Abstract
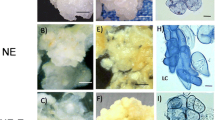
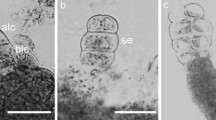
A SOMATIC EMBRYOGENSIS RECEPTOR KINASE (SERK) gene has been linked to somatic embryogenesis in many plant species. We have developed a culture model that enabled investigation of the relationship between embryogenesis and the expression of various ZmSERK genes at different developmental stages and following treatment with hormones. The results indicate that auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) enhanced transcription activity of ZmSERK and promoted somatic embryogenesis. The cytokinin 6-benzyladenine (BA) inhibited embryogenesis and reduced the expression of ZmSERK1 and ZmSERK2, but it significantly increased the expression of ZmSERK3. The application of 2, 4-D and BA promoted the transcription of ZmSERK3 and inhibited that of ZmSERK1 and ZmSERK2, suggesting a fine regulation of embryogenesis by ZmSERK. The immature embryo at 12 and 15 days after pollination (DAP) showed the highest competence for embryogenesis and displayed the strongest ZmSERK gene expression, respectively. Based on these observations, we conclude that the expression profiles of ZmSERKs are closely related to hormone signaling and the developmental stages of the embryo during embryogenesis. ZmSERK1 and ZmSERK2 appear to play an important role in maintaining embryogenesis, while ZmSERK3 appears to have a dual role in embryogenesis by modulating its expression level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini E, Marconi G, Reale L, Barcaccia G, Porceddu A, Ferranti F, Falcinelli M (2005) SERK and APOSTART: candidate genes for apomixis in Poa pratensis. Plant Physiol 138:2185–2199
Albrecht C, Russinova E, Kemmerling B, Kwaaitaal M, de Vries SC (2008) Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE proteins serve brassinosteroid-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Plant Physiol 2008; 148:611–619
Baudino S, Hansen S, Brettshneider R, Hecht VFG, Dresselhaus T, Lors H, Dumas C, Rogowsky PM (2001) Molecular characterization of two novel maiz LRR receptor-like kinase, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 213:1–10
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu CM, Van Lammeren AAM, Miki BLA (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 14:1737–1749
Frame BR, Shou H, Chikwamba RK et al (2002) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of maize embryos using a standard binary vector system. Plant Physiol 129:13–22
Fu FL, Li WC, Rong TZ (2005) Effect of Ca2+ and uniconazole appended in N6 medium on immature embryos culture in maize. Acta Agron Sin 31:634–639
Fu FL, Feng ZL, Qu BY, Li WC (2006) Relationships between inducton rate of embryogenic callus and endogenous hormones content in maize. J Nucl Agric Sci 20:10–14
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada JP, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Hu H, Xiong L, Yang Y (2005) Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 222:107–117
Huang X, Lu XY, Zhao JT, Chen JK, Dai XM, Xiao W, Chen YP, Chen YF, Huang XL (2009) MaSERK1 gene expression associated with somatic embryogenic competence and disease resistance response in banana (Musa spp.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:309–316
Lotan T, Ohto M, Yee MK, West MA, Lo R, Kwong RW, Yamagishi K, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (1998) Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON 1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative tissue. Cell 93:1195–1205
Maillot P, Lebel S, Schellenbaum P, Jacques A, Walter B (2009) Differential regulation of SERK, LEC-like and pathogenesis-related genes during indirect secondary somatic embryogenesis in grapevine. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:743–752
Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Rose RJ (2003) Auxin up-regulates MtSERK1 expression in both Medicago truncatula root-forming and embryogenic cultures. Plant Physiol 33:218–230
Nolan KE, Kurdyukov S, Rose RJ (2009) Expression of the SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 (SERK1) gene is associated with developmental change in the life cycle of the model legume Medicago truncatula. J Exp Bot 60:1759–1771
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Santa-Catarina C, Hanai LR, Dornelas MC, Viana AM, Floh EIS (2004) SERK gene homology expression, polyamines and amino acids associated with somatic embryogenic competence of Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae). Plant Cell Tiss Org 79:53–61
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Shimada T, HirabayashI T, Endo T, Fujii H, Kita M, Omura M (2005) Isolation and characterization of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase gene homologue, (CitSERK1)from Citrus unshiu Marc. Sci Hortic 103:233–238
Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2008) Characterization of three somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase genes from wheat, Triticum aestivum. Plant Cell Rep 27:833–843
Somleva MN, Schmidt EDL, de Vries SC (2000) Embryogenic cells in Dactylis glomerata L. (Poaceae) explants identified by cell tracking and by SERK expression. Plant Cell Rep 19:718–726
Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Lepiniec L, Fischer RL, Golberg RB, Harada JJ (2001) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes a B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11806–11811
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thomas C, Meyer D, Himber C, Steinmetz A (2004) Spatial expression of a sunflower SERK gene during induction of somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:35–42
Wang Y, Fu SH, Wen Y, Zhang ZM, Xia YL, Yuzhen Liu, Rong TZ, Pan GT (2007) Selection of maize Inbred lines with high regeneration and susceptibility to Agrobacterium tumifaciens. J Genet Genom 34:749–755
Zhang SZ, Rong TZ (2008) Advance of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation system of maize (Zea mays L.). Hereditas 30:1249–1256
Zhao ZY, Gu W, Cai T et al (1998) Molecular analysis of T0 plants transformed by Agrobacterium and comparison of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation with bombardment transformation in maize. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 72:34–37
Zhao Z, Gu W, Cai T et al (2001) High throughput genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in maize. Mol Breed 8:323–333
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5:1411–1423
Zuo J, Niu QW, Frugis G, Chua NH (2002) The WUSCHEL gene promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 30:349–359
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Xin Yu and Jinye Mou for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30800687 and No. 31071434), the Foundation for Young Scientists of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (No. 09ZB051), the Applied Basic Research Program of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department (No. 2008JY0096), and the Social Non-profit Fund of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department (2008NG0013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Liu, X., Lin, Y. et al. Characterization of a ZmSERK gene and its relationship to somatic embryogenesis in a maize culture. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 105, 29–37 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9834-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9834-1