Abstract
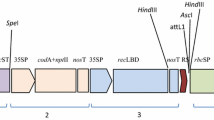
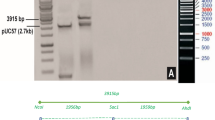
The rice water weevil (RWW), Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel, is the most widely distributed and destructive early season insect pest of rice, Oryza sativa L. worldwide. The rice plants were transformed with cryIIIA insecticidal gene as well as with the bar gene coding phosphinothricin acetyltransferase. CryIIIA gene under the control of a modified RCg2 promoter drives the insect-toxic gene expression in roots and/or leaves. The cryIIIA gene was transferred into O. sativa L. cv. Nakdong by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Stable integration of the transgene was confirmed in putative transformed rice by Southern blot analysis. The expression of the cryIIIA toxin gene in the roots of transgenic rice plants was verified by RT-PCR and immunoblot analysis. Transgenic rice plants were also evaluated for resistance to natural infestations of the RWW under field conditions between 2007 and 2011. The transgenic Btt8R and Btt12R lines reduced the growth rate of RWW larvae and pupae populations compared with non-transgenic control plants by approximately 52 and 58 %, respectively. To further examine the efficacy of the RWW bioassay, we used pots and performed experiments in trays and under field conditions in 2012. The Btt12R line reduced the total populations of RWW larvae and pupae in trays and under field conditions by 56 and 45 %, respectively. The bioassay experiments conducted over 6 years, showed a significant reduction rate of RWW larvae and pupae populations demonstrating that the cryIIIA gene in transgenic rice confers resistance to RWW.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bar :
-
Phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene
- MAR:
-
Matrix attachment region
- Nos:
-
Nopaline synthase
- pinII:
-
Proteinase inhibitor II
- PPT:
-
DL-phosphinothricin
- RCg2 :
-
Oryza sativa root-specific gene
- RWW:
-
Rice water weevil (Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel)
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen J, Dai LY, Wang XP, Tian YC, Lu MZ (2005) The Cry3Aa gene of Bacillus thuringiensis Bt886 encodes a toxin against long-horned beetles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:351–356
Chu CC, Wang CC, Sun CS, Hsu C, Yin KC, Chu CY, Bi FY (1975) Establishment of an efficient medium for another culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci Sin 18:659–668
Dale D (1994) Insect pests of the rice plant—their biology and ecology. In: Heinrichs EA (ed) Biology and management of rice insects. Wiley, New Delhi, pp 363–485
Espino L, Way MO, Pearson R, Nunez M (2009) Effect of planting date on Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) density-yield relationship on rice in southeastern texas. J Econ Entomol 102:1536–1545
FAO (2011) FAOSTAT. http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/default.aspx#ancor. Assessed 16 Jan 2013
Garcia-Canas V, Simo C, Leon C, Ibanez E, Cifuentes A (2011) MS-based analytical methodologies to characterize genetically modified crops. Mass Spectrom 30:396–416
Genissel A, Leple JC, Millet N, Augustin S, Jouanin L, Pilate G (2003) High tolerance against Chrysomela tremulae of transgenic poplar plants expressing a synthetic cry3Aa gene from Bacillus thuringiensis ssp tenebrionis. Mol Breed 11:103–110
González RG, Sánchez DS, Guerra ZZ, Campos JM, Quesada AL, Valdivia RM, Arencibia AD, Bravo KQ, Caligari PDS (2008) Efficient regeneration and Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation of recalcitrant sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) cultivars. Asia Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol 16:25–33
Hibbard BE, Clark TL, Ellersieck MR, Meihls LN, El Khishen AA, Kaster V, Steiner HY, Kurtz R (2010) Mortality of western corn rootworm larvae on MIR604 transgenic maize roots: field survivorship has no significant impact on survivorship of F1 progeny on MIR604. J Econ Entomol 103:2187–2196
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Hoefte H, Whiteley HR (1989) Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev 53:242–255
Jang IC, Nabm BH, Kim JK (1999) Subcellular targeting of green fluorescent protein to plastids in transgenic rice plants provide a high-level expression system. Mol Breed 5:453–461
Jouzani GS, Goldenkova IV, Piruzian ES (2008) Expression of hybrid cry3aM–licBM2 genes in transgenic potatoes (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 92:321–325
Krattiger AF (1997) A case study of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) and its transfer to developing countries. ISAAA Briefs 2:42, ISAAA, Ithaca, NY
Krieg A, Huger A, W Schnetter (1989) Protein tokin from Bacillus thiringiensis which is toxic to Coleoptera. Patent US 4889918
Lee AI, Lee S-H, Koo JC, Chum HJ, Lim CO, Mun JH (1999) Soybean Kunitz trypsin inhibitor (SKTI) confers resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) in transgenic rice. Mol Breed 5:1–9
Maqbool SB, Riazuddin S, Loc NT, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA, Christou P (2001) Expression of multiple insecticidal genes confers broad resistance against a range of different rice pests. Mol Breed 7:85–93
Mochizuki A, Nishizawa Y, Onodera H, Tabei Y (1999) Transgenic rice plants expressing a trypsin inhibitor are resistant against rice stem borers, Chilo suppressalis. Entomol Exp Appl 93:173–178
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murray M, Thopson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acid Res 8:4321–4325
Pardo-Lopez L, Munoz-Garay C, Porta H, Rodriguez-Almazan C, Soberon M, Bravo A (2009) Strategies to improve the insecticidal activity of Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. Peptides 30:589–595
Park Y, Abdullah MA, Taylor MD, Rahman K, Adang MJ (2009) Enhancement of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Aa and Cry3Bb toxicities to coleopteran larvae by a toxin-binding fragment of an insect cadherin. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3086–3092
Philip MG, Bowler C (2002) Molecular plant biology volume one: a practical approach, vol 258. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 17–23
Ramana Rao MV, Behera KS, Baisakh N, Datta SK, Rao GJN (2009) Transgenic indica rice cultivar ‘Swarna’ expressing a potato chymotrypsin inhibitor pin2 gene show enhanced levels of resistance to yellow stem borer. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 99:277–285
Rausell C, Garcia-Robles I, Sanchez J, Munoz-Garay C, Martinez-Ramirez AC, Real MD, Bravo A (2004) Role of toxin activation on binding and pore formation activity of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3 toxins in membranes of Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Biochim Biophys Acta 1660:99–105
Rausell C, Ochoa-Campuzano C, Martinez-Ramirez AC, Bravo A, Real MD (2007) A membrane associated metalloprotease cleaves Cry3Aa Bacillus thuringiensis toxin reducing pore formation in Colorado potato beetle brush border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:2293–2299
Rhim SL, Cho HW, Kim BD, Schnetter W, Geider K (1995) Development of insect resistance in tomato plants expressing the δ-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis. Mol Breed 1:229–236
Rhim SL, Kim IG, Jin TE, Lee JH, Kuo CI, Suh SC, Huang LC (2004) Transformation of citrus with coleopteran specific δ-endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. tenebrionis. J Plant Biotechnol 6:21–24
Rice WC, Croughan TP, Ring DR, Muegge MA, Stout MJ (1999) Delayed flood for management of rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 28:1130–1135
Saito T, Hirai K, Way MO (2005) The rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 40:31–39
Shang H, Stout MJ, Zhang Z, Cheng J (2004) Rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) population dynamics in Louisiana. J Entomol 39:623–642
Shi XG (2009) Study of gene silencing in rice: a root-preferential gene RCg2. Doctoral dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station
Simon R (1984) High frequency mobilization of gram negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet 196:413–420
Smith CM (1983) The rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel. In: Singh KG (ed) Exotic plant quarantine pests and procedures for introduction of plant materials. Selangor, Malaysia, pp 3–9
Smith DS, Maxwell PW, De Boer SH (2004) Method for the detection of synthetic cry3A in transgenic potatoes. J Agric Food Chem 25:809–815
Stout MJ, Frey MJ (2007) Evaluation of thiamethoxam as a seed treatment against the rice water weevil. Ann Res Rpt Rice Res Stn LSU Agric Ctr 99:299–300
Stout MJ, Rice WC, Riggio RM, Ring DR (2000) The effects of four insecticides on the population dynamics of the rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel. J Entomol Sci 35:48–61
Stout MJ, Riggio MR, Zou L, Roberts R (2002) Flooding influences ovipositional and feeding behavior of the rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Econ Entomol 95:715–721
Thompson RA, Quisenberry SS, Trahan GB, Heagler AM, Giesler G (1994) Water management as a cultural control tactic for the rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in southwest Louisiana. J Econ Entomol 87:223–230
Tohidfar M, Zare N, Jouzani GS, Eftekhari SM (2013) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) using a synthetic cry3a gene to enhance resistance against alfalfa weevil. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 113:227–235
Xu Y, Buchholz WG, DeRose RT, Hall TC (1995) Characterization of a rice gene family encoding root-specific proteins. Plant Mol Biol 27:237–248
Xu D, Xue Q, McElroy D, Mawai Y, Líder V, Wu R (1996) Constitutive expression of a cowpea trypsin inhibitor gene, CpTi, in transgenic rice plants confers resistance to two major insect pests. Mol Breed 2:167–173
Zhang B, Chen M, Zhang X, Luan H, Diao S, Tian Y, Su X (2011) Laboratory and field evaluation of the transgenic Populus alba × Populus glandulosa expressing double Coleopteran resistance genes. Tree Physiol 31:567–573
Zhou Z, Pang J, Guo W, Zhong N, Tian Y, Xia G, Wu J (2012) Evaluation of the resistance of transgenic potato plants expressing various levels of Cry3A against the Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say) in the laboratory and field. Pest Manag Sci 68:1595–1604
Zou L, Stout MJ, Dunand RT (2004a) The effects of feeding by the rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel, on the growth and yield components of rice, Oryza sativa. Agric For Entomol 6:47–53
Zou L, Stout MJ, Ring DR (2004b) Density-yield relationships for rice water weevil Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus on rice for different varieties and under different water management regimes. Crop Prot 23:543–550
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Academy of Agricultural Science (PJ00863404), the Rural Development, Republic of Korea. The RCg2 promoter was kindly provided by Dr. Timothy C. Hall through a cooperative research project between RDA, Korea, and Texas A&M University, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Shin, KS., Suh, SC. et al. CryIIIA toxin gene expression in transgenic rice confers resistance to rice water weevil. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 115, 243–252 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0356-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0356-5