Abstract
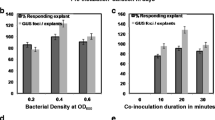
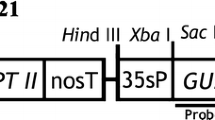
An efficient Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method has been developed for the medicinal plant Podophyllum hexandrum Royle, an important source of the anticancer agent podophyllotoxin. Highly proliferating embryogenic cells were infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens harbouring pCAMBIA 2301, which contains npt II and gusA as selection marker and reporter genes, respectively. The transformed somatic embryos and plantlets were selected on Murashige and Skoog (MS) basal medium containing kanamycin and germination medium, respectively. GUS histochemical analysis, polymerase chain reaction and Southern blot hybridisation confirmed that gusA was successfully integrated and expressed in the P. hexandrum genome. Compared with cefotaxime, 200 mg l−1 timentin completely arrested Agrobacterium growth and favoured somatic embryo development from embryogenic cells. Among the different Agrobacterium strains, acetosyringone concentrations and co-cultivation durations tested, embryogenic callus infected with A. tumefaciens EHA 105 and co-cultivated for 3 days on MS basal medium containing 100 μM acetosyringone proved to be optimal and produced a transformation efficiency of 29.64 % with respect to germinated GUS-positive plantlets. The Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method developed in the present study facilitates the transference of desirable genes into P. hexandrum to improve the podophyllotoxin content and to enhance other useful traits.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Abdallat AM, Sawwan JS, Al Zoubi B (2011) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of callus cells of Crataegus aronia. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 104:31–39
Anbazhagan VR, Ahn CH, Harada E, Kim YS, Choi YE (2008) Podophyllotoxin production via cell and adventitious root cultures of Podophyllum peltatum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 44:494–501
Anbazhagan VR, Kim YS, Choi YE (2009) Production of transgenic Podophyllum peltatum via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Biol Plantarum 53:637–642
Badhwar RL, Sharma BK (1963) A note on the germination of Podophyllum seeds. Indian For 89:445–447
Bastos JK, Burandt CL, Dhammika NP, Bryant L, McChesney JD (1996) Quantization of aryltetralin lignans in plant parts and among different populations of Podophyllum peltatum by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Nat Prod 59:406–408
Canel C, Moraes RM, Dayan FE, Ferreira D (2000) Molecules of interest podophyllotoxin. Phytochemistry 54:115–120
Canel C, Dayan FE, Ganzera M, Khan IA, Rimando A, Burandt CL, Moraes RM (2001) High yield of podophyllotoxin from leaves of Podophyllum peltatum by in situ conversion of podophyllotoxin 4-O-b-D glucopyranoside. Planta Med 67:97–99
Chattopadhyay S, Mehra RS, Srivastava AK, Bhojwani SS, Bisaria VS (2003) Effect of major nutrients on podophyllotoxin production in Podophyllum hexandrum suspension cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:541–546
Cheng ZM, Schnurr AA, Kapaun JA (1998) Timentin as an alternative antibiotic for suppression of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in genetic transformation. Plant Cell Rep 17:646–649
Dai SH, Zheng P, Marmey P, Zhang SP, Tian WZ, Chen SY, Beachy RN, Fauquet C (2001) Comparative analysis of transgenic rice plants obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and particle bombardment. Mol Breed 7:25–33
Damayanthi Y, Lown JW (1998) Podophyllotoxins: current status and recent developments. Curr Med Chem 5:205–252
Dangi B, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2012) Regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Terminalia bellerica Roxb.: a multipurpose tree species. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 48:304–312
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA mini preparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Gelvin SB (2003) Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: the biology behind the ‘gene-jockeying’ tool. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:16–37
Gelvin SB (2009) Agrobacterium in the genomics age. Plant Physiol 150:1665–1676
Giri A, Lakshmi Narasu M (2000) Production of podophyllotoxin from Podophyllum hexandrum: a potential natural product for clinically useful anticancer drugs. Cytotechnology 34:17–26
Giri A, Giri CC, Dhingra V, Narasu ML (2001) Enhanced podophyllotoxin production from Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformed cultures of Podophyllum hexandrum. Nat Prod Lett 15:229–235
Goldberg JB, Ohman DE (1984) Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved with the production of alginate. J Bacteriol 158:1115–1121
Han JL, Wang H, Ye HC, Liu Y, Li ZQ, Zhang Y, Zhang YS, Yan F, Li GF (2005) High efficiency of genetic transformation and regeneration of Artemisia annua (L.) via Agrobacterium. Plant Sci 168:73–80
He C, Zhang J, Chen J, Ye X, Du L, Dong Y, Zhao H (2007) Genetic transformation of Aloe barbadensis Miller by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Genet Genomics 34:1053–1060
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303:179–180
Hood EE, Helmer GC, Fraley RT, Chilton MD (1986) The hypervirlence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in the region of pTiBo542 outside the T-DNA. J Bacteriol 168:1291–1301
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekema A (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Ieamkhang S, Chatchawankanphanich O (2005) Augmentin as an alternative antibiotic for growth suppression of Agrobacterium for tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) transformation. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 82:213–220
Jackson DE, Dewick PM (1984) Aryltetralin lignans from Podophyllum hexandrum and Podophyllum peltatum. Phytochemistry 23:1147–1152
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan NW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kondo T, Hasegawa H, Suzuki M (2000) Transformation and regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.) by Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer. Plant Cell Rep 19:989–993
Le VQ, Belles-Isles J, Dusabenyagasani M, Tremblay FM (2001) An improved procedure for production of white spruce (Picea glauca) transgenic plants using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Exp Biol 52:2089–2095
Lee SH, Lee DG, Woo HS, Lee KW, Kim DH, Kwak SS, Kim JS, Kim H, Ahsan N, Choi MS, Yang JK, Lee BH (2006) Production of transgenic orchard grass via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of seed-derived callus tissues. Plant Sci 171:408–414
Li DD, Shi W, Deng XX (2002) Factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated embryogenic callus transformation of Valencia sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) containing the pTA29-barnase gene. Tree Physiol 23:1209–1215
Lièvre K, Hehn A, Tran TLM, Gravot A, Thomasset B, Bourgaud F, Gontiet E (2005) Genetic transformation of the medicinal plant Ruta graveolens L. by an Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method. Plant Sci 168:883–888
Manickavasagam M, Ganapathi A, Anbazhagan VR, Sudhakar B, Selvaraj N, Vasudevan A, Kasthurirengan S (2004) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation and development of herbicide-resistant sugarcane (Saccharum species hybrids) using axillary buds. Plant Cell Rep 23:134–143
Mishra S, Sangwan RS, Bansal S, Sangwan NS (2012) Efficient genetic transformation of Withania coagulans (Stocks) dunal mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens from leaf explants of in vitro multiple shoot culture. Protoplasma. doi:10.1007/s00709-012-0428-0
Mondal TK, Bhattacharya A, Ahuja PS, Chand PK (2001) Transgenic tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze cv. Kangra Jat] plants obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 20:712–720
Moraes RM, Burandt C, Ganzera M, Li XL, Khan I, Canel C (2002) The American may apple revisited: Podophyllum peltatum: still a potential cash crop? Econ Bot 54:471–476
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Naing AH, Kim CK, Yun BJ, Jin JY, Lim KB (2012) Primary and secondary somatic embryogenesis in Chrysanthemum cv. Euro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. doi:10.1007/s11240-012-0243-5
Palomo-Ríos E, Barceló-Muňoz A, Mercado JA, Pliego-Alfaro F (2012) Evaluation of key factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of somatic embryos of avocado (Persea americana Mill.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:201–211
Sagar PS, Zafar R (2005) In vitro enhanced production of podophyllotoxinin in phytohormonal induced and regenerated roots of Podophyllum hexandrum. Pharm Biol 43:404–410
Sambrook J, Fritch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, Harbor
Selvaraj N, Kasthurirengan S, Vasudevan A, Manickavasagam M, Choi CW, Ganapathi A (2010) Evaluation of green fluorescent protein as a reporter gene and phosphinothricin as the selective agent for achieving a higher recovery of transformants in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. cv. Poinsett76) via Agrobacterium tumefaciens. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 46:329–337
Srivastava T, Das S, Sopory SK, Srivastava PS (2009) A reliable protocol for transformation of Catharanthus roseus through Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Physiol Mol Biol 15:93–98
Subramaniam S, Rathinam X (2010) Emerging factors that influence efficiency of T-DNA gene transfer into Phalaenopsis violacea orchid via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation system. Int J Biol 2:64–73
Subramanyam K, Subramanyam K, Sailaja KV, Srinivasulu M, Lakshmidevi K (2011) Highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of banana cv. Rasthali (AAB) via sonication and vacuum infiltration. Plant Cell Rep 30:425–436
Sultan P, Shawl AS, Ramteke PW, Jan A (2006) In vitro propagation for mass multiplication of Podophyllum hexandrum: a high value medicinal herb. Asian J Plant Sci 5:179–184
Suma B, Keshavachandran R, Nybe EV (2008) Agrobacetrium tumefaciens-mediated transformation and regeneration of ginger (Zinger officinale Rosc.). J Trop Agr 46:38–44
Tang H, Ren Z, Krczal Z (2000) An evaluation of antibiotics for the elimination of Agrobacterium tumefaciens from walnut somatic embryos and for the effects on the proliferation of somatic embryos and regeneration of transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 19:881–887
Thiruvengadam M, Chung IM (2011) Establishment of an efficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated leaf disc transformation of spine gourd (Momordica dioica Roxb. ex Willd). Afr J Biotechnol 10:19337–19345
Thiruvengadam M, Praveen N, Chung IM (2012) An efficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.). Aust J Crop Sci 6:1094–1100
Travella S, Ross SM, Harden J, Everett C, Snape JW, Harwood WA (2005) A comparison of transgenic barley lines produced by particle bombardment and Agrobacterium-mediated techniques. Plant Cell Rep 23:780–789
Van Uden W, Pras N, Visser JF, Malingre TM (1989) Detection and identification of podophyllotoxin produced by cell cultures derived from Podophyllum hexandrum royle. Plant Cell Rep 8:165–168
Vancanneyt G, Schmidt R, O’Connor-Sanchez A, Willmitzer L, Rocha-Sosa M (1990) Construction of an intron-containing marker gene: splicing of the intron in transgenic plants and its use in monitoring early events in Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Mol Genet Genomics 220:245–250
Vengadesan G, Ganapathi A, Anbazhagan VR (2002) Somatic embryogenesis in cell suspension cultures of Acacia sinuata (Lour.) Merr. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:52–57
Wang HM, To KY (2004) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in the high-value medicinal plant Echinacea purpurea. Plant Sci 166:1087–1096
Wei X, Gou X, Yuan T, Russell SD (2006) A highly efficient in vitro plant regeneration system and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in Plumbago zeylanica. Plant Cell Rep 25:513–521
Yan YP, Wang ZZ (2007) Genetic transformation of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 88:175–184
Zhi-neng L, Guo-feng L, Fang F, Man-zhu B (2007) Adventitious shoot regeneration of Platanus acerifolia Willd. facilitated by timentin, an antibiotic for suppression of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in genetic transformation. For Stud China 9:14–18
Zhu Q, Wu F, Ding F, Ye D, Chen Y, Li Y, Zhifan Y (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Dioscorea zingiberensis Wright, an important pharmaceutical crop. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 96:317–324
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Life Science Research Board, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Govt. of India for financial support (DLS/81/48222/LSRB–171 BTB/2008) used to carry out the present work. The corresponding author is thankful to the University Grants Commission (UGC), Govt. of India, for providing an Emeritus fellowship under the BSR scheme. The authors are also thankful to Prof. S.K. Nandi, G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment and Development, Almora, Uttarakhand, India and Prof. M.C. Nautiyal, H.N.B. Garhwal University, Garhwal Srinagar, Uttarakhand, India, for help with the collection of Podophyllum hexandrum seeds. The authors are thankful to Dr. A.S. Rao for his valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajesh, M., Jeyaraj, M., Sivanandhan, G. et al. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the medicinal plant Podophyllum hexandrum Royle (syn. P. emodi Wall. ex Hook.f. & Thomas). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 114, 71–82 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0307-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0307-1