Abstract
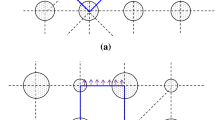
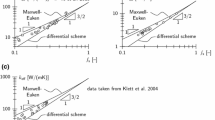
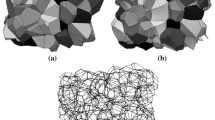
This paper presents a fully analytical model for the effective thermal conductivity of two-phase porous media with two-/three-dimensional closed cells, applicable to honeycombs and closed-cell foams. The present model combines an existing analytical expression derived based on the Laplace heat conduction equation with an analytical shape factor which corrects the deviation caused from a non-circular (or non-spherical) pore inclusion. Results demonstrate the validity of the present model capable of analytically estimating the effective thermal conductivity of closed-cell porous media. The simple yet accurate model provides the physical mechanisms of how effective thermal conductivity depends upon the shape of pores.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A\) :
-
Area of a regular polygon (\(\hbox {m}^{2})\)
- \(C\) :
-
Perimeter of a representative pore (m)
- \(C_\mathrm{{ref}}\) :
-
Perimeter of a reference circular pore (m)
- \(k_\mathrm{{c}} \) :
-
Thermal conductivity of a continuous phase (\(\hbox {W m}^{-1 }\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(k_\mathrm{{e}}\) :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of porous media (\(\hbox {W m}^{-1 }\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(k_\mathrm{{p}}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of a discrete phase (pores) (\(\hbox {W m}^{-1 }\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(n\) :
-
Number of the sides of a regular polygon
- \(R\) :
-
Radius of a reference circular pore (m)
- \(S\) :
-
Surface area of a polyhedral pore (\(\hbox {m}^{2})\)
- \(S_\mathrm{{ref}}\) :
-
Surface area of a reference spherical pore (\(\hbox {m}^{2})\)
- \(V\) :
-
Total volume in a porous medium (\(\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(V_0\) :
-
Total volume of an unperturbed continuous medium (\(\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(\beta \) :
-
Shape factor of a representative pore
- \(\beta _2\) :
-
Two-dimensional shape factor
- \(\beta _3\) :
-
Three-dimensional shape factor
- \(\varepsilon \) :
-
Porosity
References
Amjad, S.: Thermal conductivity and noise attenuation in aluminium foams. University of Cambridge, M. Ph. dissertation (2001)
Babcsán, N., Mészáros, I., Hegman, N.: Thermal and electrical conductivity measurements on aluminum foams. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 34(4), 391–394 (2003)
Bauer, T.: A general analytical approach toward the thermal conductivity of porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 36(17), 4181–4191 (1993)
Belova, I., Murch, G.: Monte Carlo simulation of the effective thermal conductivity in two-phase material. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 153, 741–745 (2004)
Bruggeman, D.: The calculation of various physical constants of heterogeneous substances. I. The dielectric constants and conductivities of mixtures composed of isotropic substances. Ann. Phys. 24(132), 636–679 (1935)
Collishaw, P., Evans, J.: An assessment of expressions for the apparent thermal conductivity of cellular materials. J. Mater. Sci. 29(2), 486–498 (1994)
Coquard, R., Baillis, D.: Numerical investigation of conductive heat transfer in high-porosity foams. Acta Materialia 57(18), 5466–5479 (2009)
Coquard, R., Rochais, D., Baillis, D.: Experimental investigations of the coupled conductive and radiative heat transfer in metallic/ceramic foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(21), 4907–4918 (2009)
Coquard, R., Rochais, D., Baillis, D.: Conductive and radiative heat transfer in ceramic and metal foams at fire temperatures. Fire Technol. 48(3), 699–732 (2012a)
Coquard, R., Rousseau, B., Echegut, P., Baillis, D., Gomart, H., Iacona, E.: Investigations of the radiative properties of Al-NiP foams using tomographic images and stereoscopic micrographs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55(5), 1606–1619 (2012b)
Doermann, D., Sacadura, J.: Heat transfer in open cell foam insulation. J. Heat Transf. 118(1), 88–93 (1996)
Eucken, A.: Allgemeine Gesetzmäßigkeiten für das Wärmeleitvermögen verschiedener Stoffarten und Aggregatzustände. Forschung im Ingenieurwesen 11(1), 6–20 (1940)
Fiedler, T., Belova, I., Murch, G.: Theoretical and Lattice Monte Carlo analyses on thermal conduction in cellular metals. Comput. Mater. Sci. 50(2), 503–509 (2010)
Gibson, L.J., Ashby, M.F.: Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge university press, Cambridge (1999)
Hamilton, R., Crosser, O.: Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1(3), 187–191 (1962)
Hashin, Z., Shtrikman, S.: A variational approach to the theory of the effective magnetic permeability of multiphase materials. J. Appl. Phys. 33(10), 3125–3131 (1962)
Hyun, S., Torquato, S.: Effective elastic and transport properties of regular honeycombs for all densities. J. Mater. Res. Pittsbg. 15(9), 1985–1993 (2000)
Hyun, S., Torquato, S.: Optimal and manufacturable two-dimensional, Kagome-like cellular solids. J. Mater. Res. Pittsbg. 17(1), 137–144 (2002)
Kaviany, M.: Principles of heat transfer in porous, media. Springer, New York (1991)
Kirkpatrick, S.: Percolation and conduction. Rev. Mod. Phys. 45(4), 574 (1973)
Klett, J., McMillan, A., Gallego, N., Walls, C.: The role of structure on the thermal properties of graphitic foams. J. Mater. Sci. 39(11), 3659–3676 (2004)
Landauer, R.: The electrical resistance of binary metallic mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 23(7), 779–784 (1952)
Lu, T.J.: Heat transfer efficiency of metal honeycombs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42(11), 2031–2040 (1998)
Lu, T.J., Chen, C.: Thermal transport and fire retardance properties of cellular aluminium alloys. Acta Materialia 47(5), 1469–1485 (1999)
Lu, T.J., Stone, H., Ashby, M.: Heat transfer in open-cell metal foams. Acta Materialia 46(10), 3619–3635 (1998)
Maxwell, J.C.: A treatise on electricity and magnetism, vol. 1. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1881)
Miyoshi, T., Itoh, M., Akiyama, S., Kitahara, A.: ALPORAS aluminum foam: production process, properties, and applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2(4), 179–183 (2000)
Norton, F.J.: Thermal conductivity and life of polymer foams. J. Cell. Plast. 3(1), 23–37 (1967)
Progelhof, R., Throne, J.: Cooling of structural foams. J. Cell. Plast. 11(3), 152–163 (1975)
Progelhof, R., Throne, J., Ruetsch, R.: Methods for predicting the thermal conductivity of composite systems: a review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 16(9), 615–625 (1976)
Ratcliffe, E.: Estimation of the effective thermal conductivities of two-phase media. J. Appl. Chem. 18(1), 25–30 (1968)
Rayleigh, L.: LVI. On the influence of obstacles arranged in rectangular order upon the properties of a medium. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 34(211), 481–502 (1892)
Russell, H.: Principles of heat flow in porous insulators. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 18(1–12), 1–5 (1935)
Sahimi, M., Gavalas, G.R., Tsotsis, T.T.: Statistical and continuum models of fluid-solid reactions in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 45(6), 1443–1502 (1990)
Schumacher, P., Greer, A.: Nucleation of a-Al On grain refining particles studied in crystallization Of amorphous Al-alloys. In: Proceeding 4th international conference on aluminum alloys, Atlanta. Georgia, 1. pp. 11–16 (1994)
Solórzano, E., Reglero, J., Rodríguez-Pérez, M., Lehmhus, D., Wichmann, M., De Saja, J.: An experimental study on the thermal conductivity of aluminium foams by using the transient plane source method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(25), 6259–6267 (2008a)
Solórzano, E., Rodriguez-Perez, M., de Saja, J.: Thermal conductivity of cellular metals measured by the transient plane sour method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10(4), 371–377 (2008b)
Temu, A., Naess, E., Sønju, O.: Development and testing of a probe to monitor gas-side fouling in cross flow. Heat Transf. Eng. 23(3), 50–59 (2002)
Thompson, M.: On the division of space with minimum partitional area. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 5(24), 503–514 (1887)
Tsotsas, E., Martin, H.: Thermal conductivity of packed beds: a review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 22(1), 19–37 (1987)
Wadell, H.: Volume, shape, and roundness of rock particles. J. Geol. 41, 443–451 (1932)
Wadell, H.: Sphericity and roundness of rock particles. J. Geol. 41, 310–331 (1933)
Wang, M., He, J., Yu, J., Pan, N.: Lattice Boltzmann modeling of the effective thermal conductivity for fibrous materials. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46(9), 848–855 (2007)
Wang, M., Wang, J., Pan, N., Chen, S., He, J.: Three-dimensional effect on the effective thermal conductivity of porous media. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40(1), 260 (2006)
Woodside, W.T., Messmer, J.: Thermal conductivity of porous media. I. Unconsolidated sands. J. Appl. Phys. 32(9), 1688–1699 (1961)
Wyllie, M., Gregory, A.: Formation factors of unconsolidated porous media: influence of particle shape and effect of cementation. J. Petroleum Technol. 5(4), 103–110 (1953)
Yamada, E., Ota, T.: Effective thermal conductivity of dispersed materials. Heat Mass Transf. 13(1), 27–37 (1980)
Zhang, B., Kim, T., Lu, T.J.: Analytical solution for solidification of close-celled metal foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(1), 133–141 (2009)
Zhang, Q.C., Lu, T.J., He, S.Y., He, D.P.: Control of pore morphology in closed-celled aluminum foams. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 41, 255–270 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National 111 Project of China (B06024), the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB610305), the Major International Joint Research Program of China (11120101002) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51206128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Lu, T. & Kim, T. Effective Thermal Conductivity Modelling for Closed-Cell Porous Media with Analytical Shape Factors. Transp Porous Med 100, 211–224 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0212-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0212-4