Abstract
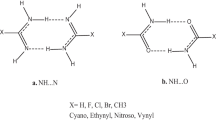
We have theoretically analyzed Watson–Crick AT and GC base pairs in which purine C8 and/or pyrimidine C6 positions carry a substituent X = H, F, Cl or Br, using the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) of density functional theory at BP86/TZ2P. The purpose is to study the effects on structure and hydrogen bond strength if X = H is substituted by a halogen atom. Furthermore, we wish to explore the relative importance of electrostatic attraction versus orbital interaction in the above multiply hydrogen-bonded systems, using a quantitative bond energy decomposition scheme. We find that replacing X = H by a halogen atom has relatively small yet characteristic effects on hydrogen bond lengths, strengths and bonding mechanism. In general, it reduces the hydrogen-bond-accepting- and increases the hydrogen-bond-donating capabilities of a DNA base. The orbital interaction component in these hydrogen bonds is found for all substituents (X = H, F, Cl, and Br) to contribute about 41% of the attractive interactions and is thus of the same order of magnitude as the electrostatic component, which provides the remaining 59% of the attraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
(a) Stryer, L. Biochemistry; Freeman: New York, 1988. (b) Jeffrey, G. A.; Saenger, W. Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Structures; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1991. (c) Jeffrey, G. A. An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding; Oxford University Press: New York, 1997.
(a) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M. Angew. Chem. 1999, 111, 3120; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2942. (b) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M.; Snijders, J. G.; Baerends, E. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4117. (c) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M.; Snijders, J. G.; Baerends, E. J. Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 3581. (d) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Baerends, E. J.; Bickelhaupt, F. M. Crystal Growth Design 2002, 2, 239. (e) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M. Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 2194; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2092. (f) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 4262. (g) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Bickelhaupt, F. M.; Baerends, E. J. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2004, 5, 481.
(a) Hobza, P.; Sponer, J. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3247. (b) Bertran, J.; Oliva, A.; Rodríguez-Santiago, L.; Sodupe, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 8159. (c) Brameld, K.; Dasgupta, S.; Goddard, W. A. III. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 4851. (d) Sponer, J.; Leszczynski, J.; Hobza, P. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 1965. (e) Gould, I. R.; Kollman, P. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2493. (f) Santamaria, R.; Vázquez, A. J. Comp. Chem. 1994, 15, 981. (g) Sponer, J.; Hobza, P. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 4592. (h) Hobza, P.; Sponer, J.; Cubero, E.; Orozco, M.; Luque, F. J. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 6286. (i) Poater, J.; Fradera, X.; Solà, M.; Duran, M.; Simon, S. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 369, 248.
Bickelhaupt, F. M.; Baerends, E. J. In Rev. Comput. Chem.; Lipkowitz, K. B.; Boyd, D. B., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: New York, 2000; Vol. 15, pp. 1–86.
(a) te Velde, G.; Bickelhaupt, F. M.; van Gisbergen, S. J. A.; Fonseca Guerra, C.; Baerends, E. J.; Snijders, J. G.; Ziegler, T. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 931. (b) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Visser, O.; Snijders, J. G.; te Velde, G.; Baerends, E. J. In Methods and Techniques for Computational Chemistry; Clementi, E.; Corongiu, G.; Eds.; STEF: Cagliari, 1995, pp. 305–395. (c) Baerends, E. J.; Ellis, D. E.; Ros, P. Chem. Phys. 1973, 2, 41. (d) Baerends, E. J.; Ros, P. Chem. Phys. 1975, 8, 412. (e) Baerends, E. J.; Ros, P. Int. J. Quantum Chem. Symp. 1978, 12, 169. (f) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Snijders, J. G.; te Velde, G.; Baerends, E. J. Theor. Chem. Acc. 1998, 99, 391. (g) Boerrigter, P. M.; te Velde, G.; Baerends, E. J. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1988, 33, 87. (h) te Velde, G.; Baerends, E. J. J. Comp. Phys. 1992, 99, 84. (i) Snijders, J. G.; Baerends, E. J.; Vernooijs, P. At. Nucl. Data Tables 1982, 26, 483. (j) Krijn, J.; Baerends, E. J. Fit-Functions in the HFS-Method (internal report in Dutch); Vrije Universiteit: Amsterdam, 1984. (k) Versluis, L.; Ziegler, T. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 88, 322. (l) Slater, J. C. Quantum Theory of Molecules and Solids; McGraw-Hill: New York, 1974; Vol. 4. (m) Becke, A. D. J. Chem. Phys. 1986, 84, 4524. (n) Becke, A. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098. (o) Vosko, S. H.; Wilk, L.; Nusair, M. Can. J. Phys. 1980, 58, 1200. (p) Perdew, J. P. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 8822; Erratum: Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 7406. (q) Fan, L.; Ziegler, T. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 94, 6057.
Vögtle, F. Supramolecular Chemistry; Wiley: Chichester, 1993.
Crooke, S. T., Ed. Antisense Research and Application; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1998.
(a) Kawahara, S.-I.; Uchimaru, T.; Taira, K.; Sekine, M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 3207. (b) Kawahara, S.-I.; Kobori, A.; Sekine, M.; Taira, K.; Uchimaru, T. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, 105, 10596. (c) Kawahara, S.-I; Uchimaru, T.; Taira, K.; Sekine, M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 3894. (d) Kawahara, S.-I.; Wada, T.; Kawauchi, S.; Uchimaru, T.; Sekine, M. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 8516.
Meng, F.; Liu, C.; Xu, W. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 373, 72.
(a) Morokuma, K. Chem. Phys. 1971, 55, 1236. (b) Kitaura, K.; Morokuma, K. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1976, 10, 325.
(a) Ziegler, T.; Rauk, A. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 18, 1755. (b) Ziegler, T.; Rauk, A. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 18, 1558; (c) Ziegler, T.; Rauk, A. Theor. Chim. Acta 1977, 46, 1.
(a) Stone, A. J. The Theory of Intermolecular Forces; Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1996. (b) Stone, A. J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 211, 101.
(a) Fonseca Guerra, C.; Handgraaf, J.-W.; Baerends, E. J; Bickelhaupt, F. M. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 189. (b) Bickelhaupt, F. M.; van Eikema Hommes, N. J. R.; Fonseca Guerra, C.; Baerends, E. J. Organometallics 1996, 15, 2923.
(a) Voronoi, G. F.; Reine, Z. Angew. Math. 1908, 134, 198. (b) Kittel, C. Introduction to Solid State Physics; Wiley: New York, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra, C.F., van der Wijst, T. & Bickelhaupt, F.M. Substituent Effects on Hydrogen Bonding in Watson–Crick Base Pairs. A Theoretical Study. Struct Chem 16, 211–221 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-005-4453-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-005-4453-x