC (2008) Absence of transmission of potentially xenotic viruses in a prospective pig to primate islet xenotransplantation study. J Med Virol 80(11):2046–2052
Harrison I, Takeuchi Y, Bartosch B, Stoye JP (2004) Determinants of high titer in recombinant porcine endogenous retroviruses. J Virol 78(24):13871–13879
Hofmann-Lehmann R, Cattori V, Tandon R, Boretti FS, Meli ML, Riond B, Pepin AC, Willi B, Ossent P, Lutz H (2007) Vaccination against the feline leukaemia virus: outcome and response categories and long-term follow-up. Vaccine 25(30):5531–5539
Hwang S, Jung YD, Cho K, Ock SA, Oh KB, Kim HS, Yun IJ, Ahn C, Park JK, Im S (2014) No expression of porcine endogenous retrovirus after pig to monkey xenotransplantation. Lab Anim Res 30(2):90–93
Kaulitz D, Fiebig U, Eschricht M, Wurzbacher C, Kurth R, Denner J (2011) Generation of neutralizing antibodies against porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs). Virology 411(1):78–86
Kimsa M, Strzalka-Mrozik B, Kimsa M, Adamska J, Gola J, Lopata K, Mazurek U (2012) Quantitative estimation of porcine endogenous retrovirus release from PK15 cells. Pol J Microbiol 61:211–215
Li ZG, Liu GB, Pan MX, Wu QS, Ge M, Du J, Wang Y, Gao Y (2013) Knockdown of porcine endogenous retroviruses by RNA interference in Chinese experimental miniature pig fibroblasts. Transplant Proc 45(2):748–755
Lipinski D, Jura J, Zeyland J, Juzwa W, Maly E, Kalak R, Bochenek M, Plawski A, Szalata M, Smorag Z, Slomski R (2010) Production of transgenic pigs expressing human α1,2-fucosyltransferase to avoid humoral xenograft rejection. Med Weter 66:316–322
Lipinski D, Zeyland J, Plawski A, Slomski R (2012) Determination of the absolute number of transgene copies in CMVFUT transgenic pigs. Ann Anim Sci 12:349–356
Machnik G, Sypniewski D, Gałka S, Loch T, Sołtysik D, Błaszczyk D, Bednarek I (2010) Changes of syncytin I expression level in HEK293 cells line after infection buy porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV) (in Polish). Farmaceutyczny Przegląd Naukowy 12:14–20
Mazurek U, Kimsa MC, Strzalka-Mrozik B, Kimsa MW, Adamska J, Lipinski D, Zeyland J, Szalata M, Slomski R, Jura J, Smorag Z, Nowak R, Gola J (2013) Quantitative analysis of porcine endogenous retroviruses in different organs of transgenic pigs generated for xenotransplantation. Curr Microbiol 67(4):505–514
Meije Y, Tönjes RR, Fishman JA (2010) Retroviral restriction factors and infectious risk in xenotransplantation. Am J Transplant 10(7):1511–1516
Niemann H (2001) Current status and perspectives for the generation of transgenic pigs for xenotransplantation. Ann Transpl 6:6–9
Oldmixon BA, Wood JC, Ericsson TA, Wilson CA, White-Scharf ME, Andersson G, Greenstein JL, Schuurman HJ, Patience C (2002) Porcine endogenous retrovirus transmission characteristics of an inbred herd of miniature swine. J Virol 76(6):3045–3048
Patience C, Takeuchi Y, Weiss RA (1997) Infection of human cells by an endogenous retrovirus of pigs. Nat Med 3(3):282–286
Ramsoondar J, Vaught T, Ball S, Mendicino M, Monahan J, Jobst P, Vance A, Duncan J, Wells K, Ayares D (2009) Production of transgenic pigs that express porcine endogenous retrovirus small interfering RNAs. Xenotransplantation 16(3):164–180
Scobie L, Padler-Karavani V, Le Bas-Bernardet S, Crossan C, Blaha J, Matouskova M, Soulillou JP (2013) Long-term IgG response to porcine Neu5Gc antigens without transmission of PERV in burn patients treated with porcine skin xenografts. J Immunol 191(6):2907–2915
Semaan M, Kaulitz D, Petersen B, Niemann H, Denner J (2012) Long-term effects of PERV-specific RNA interference in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 19(2):112–121
Sheridan RL, Tompkins RG (1999) Skin substitutes in burns. Burns J Int Soc Burn Inj 25(2):97–103
Shevchenko RV, James SL, James SE (2010) A review of tissue-engineered skin bioconstructs available for skin reconstruction. J R Soc Interface 7(43):229–258
Strzalka-Mrozik B, Stanik-Walentek A, Kapral M, Kowalczyk M, Adamska J, Gola J, Mazurek U (2010) Differential expression of transforming growth factor-β isoforms in bullous keratopathy corneas. Mol Vis 16:161–166
Sypniewski D, Machnik G, Mazurek U, Wilczok T, Smorąg Z, Jura J, Gajda B (2005) Distribution of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) DNA in organs of a domestic pigs. Ann Transpl 10(2):46–51
Takeuchi Y, Patience C, Magre S, Weiss RA, Banerjee PT, Le Tissier P, Stoye JP (1998) Host range and interference studies of three classes of pig endogenous retrovirus. J Virol 72:9986–9991
Torres AN, O’Halloran KP, Larson LJ, Schultz RD, Hoover EA (2010) Feline leukemia virus immunity induced by whole inactivated virus vaccination. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 134(1–2):122–131
Valdes-Gonzalez R, Dorantes LM, Bracho-Blanchet E, Rodríguez-Ventura A (2010) No evidence of porcine endogenous retrovirus in patients with type 1 diabetes after long-term porcine islet xenotransplantation. J Med Virol 82(2):331–334
van der Laan LJ, Lockey C, Griffeth BC, Frasier FS, Wilson CA, Onions DE (2000) Infection by porcine endogenous retrovirus after islet xenotransplantation in SCID mice. Nature 407(6800):90–94
Waechter A, Denner J (2014) Novel neutralising antibodies targeting the N-terminal helical region of the transmembrane envelope protein p15E of the porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV). Immunol Res 58(1):9–19
Wieczorek J, Słomski R, Kowalski W, Smorąg Z (2011) Effect of genetic modification on the health status of transgenic pigs produced with the human α-1,2-fucosyltransferase gene. Med Weter 67:462–466
Yang YG, Wood JC, Lan P, Wilkinson RA, Sykes M, Fishman JA, Patience C (2004) Mouse retrovirus mediates porcine endogenous retrovirus transmission into human cells in long-term human-porcine chimeric mice. J Clin Invest 114(5):695–700
Zeyland J, Woźniak A, Gawrońska B, Juzwa W, Jura J, Nowak A, Słomski R, Smorąg Z, Szalata M, Mazurek U, Lipiński D (2014) Double transgenic pigs with combined expression of human α1,2-fucosyltransferase and α-galactosidase designed to avoid hyperacute xenograft rejection. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 62(5):411–422
Zhang P, Yu P, Wang W, Zhang L, Li S, Bu H (2010) An effective method for the quantitative detection of porcine endogenous retrovirus in pig tissues. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 46(5):408410
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the project: Development of an innovative technology using transgenic porcine tissues for biomedical purposes. Acronym MEDPIG. Program INNOMED (No. INNOMED 1/20106/07/2013/6), which was financed by the National Centre for Research and Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimsa-Dudek, M., Strzalka-Mrozik, B., Kimsa, M.W. et al. Screening pigs for xenotransplantation: expression of porcine endogenous retroviruses in transgenic pig skin. Transgenic Res 24, 529–536 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9871-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9871-y