Abstract
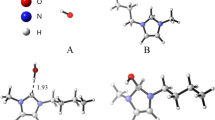
The hydrogen-bonding abilities of a few amino acid side chains have been studied through aggregation of methylamine, methanol, and acetic acid (as model molecules) with formo- and thioformo- hydroxamic acids using ab initio calculations. Forty six aggregates representing all possible H-bond interactions between these amino acid side chain groups and two most stable keto and enol tautomeric forms of both hydroxamic acids have been optimized. Although participation of conventional H-bond donors and acceptors leads to significant stabilization energies, yet C–H···O, C–H···N, S–H···O, and S–H···N etc. unconventional H-bonds also contribute to stabilize interactions in many aggregates. Strength of H-bonds of the molecules with formo- and thioformo- hydroxamic acid studied follows the order acetic acid > methylamine > methanol. A comparative study of atomic charges and orbital interactions employing NBO analysis has been carried out to explore the role of bond polarizations, charge transfer, and electron delocalizations as contributors to stabilization energy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berka K, Laskowski R, Riley KE, Hobza P, Vondràšek J (2009) J Chem Theory Comput 5:982
Scheiner S, Kar T, Pattanayak J (2002) J Am Chem Soc 124:13257
Nagy PI, Erhardt PW (2008) J Phys Chem A 112:4342
Banerjee R, Sen M, Bhattacharya D, Saha P (2003) J Mol Biol 333:211
Chakrabarti P, Bhattacharya R (2007) Prog Biophys Mol Biol 95:83
Misura KMS, Morozov AV, Baker D (2004) J Mol Biol 342:651
Mitchell JBO, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1998) Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 29:370
Braiman MS, Briercheck DM, Kriger KM (1999) J Phys Chem B 103:4744
Yang JM, Tsai CH, Hwang MJ, Tsai HK, Hwang JK, Kao CY (2002) Protein Sci 11:1897
Phillips ST, Piersanti G, Bartlett PA (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13727
Myers JK, Pace CN (1996) Biophys J 71:2033
Stickle DF, Presta LG, Dill KA, Rose GD (1992) J Mol Biol 226:1143
Bauer L, Exner O (1974) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 13:376
El Yazal J, Pang Y-P (2000) J Phys Chem B 104:6499
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Zakrzewski VG, Montgomery JA, Stratmann RE, Burant JC, Dapprich S, Millam JM, Daniels AD, Kudin KN, Strain MC, Farkas O, Tomasi J, Barone V, Cossi M, Cammi R, Mennucci B, Pomelli C, Adamo C, Clifford S, Ochterski J, Petersson GA, Ayala PY, Cui Q, Morokuma K, Rega N, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Cioslowski J, Ortiz JV, Baboul AG, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Gomperts R, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, AlLaham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Andres JL, Gonzalez C, Head-Gordon M, Replogle ES and Pople JA (2001) Gaussian Inc, Pittsburgh PA
Hehre WJ, Radom L, Schleyer PVR, Pople JA (1986) Ab initio molecular orbital theory. Wiley, New York
Foresman JB, Frisch E (1996) Exploring chemistry with electronic structure methods. Gaussian Inc, Pittsburgh, PA
Boys SF, Bernardi F (1970) Mol Phys 19:553
Aleman C (2001) J Phys Chem A 105:6717
Reed AE, Weinstock RB, Weinhold F (1985) J Chem Phys 83:735
Reed AE, Curtiss LA, Weinhold F (1988) Chem Rev 88:899
Kaur D, Kohli R (2008) Int J Quantum Chem 108:119
Kaur D, Kohli R, Kaur RP (2008) J Mol Struc (Theochem) 864:72
Kaur D, Kohli R (2011) Int J Quantum Chem 111:2931
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material. Supplementary data of the paper can be obtained from journal website. Data include Tables (S1–S15) incorporating electron delocalizations, atomic charges, and geometrical parameters of aggregates of both the HAs with MeNH2, MeOH, and AcOH.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
kaur, D., Kohli, R. Understanding hydrogen bonding of hydroxamic acids with some amino acid side chain model molecules. Struct Chem 23, 161–173 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9840-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9840-x