Abstract
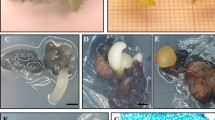
A somatic embryogenesis protocol for plant regeneration of northern red oak (Quercus rubra) was established from immature cotyledon explants. Embryogenic callus cultures were induced on Murashige and Skoog medium (MS) containing 3% sucrose, 0.24% Phytagel™, and various concentrations of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-d) after 4 weeks of culture in darkness. A higher response (66%) of embryogenic callus was induced on 0.45 μM 2,4-d. Higher numbers of globular- (31), heart- (17), torpedo- (12), and cotyledon-stage (8) embryos per explant were obtained by culturing embryogenic callus on MS with 3% sucrose, 0.24% Phytagel™, and devoid of growth regulators after 8 weeks culture in darkness. Continuous sub-culturing of embryogenic callus on medium containing 2,4-d yielded only compact callus. Desiccation of embryos for 3 days in darkness at 25 ± 2°C followed by cold storage at 4°C in darkness for 8 weeks favored embryo germination and development of plantlets. Cotyledon-stage embryos subjected to desiccation and chilling treatment cultured on MS with 3% sucrose, 0.24 Phytagel™, 0.44 μM 6-benzylaminopurine (BA), and 0.29 μM gibberellic acid germinated at a higher frequency (61%) than with 0.44 μM BA alone and control cultures. Germinated plantlets developed a shoot and root, were acclimatized successfully, and maintained in a growth room for plantlet development.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-d :
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- NRO:
-
Northern red oak
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
References
Bueno MA, Astorga R, Manzanera JA (1992) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in Quercus suber. Physiol Plant 85:30–34. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb05259.x
Chalupa AV (1987) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Picea, Quercus, Betula, Tilia, Robinia, Fagus, and Aesculus. Commun Inst For Cechoslov 15:133–148
Chalupa AV (1990) Plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis from cultured immature embryos of oak (Quercus robur L.) and linden (Tilia cordata Mill.). Plant Cell Rep 9:398–401. doi:10.1007/BF00232408
Cuenca B, San-José MC, Martínez MT, Ballester A, Vieitez AM (1999) Somatic embryogenesis from stem and leaf explant of Quercus robur L. Plant Cell Rep 18:538–543. doi:10.1007/s002990050618
Deng M-D, Cornu D (1992) Maturation and germination of walnut somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 28:195–202. doi:10.1007/BF00055517
Endemann M, Wilhelm E (1999) Factors influencing the induction and viability of somatic embryos of Quercus robur L. Biol Plant 42:499–504. doi:10.1023/A:1002690309666
Fernández-Guijarro B, Celestino C, Toribio M (1995) Influence of external factors on secondary embryogenesis and germination in somatic embryos from leaves of Quercus suber. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 41:99–106. doi:10.1007/BF00051578
Galford JR, Weiss-Cottrill D (1991) Response of insects to damaged and undamaged germinating acorns. USDA Forest Service, Northeastern Forest Experiment Station, Radnor, PA Res Pap NE-656, 3 pp
Galford J, Auchmoody LR, Smith HC, Walters RS (1991) Insects affecting establishment of northern red oak seedlings in central Pennsylvania. In: McCormick LH, Gottschalk KW (eds) Proceedings of the eighth central hardwood forest conference, University Park, PA. USDA Forest Service, Northeastern Forest Experiment Station, Gen Tech Rep NE-148, pp 271–280
García-Martín G, Gonzalez-Benito ME, Manzanera JA (2001) Quercus suber L. somatic embryo germination and plant conversion: pretreatments and germination conditions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 37:190–198. doi:10.1007/s11627-001-0033-y
García-Martín G, Manzanera JA, González-Benito ME (2005) Effect of exogenous ABA on embryo maturation and quantification of endogenous levels of ABA and IAA in Quercus suber somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 80:171–177. doi:10.1007/s11240-004-1056-y
Gingas VM (1991) Asexual embryogenesis and plant regeneration from male catkins of Quercus. HortScience 26:1217–1218
Gingas VM, Lineberger RD (1989) Asexual embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Quercus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 17:191–203. doi:10.1007/BF00046867
González-Benito ME, García-Martín G, Manzanera JA (2002) Shoot development in Quercus suber L. somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:477–480. doi:10.1079/IVP2002318
Hernández I, Celestino C, Toribio M (2003a) Vegetative propagation of Quercus suber L. by somatic embryogenesis I. Factors affecting the induction in leaves from mature cork oak trees. Plant Cell Rep 21:759–764
Hernández I, Celestino C, Alegre J, Toribio M (2003b) Vegetative propagation of Quercus suber L. by somatic embryogenesis II. Plant regeneration from selected cork oak trees. Plant Cell Rep 21:765–770
Hübner E, Müller K, Heyder J, Schmitt HP (1995) Somatische embryogenese und sprossentwicklung in abhängigkeit von 2, 4-D- und BAP-konzentrationen an zygotischen embryonen der spätaustreibenden stieleiche (Quercus robur L.) [Somatic embryogenesis and shoot formation in relation with 2, 4-D and BAP concentration in zygotic embryos of late flushing Quercus robur]. Silvae Genet 44:225–229
Ishii K, Thakur R, Jain SM (1999) Somatic embryogenesis and evaluation of variability in somatic seedlings of Quercus serrata by RAPD markers. In: Mohan JS, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol 4. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 403–414
Jörgensen J (1993) Embryogenesis in Quercus petraea. Ann Sci For 50:344s–350s. doi:10.1051/forest:19930738
Kim YW, Lee SK, Lee BC, Jang SS (1992) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from mature embryos Quercus acutissima. Korean Soc Plant Tissue Cult 19:363–368
Kim YW, Lee BC, Lee SK, Jang SS (1994) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Quercus acutissima. Plant Cell Rep 13:315–318
Kim YW, Youn Y, Noh ER, Kim JC (1997) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature embryos of five families of Quercus acutissima. Plant Cell Rep 16:869–873. doi:10.1007/s002990050336
Lelu MAP, Bornman CH (1990) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in excised cotyledons of Picea glauca and Picea mariana. Plant Physiol Biochem 28:785–791
Lloyd G, McCown B (1980) Commercially-feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot tip culture. Comb Proc Int Plant Propag Soc 30:421–427
Manzanera JA (1992) Inducción de embryogénesis somática en roble (Quercus robur L.). Investigación Agraria. Ser Sist Recur For 1(1):73–81
Manzanera JA, Astorga R, Bueno MA (1993) Somatic embryo induction and germination in Quercus suber L. Silvae Genet 42:90–93
Manzanera JA, Bueno MA, Pardos JA (1996) Querucs robur L. (pendunculate oak). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Vol 35 Trees IV. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 321–341
Merkle SA, Nairn CJ (2005) Hardwood tree biotechnology. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 41:602–619. doi:10.1079/IVP2005687
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Park YS, Barrett JD, Bonga JM (1998) Application of somatic embryogenesis in high-value clonal forestry: deployment, genetic control and stability of cryopreserved clones. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 34:231–239. doi:10.1007/BF02822713
Pijut PM, Woeste KE, Vengadesan G, Michler CH (2007) Technological advances in temperate hardwood tree improvement including breeding and molecular marker applications. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:283–303. doi:10.1007/s11627-007-9026-9
Pond SE, von Aderkas P, Bonga JM (2002) Improving tolerance of somatic embryos of Picea glauca to flash desiccation with a cold treatment (desiccation after cold acclimation). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:334–341. doi:10.1079/IVP2002304
Rancillac M, Klinguer A, Klinguer S (1991) Plant biotechnologies applied to a forest tree, the American red oak (Quercus rubra L.). Acta Hortic 289:341–342
Rancillac M, Klinguer A, Klinguer S, Millet B (1996) Preliminary investigations on somatic embryogenesis from leaf discs of red oak (Quercus rubra L.). Plant Growth Regul 20:67–73. doi:10.1007/BF00024061
Sánchez MC, Martínez MT, Valladares S, Ferro E, Vieitez AM (2003) Maturation and germination of oak somatic embryos originated from leaf and stem explants: RAPD markers for genetic analysis of regenerants. J Plant Physiol 160:699–707. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-00754
Sánchez N, Manzanera JA, Pintos B, Bueno MA (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cork oak (Quercus suber L.) somatic embryos. New Forest 29:169–176. doi:10.1007/s11056-005-0208-1
SAS Institute Inc (2001) SAS/START user’s guide version 8.2. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Sasaki Y, Shoyama Y, Nishioka I, Suzaki T (1988) Clonal propagation of Quercus acustissima Carruth. by somatic embryogenesis from embryonic axes. J Fac Agr Kyushu Univ 33:95–101
Schenk RU, Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can J Bot 50:199–204. doi:10.1139/b72-026
Seckinger GR, McCown BH, Struckmeyer BE (1979) Production of anomalous structures in Quercus rubra L. callus cultures. Am J Bot 66:993–996. doi:10.2307/2442244
Shekhawat UKS, Ganapathi TR, Srinivas L, Bapat VA, Rathore TS (2008) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Santalum album L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 92:261–271. doi:10.1007/s11240-007-9330-4
Sommer HE, Brown CL, Kormanik PP (1975) Differentiations of plantlets in longleaf pine (Pinus palustris Mill.) tissue cultured in vitro. Bot Gaz 136:196–200. doi:10.1086/336802
Tang HR, Ren ZL, Krczal G (2000) Improvement of English walnut somatic embryo germination and conversion by desiccation treatments and plantlet development by lower medium salts. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:47–50. doi:10.1007/s11627-000-0011-9
Toribio M, Fernández C, Celestino C, Martínez MT, San-José MC, Vieitez AM (2004) Somatic embryogenesis in mature Quercus robur trees. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 76:283–287. doi:10.1023/B:TICU.0000009245.92828.26
Valladares S, Sánchez C, Martínez MT, Ballester A, Vieitez AM (2006) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from tissues of mature oak trees: true-to-type conformity of plantlets by RAPD analysis. Plant Cell Rep 25:879–886. doi:10.1007/s00299-005-0108-z
Wilhelm E (2000) Somatic embryogenesis in oak (Quercus spp.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:349–357. doi:10.1007/s11627-000-0062-y
Wilhelm E, Endemann M, Hristoforogulu K, Prewein C, Tutkova M (1999) Somatic embryogenesis in oak (Quercus robur L.) and production of artificial seeds. In: Espinel S, Ritter E (eds) Proceedings of application of biotechnology to forest genetics. Biofor 99, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, pp 213–225
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the van Eck Foundation for Purdue University for providing financial support. We gratefully acknowledge Drs. Wagner A. Vendrame and Eva Wilhelm, and Gisele Andrade for their constructive review and suggestions for improvement of this manuscript; and Jim McKenna and Dr. Francis Salifu (HTIRC, Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Purdue University) for their valuable assistance in gathering acorns and statistical analysis, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vengadesan, G., Pijut, P.M. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of northern red oak (Quercus rubra L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 97, 141–149 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9508-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9508-z