Abstract
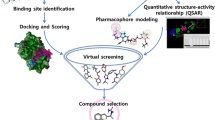
Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT) plays a key in the life cycle of HIV-1. It is considered to be one of the promising targets for treating HIV/AIDS which contains two drug binding sites, a substrate binding site, and an allosteric site. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are a class of RT inhibitors that bind to allosteric sites on HIV-1 RT in a non-competitive manner and thereby disrupting the conformation of RT. Hence, they can act as potent inhibitors against HIV-1 RT. In present study, the key structural requirements for enhancing HIV-1 RT inhibitory activity were explored from combined docking and three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship (3D QSAR) protocols. Initially, multiple-receptor conformation docking (MRCD) was performed using a series of diaryl pyridine and pyrimidine derivatives into the active site of ten X-ray crystal structures and one NMR-resolved conformation of HIV-1 RT. Later, the dock poses obtained from docking were clustered and 3D QSAR models were developed using comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity index analysis (CoMSIA) methods. Finally, a robust model was established using cross-validation techniques and the robustness of the model was confirmed through high accuracy of q2loo of 0.843 and 0.682, r2ncv of 0.977 and 0.949, and r2pred of 0.702 and 0.690, respectively, for CoMFA and CoMSIA. Based on the outcome of the results, new pyrimidine derivatives having potential inhibitory against HIV-1 RT were designed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sergeyev S, Yadav AK, Franck P, Michiels J, Lewi P, Heeres J, Vanham G, Arien KK, Christophe ML, Velde V, De Winter H, Maes BUW (2016) 2,6-Di(arylamino)-3-fluoropyridine derivatives as HIV non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Med Chem 59:1854–1868
Jochmans D (2008) Novel HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Virus Res 134:171–185
De Corte BL (2005) From 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methylimidazo[4,5,1-jk](1,4)benzodiazepin-2(1H)-one (TIBO) to etravirine (TMC125): fifteen years of research on non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Med Chem 48:1689–1696
Pauwels R (2004) New non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in development for the treatment of HIV infections. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:437–446
Tantillo C, Ding J, Jacobo-Molina A, Nanni RG, Boyer PL, Hughes SH, Pauwels R, Andries K, Janssen PA, Arnold E (1994) Locations of anti-AIDS drug binding sites and resistance mutations in the three-dimensional structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: Implications for mechanisms of drug inhibition and resistance. x 243:369–387
Bec G, Meyer B, Gerard MA, Steger J, Fauster K, Wolff P, Burnouf D, Micura R, Dumas P, Ennifar E (2013) Thermodynamics of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in action elucidates the mechanism of action of non-nucleoside inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 135:9743–9752
Xia Q, Radzio J, Anderson KS, Sluis-Cremer N (2007) Probing non-nucleoside inhibitor-induced active-site distortion in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by transient kinetic analyses. Protein Sci 16:1728–1737
Martins S, Ramos MJ, Fernandes PA (2008) The current status of the NNRTI family of antiretrovirals used in the HAART regime against HIV infection. Curr Med Chem 15:1083–1095
Das K, Clark AD, Lewi PJ, Heeres J, de Jonge MR, Koymans LM, Vinkers HM, Daeyaert F, Ludovici DW, Kukla MJ, De Corte B, Kavash RW, Ho CY, Ye H, Lichtenstein MA, Andries K, Pauwels R, De Béthune MP, Boyer PL, Clark P, Hughes SH, Janssen PA, Arnold E (2004) Roles of conformational and positional adaptability in structure-based design of TMC125-R165335 (etravirine) and related non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors that are highly potent and effective against wild-type and drug-resistant HIV-1 variants. J Med Chem 47:2550–2560
Dueweke TJ, Poppe SM, Romero DL, Swaney SM, So AG, Downey KM, Althaus IW, Reusser F, Busso M, Resnick L (1993) U-90152, a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37:1127–1131
Young SD, Britcher SF, Tran LO, Payne LS, Lumma WC, Lyle TA, Huff JR, Anderson PS, Olsen DB, Carroll SS (1995) L-743, 726 (DMP-266): a novel, highly potent non-nucleoside inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:2602–2605
Azijn H, Tirry I, Vingerhoets J, de Bethune MP, Kraus G, Boven K, Jochmans D, Van Craenenbroeck E, Picchio G, Rimsky LT (2010) TMC278, a next generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), active against wild-type and NNRTI-resistant HIV-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:718–727
Chen X, Zhan P, Li D, De Clercq E, Liu X (2011) Recent advances in DAPYs and related analogues as HIV-1 NNRTIs. Curr Med Chem 18:359–376
Mitsuya H, Weinhold KJ, Furman PA, St Clair MH, Lehrman SN, Gallo RC, Bolognesi D, Barry DW, Broder S (1985) 3′-Azido-3′-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:7096–7100
Zhan P, Pannecouque C, De Clercq E, Liu X (2016) Anti-HIV drug discovery and development: current innovations and future trends. J Med Chem 59:2849–2878
Schöller-Gyüre M, Kakuda TN, De Smedt G, Vanaken H, Bouche MP, Peeters M, Woodfall B, Hoetelmans RM (2008) A pharmacokinetic study of etravirine (TMC125) co-administered with ranitidine and omeprazole in HIV-negative volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 66:508–516
Seminari E, Castagna A, Lazzarin A (2008) Etravirine for the treatment of HIV infection. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 6:427–433
Fatima S, Jatavath MB, Bathini R, Sivan SK, Manga V (2014) Multiple receptor conformation docking, dock pose clustering and 3D QSAR studies on human poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitors. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 34:417–430
Peddi SR, Sivan SK, Manga V (2016) An integrated molecular modeling approach for in silico design of new tetracyclic derivatives as ALK inhibitors. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 36:488–504
Sivan SK, Manga V (2012) Multiple receptor conformation docking and dock pose clustering as tool for CoMFA and CoMSIA analysis—a case study on HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J Mol Model 18:569–582
Chong P, Sebahar P, Youngman M, Garrido D, Zhang H, Stewart EL, Nolte RT, Wang L, Ferris RG, Edelstein M, Weaver K, Mathis A, Peat A (2012) Rational design of potent non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Med Chem 55:10601–10609
Cote B, Burch JD, Asante-Appiah E, Bayly C, Bedard L, Blouin M, Campeau LC, Cauchon E, Chan M, Chefson A, Coulombe N, Cromlish W, Debnath S, Deschenes D, Dupont-Gaudet K, Falgueyret JP, Forget R, Gagne S, Gauvreau D, Girardin M, Guiral S, Langlois E, Li CS, Nguyen N, Papp R, Plamondon S, Roy A, Roy S, Seliniotakis R, St-Onge M, Ouellet S, Tawa P, Truchon JF, Vacca J, Wrona M, Yan Y, Ducharme Y (2014) Discovery of MK-1439, an orally bioavailable non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor potent against a wide range of resistant mutant HIV viruses. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:917–922
Gomez R, Jolly SJ, Williams T, Vacca JP, Torrent M, McGaughey G, Lai MT, Felock P, Munshi V, Distefano D, Flynn J, Miller M, Yan Y, Reid J, Sanchez R, Liang Y, Paton B, Wan BL, Anthony N (2011) Design and synthesis of conformationally constrained inhibitors of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase. J Med Chem 54:7920–7933
Kertesz DJ, Brotherton-Pleiss C, Yang M, Wang Z, Lin X, Qiu Z, Hirschfeld DR, Gleason S, Mirzadegan T, Dunten PW, Harris SF, Villasenor AG, Hang JQ, Heilek GM, Klumpp K (2010) Discovery of piperidin-4-yl-aminopyrimidines as HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. N-benzyl derivatives with broad potency against resistant mutant viruses. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:4215–4218
Lansdon EB, Brendza KM, Hung M, Wang R, Mukund S, Jin D, Birkus G, Kutty N, Liu X (2010) Crystal structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with etravirine (TMC125) and rilpivirine (TMC278): implications for drug design. J Med Chem 53:4295–4299
Laplante SR, Bilodeau F, Aubry N, Gillard JR, O’Meara J, Coulombe R (2013) N- versus O-alkylation: utilizing NMR methods to establish reliable primary structure determinations for drug discovery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:4663–4668
Parrish J, Tong L, Wang M, Chen X, Lansdon EB, Cannizzaro C, Zheng X, Desai MC, Xu L (2013) Synthesis and biological evaluation of phosphonate analogues of nevirapine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:1493–1497
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK, Shaw ED, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Wang L, Tian Y, Chen W, Liu H, Zhan P, Li D, Liu H, De Clercq E, Pannecouque C, Liu X (2014) Fused heterocycles bearing bridgehead nitrogen as potent HIV-1 NNRTIs. Part 2: discovery of novel [1,2,4] triazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidines using a structure-guided core-refining approach. Eur J Med Chem 85:293–303
Wan Z, Yao J, Tao Y, Mao T, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang H, Yin H, Wu Y, Chen F, De Clercq E, Daelemans D (2015) Discovery of piperidin-4-yl-aminopyrimidine derivatives as potent non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 97:1–9
Yang J, Chen W, Kang D, Lu X, Li X, Liu Z, Huang B, Daelemans D, Pannecouque C, De Clercq E, Zhan P, Liu X (2016) Design, synthesis and anti-HIV evaluation of novel diarylpyridine derivatives targeting the entrance channel of NNRTI binding pocket. Eur J Med Chem 109:294–304
Schrödinger LLC, 2010 Glide, Version 5.6. New York, NY
Sivan SK, Manga V (2010) Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies on triazolinone and pyridazinone, non-nucleoside inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Mol Model 16:1169–1178
Sybyl-X-2.1 version, 2013. Tripos Inc., and Certara, St. Louis (MO)
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228
Chitta A, Sivan SK, Manga V (2014) 3D QSAR based design of novel oxindole derivative as 5HT7 inhibitors. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 34:185–194
Cramer RDIII, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Singh U, Gangwal RP, Dhoke GV, Prajapati R, Damre M, Sangamwar AT (2017) 3D-QSAR and molecular docking analysis of (4-piperidinyl)-piperazines as acetyl-CoA carboxylases inhibitors. Arab J Chem 10:S617–S626
Pires DE, Blundell TL, Ascher DB (2015) pkCSM: predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J Med Chem 58:4066–4072
Acknowledgements
We greatly acknowledge Tripos Inc., USA, and Schrödinger LLC, New York, for providing the software. The author Saikiran Reddy Peddi (IF150172) would like to acknowledge the financial support from DST for a research fellowship.
Funding
This research was made possible through grants from DST-SERB (SB/EMEQ-004/2013) New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information consists of toxicity profile of dataset compounds calculated from pkCSM online server.
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peddi, S.R., Mohammed, N.A., Hussein, A.A. et al. Multiple-receptor conformation docking, dock pose clustering, and 3D QSAR-driven approaches exploring new HIV-1 RT inhibitors. Struct Chem 29, 999–1012 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-018-1082-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-018-1082-8