Abstract
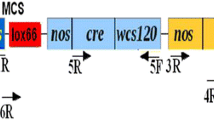
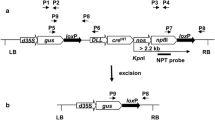
Based on the Cre/loxP system, we have developed a novel marker-free system mediating a direct auto-excision of loxP-flanked marker genes from T1 transgenic rice without any treatment or further offspring crossing. To achieve this, the floral-specific promoter OsMADS45 was isolated from rice and the expression patterns of OsMADS45 promoter was characterised by using the pOs45:GUS transgenic plants. Furthermore, the binary vector with Cre recombinase under the control of OsMADS45 promoter was constructed and introduced into rice by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and transgenic rice plants were generated. Southern blot analysis showed that auto-excision of the selective markers occurred in some T1 progeny of the transgenic plants, suggesting that a high auto-excision frequency can be achieved with our Cre/loxP system. This auto-excision strategy provides an efficient way of removing the selectable marker gene from transgenic rice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar M, Leshem B, Gilboa N, Gidoni D (1996) Visual characterization of recombination at FRT-gusA loci in transgenic tobacco mediated by constitutive expression of the native FLP recombinase. Theor Appl Genet 93:407–413
Bayley CC, Morgan M, Dale EC, Ow DW (1992) Exchange of gene activity in transgenic plants catalyzed by the Cre-lox site-specific recombination system. Plant Mol Biol 18:353–361
Coppoolse ER, de Vroomen MJ, Roelofs D et al (2003) Cre recombinase expression can result in phenotypic aberrations in plants. Plant Mol Biol 51:263–279
Cotsatifs O, Sallaud C, Breitler JC et al (2002) Transposon-mediated generation of T-DNA and marker-free rice plants expressing a Bt endotoxin gene. Mol Breed 10:165–180
Dale EC, Ow DW (1991) Gene transfer with subsequent removal of the selection gene from the host genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10558–10562
Daley M, Knauf VC, Summerfelt KR, Turner JC (1998) Co-transformation with one Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain containing two binary plasmids as a method for producing marker-free transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 17:489–496
De Block M, Debrouwer D (1991) Two T-DNAs co-transformed into Brassica napus by a double Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection are mainly integrated at the same locus. Theor Appl Genet 82:257–263
De Neve M, De Buck S, Jacobs A, Van Montagu M, Depicker A (1997) T-DNA integration patterns in co-transformed plant cells suggest that T-DNA repeats originate from co-integration of separate T-DNAs. Plant J 11:15–29
Depicker A, Herman L, Jacobs A, Schell J, van Montagu M. (1985) Frequencies of simultaneous transformation with different T-DNAs and their relevance to the Agrobacterium/plant cell interaction. Mol Gen Genet 201:477–484
Ebinuma H, Sugita K, Matsunaga E, Yamakado M (1997) Selection of marker-free transgenic plants using the isopentenyl transferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2117–2121
Ebinuma H, Sugita K, Matsunaga E, Endo K, Yamada S, Komamin A (2001) Systems for the removal of a selection marker and their combination with a positive marker. Plant Cell Rep 20:383–392
Goldsbrough PA, Lastrella CN, Yoder JI (1993) Transposition mediated re-positioning and subsequent elimination of marker genes from transgenic tomato. Biotechnology 11:1286–1292
Greco R, Stagi L, Colombo L, Angenent GC, Sari-Gorla M, Pe ME (1997) MADS box genes expressed in developing inflorescences of rice and sorghum. Mol Gen Genet 253:615–623
Hoa TTC, Bong BB, Huq E, Hodges TK (2002) Cre/lox site-specific recombination controls the excision of a transgene from the rice genome. Theor Appl Genet 104:518–525
Hoff T, Schnorr KM, Mundy J (2001) A recombinase-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 45:41–49
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Komari T, Hiei Y, Saito Y, Murai N, Kumashiro T (1996) Vectors carrying two separate T-DNAs for co-transformation of higher plants mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and segregation of transformants free from selection markers. Plant J 10:165–174
Kopertekh L, Jüttner G, Schiemann J (2005) PVX-Cre-mediated marker gene elimination from transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 55:491–500
Liu XQ, Bai XQ, Wang XJ, Chu CC (2007) OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response. J Plant Physiol 164(8):969–979
Lu HJ, Zhou XR, Gong ZX, Upadhyaya NM (2001) Generation of selectable marker-free transgenic rice using double right border (DRB) binary vectors. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:241–248
Luo A, Qian Q, Ying H, Liu X, Yin C, Lan Y, Tang J, Tang Z, Cao S, Wang X, Xia K, Fu X, Luo D, Chu C (2006) EUI1, encoding a putative cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, regulates the internodes elongation by modulating GA responses in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47(2):181–191
Luo K, Duan H, Zhao D, Zheng X, Deng W, Chen Y, Stewart CN Jr, McAvoy R, Jiang X, Wu Y, He A, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) ‘GM-gene-deleter’: fused loxP-FRT recognition sequences dramatically improve the efficiency of FLP or CRE recombinase on transgene excision from pollen and seed of tobacco plants. Plant Biotechnol J 5:263–274
McKnight TD, Lillis MT, Simpson RB (1987) Segregation of genes transferred to one plant cell from two separate Agrobacterium strains. Plant Mol Biol 8:439–445
Mlynárová L, Conner AJ, Nap JP (2006) Directed microspore-specific recombination of transgenic alleles to prevent pollen-mediated transmission of transgenes. Plant Biotechnol J 4:445-452
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Odell J, Caimi P, Sauer B, Russell S (1990) Site-directed recombination in the genome of transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 223:369–378
Onouchi H, Nishihama R, Kudo M, Machida Y, Machida C (1995) Visualization of site-specific recombination catalyzed by a recombinase from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 247:653–660
Pelucchi N, Fornara F, Favalli C et al (2002) Comparative analysis of rice MADS-box genes expressed during flower development. Sex Plant Reprod 15:113–122
Russell SH, Hoopes JL, Odell JT (1992) Directed excision of a transgene from the plant genome. Mol Gen Genet 234:49–59
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of a selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Tu J, Datta K, Oliva N et al (2003) Site-independently integrated transgenes in the elite restorer rice line Minghui 63 allow removal of a selectable marker from the gene of interest by self-segregation. Plant Biotechnol J 1:155–165
Yuan Y, Liu YJ, Wang T (2004) A new Cre/lox system for deletion of selectable marker gene. Acta Bot Sin 46:862–866
Zhang W, Subbarao S, Addae P, Shen A, Armstrong A, Peschke V et al (2003) Cre/lox-mediated marker gene excision in transgenic maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Theor Appl Genet 107:1157–1168
Zubko E, Scutt C, Meyer P (2000) Intrachromosomal recombination between attP regions as a tool to remove selectable marker genes from tobacco transgenes. Nat Biotechnol 18:442–445
Zuo J, Niu QW, Moller SG, Chua NH (2001) Chemical-regulated, site-specific DNA excision in transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. KSCX2-SW-316), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Research Projects; grants no. 2002CB111301 and 2002CCA03200) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30270758).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xianquan Bai and Qiuyun Wang contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Wang, Q. & Chu, C. Excision of a selective marker in transgenic rice using a novel Cre/loxP system controlled by a floral specific promoter. Transgenic Res 17, 1035–1043 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9182-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9182-7