Abstract
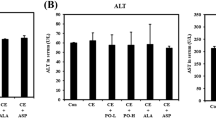
Whitmania pigra Whitman (W. pigra) has been widely employed in decoction for the treatment of blood stasis syndrome for many years in China. The aim of the present study was to explore the anti-venous thrombosis (VT) mechanism of the aqueous extract of W. pigra (AEW) in rats. Rats were orally administered with AEW. A inferior vena cava (IVC) thrombosis model was established. Thrombosed IVC was weighed and histopathological analyses were performed. Blood coagulation, blood fibrinolysis, blood cell count, blood viscosity and platelet activity were evaluated. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation was analyzed. Malondialdehyde (MDA) content in thrombosed IVC and antioxidants in serum were detected. Protein expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) in thrombosed IVC was determined. AEW significantly reduced thrombus weight. It did not affect blood coagulation, blood fibrinolysis, blood cell count, platelet activity, or whole blood viscosity. However, AEW remarkably alleviated vascular injury, reduced ROS accumulation and MDA content, enhanced the total antioxidant capacity and the activities of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase. It increased the glutathione/oxidized glutathione ratio and the protein expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1. In summary, W. pigra may prevent VT via Nrf2-mediated antioxidation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolberg AS, Rosendaal FR, Weitz JI et al (2015) Venous thrombosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15006. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.6
Byrnes JR, Wolberg AS (2017) New findings on venous thrombogenesis. Hamostaseologie 37(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.5482/HAMO-16-09-0034
Furie B, Furie BC (2008) Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N Engl J Med 359(9):938–949. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0801082
Versteeg HH, Heemskerk JW, Levi M, Reitsma PH (2013) New fundamentals in hemostasis. Physiol Rev 93(1):327–358. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00016.2011
Engelmann B, Massberg S (2013) Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13(1):34–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3345
Konukoglu D, Uzun H (2017) Endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol 956:511–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/5584_2016_90
Chen B, Lu Y, Chen Y, Cheng J (2015) The role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced endothelial injuries. J Endocrinol 225(3):R83–R99. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-14-0662
Sies H, Berndt C, Jones DP (2017) Oxidative stress. Annu Rev Biochem 86:715–748. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-045037
Baird L, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2011) The cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol 85(4):241–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0674-5
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res 1865(5):721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010
Stocker R, Keaney JF Jr (2004) Role of oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiol Rev 84(4):1381–1478. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00047.2003
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2016) Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(17):3221–3247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2223-0
Zhou C, Chen W, Zhang Z et al (2017) Antithrombotic comparison between colon delayed-release pellets and regular pellets of Whitmania pigra Whitman extract. Zhong Yao Xin Yao Yu Lin Chuang Yao Li 28(5):569–574
Wang X, Smith PL, Hsu MY, Ogletree ML, Schumacher WA (2006) Murine model of ferric chloride-induced vena cava thrombosis: evidence for effect of potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor. J Thromb Haemost 4(2):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01703.x
Demirci S, Sekeroğlu MR, Noyan T et al (2011) The importance of oxidative stress in patients with chronic renal failure whose hypertension is treated with peritoneal dialysis. Cell Biochem Funct 29(3):249–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.1744
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Editorial Committee (2015) Hirudo. In: Chinese pharmacopoeia editorial committee. The pharmacopoeia of the People’s republic of China. China Medical Science Press, Beijing, pp 83–84
Ren Y, Yang Y, Wu W, Zhang M, Wu H, Li X (2016) Identification and characterization of novel anticoagulant peptide with thrombolytic effect and nutrient oligopeptides with high branched chain amino acid from Whitmania pigra protein. Amino Acids 48(11):2657–2670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2299-8
Zheng X, Li J, Chen Z, Liu Y, Chen K (2015) Purification and characterization of an anticoagulant oligopeptide from Whitmania pigra Whitman. Pharmacogn Mag 11(43):444–448. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.160446
Chu F, Wang X, Sun Q et al (2016) Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from Whitmania pigra Whitman. Clin Exp Hypertens 38(7):594–601. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2016.1174254
Liu X, Wang C, Ding X, Liu X, Li Q, Kong Y (2016) A novel selective inhibitor to thrombin-induced platelet aggregation purified from the leech Whitmania pigra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473(1):349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.117
Yao XL, Liu H, Li P et al (2020) Aqueous extract of Whitmania Pigra Whitman alleviates thrombus burden via sirtuin 1/NF-κB pathway. J Surg Res 245:441–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2019.07.094
von Brühl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A et al (2012) Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J Exp Med 209(4):819–835. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20112322
Swystun LL, Liaw PC (2016) The role of leukocytes in thrombosis. Blood 128(6):753–762. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-05-718114
Ciciliano JC, Sakurai Y, Myers DR et al (2015) Resolving the multifaceted mechanisms of the ferric chloride thrombosis model using an interdisciplinary microfluidic approach. Blood 126(6):817–824. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-02-628594
Barr JD, Chauhan AK, Schaeffer GV, Hansen JK, Motto DG (2013) Red blood cells mediate the onset of thrombosis in the ferric chloride murine model. Blood 121(18):3733–3741. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-11-468983
Diaz JA, Obi AT, Myers DD Jr et al (2012) Critical review of mouse models of venous thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(3):556–562. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.244608
Budnik I, Brill A (2018) Immune factors in deep vein thrombosis initiation. Trends Immunol 39(8):610–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2018.04.010
Woollard KJ, Sturgeon S, Chin-Dusting JP, Salem HH, Jackson SP (2009) Erythrocyte hemolysis and hemoglobin oxidation promote ferric chloride-induced vascular injury. J Biol Chem 284(19):13110–13118. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809095200
Song D, Cheng Y, Li X et al (2017) Biogenic nanoselenium particles effectively attenuate oxidative stress-induced intestinal epithelial barrier injury by activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(17):14724–14740. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03377
Du L, Hu X, Chen C, Kuang T, Yin H, Wan L (2017) Seabuckthorn paste protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through attenuation of oxidative stress. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:4130967. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4130967
Xing X, Jiang Z, Tang X et al (2016) Sodium butyrate protects against oxidative stress in HepG2 cells through modulating Nrf2 pathway and mitochondrial function. J Physiol Biochem 73(3):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0568-y
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Open Project Program of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Non-clinical Evaluation and Research (No. 2018B030323024), Guangzhou Science and Technology Basic and Applied Basic Research Project (No. 202002030108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Baoqin Lin; Methodology: Peng Li, Bingqing Lin; Preparing first draft: Peng Li, Ping Tang; Formal analysis: Yuxin Ye, Zhongrui Wu; Critical editing of manuscript: Shuhua Gui, Yaxian Zhan, Wei Yang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Lin, B., Tang, P. et al. Aqueous extract of Whitmania pigra Whitman ameliorates ferric chloride-induced venous thrombosis in rats via antioxidation. J Thromb Thrombolysis 52, 59–68 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02337-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02337-8