Abstract
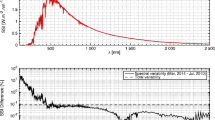
An understanding of solar variability over a broad spectral range and broad range of timescales is needed by scientists studying Earth’s climate. The Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor (TSIS) Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SIM), is designed to measure solar spectral irradiance (SSI) with unprecedented accuracy from 200 nm to 2400 nm. SIM started daily observations in March 2018. To maintain its accuracy over the course of its anticipated 5-year mission and beyond, TSIS SIM needs to be corrected for optical degradation, common for solar viewing instruments. The differing long-term trends of various independent solar-irradiance records attest to the challenge at hand.
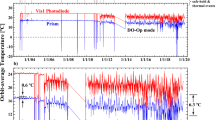
The correction of TSIS SIM for optical degradation is based on piecewise linear fits that bring the three instrument channels into agreement. It is fundamentally different to the correction applied to the TSIS SIM predecessor on SORCE. The correction facilitates reproducibility, uncertainty estimation and is measurement-based. Corrected, integrated TSIS SIM SSI agrees with independent observations of total solar irradiance to within 45 ppm as well as various solar-irradiance models. TSIS SIM SSI is available at: http://lasp.colorado.edu/lisird/.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Béland, S., Harder, J., Woods, T.: 2013, 10 years of degradation trends of the SORCE SIM instrument. In: SPIE 8862. 88620O.
Béland, S., Harder, J., Woods, T.: 2014, Eleven years of tracking the SORCE SIM instrument degradation caused by space radiation and solar exposure. In: Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2014: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave. 91434W.
BenMoussa, A., Gissot, S., Schühle, U., Del Zanna, G., Auchère, F., Mekaoui, S., Jones, A.R., Walton, D., Eyles, C.J., et al.: 2013, On-orbit degradation of solar instruments. Solar Phys. 288, 389. DOI.
Coddington, O., Lean, J.L., Pilewskie, P., Snow, M., Lindholm, D.: 2015, A solar irradiance climate data record. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 1265. DOI.
Dewitte, S., Crommelynck, D., Joukoff, A.: 2004, Total solar irradiance observations from DIARAD/VIRGO. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A02102. DOI.
Dudok de Wit, T., Kopp, G., Fröhlich, C., Schöll, M.: 2017, Methodology to create a new total solar irradiance record: Making a composite out of multiple data records. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 1196. DOI.
Ermolli, I., Matthes, K., Dudok De Wit, T., Krivova, N.A., Tourpali, K., Weber, M., Unruh, Y.C., Gray, L., Langematz, U., et al.: 2013, Recent variability of the solar spectral irradiance and its impact on climate modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13, 3945. DOI.
Fligge, M., Solanki, S.K., Unruh, Y.C.: 2000, Modelling irradiance variations from the surface distribution of the solar magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 353, 380.
Gray, L.J., Beer, J., Geller, M., Haigh, J.D., Lockwood, M., Matthes, K., Cubasch, U., Fleitmann, D., Harrison, G., et al.: 2010, Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 48, RG4001. DOI.
Haberreiter, M., Schöll, M., Dudok de Wit, T., Kretzschmar, M., Misios, S., Tourpali, K., Schmutz, W.: 2017, A new observational solar irradiance composite. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 5910. DOI.
Haigh, J.D.: 1994, The role of stratospheric ozone in modulating the solar radiative forcing of climate. Nature 370, 544. DOI.
Haigh, J.D., Winning, A.R., Toumi, R., Harder, J.W.: 2010, An influence of solar spectral variations on radiative forcing of climate. Nature 467, 696. DOI.
Harder, J., Fontenla, J.M., Pilewskie, P., Richard, E.C., Woods, T.N.: 2009, Trends in solar spectral irradiance variability in the visible and infrared. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, 1. DOI.
Harder, J., Lawrence, G., Fontenla, J., Rottman, G., Woods, T.: 2005, The spectral irradiance monitor: Scientific requirements, instrument design, and operation modes. In: Rottman, G., Woods, T., George, V. (eds.) The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), Springer, New York, 141.
Kopp, G.: 2016, Magnitudes and timescales of total solar irradiance variability. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 6, A30. DOI.
Kopp, G., Lawrence, G.: 2005, The total irradiance monitor (TIM): instrument design. In: Rottman, G., Woods, T., George, V. (eds.) The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), Springer, New York, 91.
Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K., Fligge, M., Unruh, Y.C.: 2003, Reconstruction of solar irradiance variations in cycle 23: Is solar surface magnetism the cause? Astron. Astrophys. 399, L1. DOI.
Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K., Floyd, L.: 2006, Reconstruction of solar UV irradiance in cycle 23. Astron. Astrophys. 452, 631. DOI.
LASP: 2019, SORCE SIM Release Notes for Version 25, Level 3 data product. http://lasp.colorado.edu/home/sorce/files/2019/03/SORCE_SIM_Release_Notes_for_Version25.pdf. Accessed 13 Nov 2019.
Lean, J.: 2000, Evolution of the Sun’s spectral irradiance since the Maunder Minimum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 2425. DOI.
Lean, J., Rottman, G., Harder, J., Kopp, G.: 2005, SORCE contributions to new understanding of global change and solar variability. Solar Phys. 230, 27. DOI.
Lean, J.L., DeLand, M.T.: 2012, How does the Sun’s spectrum vary? J. Climate 25, 2555. DOI.
Lean, J.L., Woods, T.N.: 2010, Solar spectral irradiance: Measurements and models. In: Schrijver, C.J., Siscoe, L., George, L. (eds.) Heliophysics: Evolving Solar Activity and the Climates of Space and Earth, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 269.
Marchenko, S.V., Deland, M.T.: 2014, Solar spectral irradiance changes during cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 789, 117. DOI.
Marchenko, S.V., DeLand, M.T., Lean, J.L.: 2016, Solar spectral irradiance variability in cycle 24: Observations and models. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 40, 1. DOI.
Mauceri, S., Pilewskie, P., Richard, E., Coddington, O., Harder, J., Woods, T.: 2018, Revision of the Sun’s spectral irradiance as measured by SORCE SIM. Solar Phys. 293, 161. DOI.
Mauceri, S., Coddington, O., Lyles, D., Pilewskie, P.: 2019, Neural network for solar irradiance modeling (NN-SIM). Solar Phys. 294, 160. DOI.
Mauceri, S., Pilewskie, P., Woods, T., Beland, S., Richard, E.C.: 2020, Inter-comparing solar spectral irradiance from SORCE SIM. Earth Space Sci. 7(4), e2019EA001002. DOI.
McClintock, W.E., Rottman, G.J., Woods, T.N.: 2005, Solar-stellar irradiance comparison experiment II (SOLSTICE II): instrument concept and design. In: Rottman, G., Woods, T., George, V. (eds.) The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), Springer, New York, 225.
Pilewskie, P., Richard, E., Coddington, O., Harder, J.: 2016, Solar spectral irradiance and climate: Current understanding and future observations from the total and spectral solar irradiance sensor. In: Int. Radiat. Symp. Univ. Auckland, New Zeal.
Richard, E., Harber, D., Coddington, O., Drake, G., Rutkowski, J., Triplett, M., Pilewskie, P., Woods, T.: 2020, SI-traceable spectral irradiance radiometric characterization and absolute calibration of the TSIS-1 Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SIM). Remote Sens. 12, 1818.
Woods, T.N., Eparvier, F.G., Harder, J., Snow, M.: 2018, Decoupling solar variability and instrument trends using the Multiple Same-Irradiance-Level (MuSIL) analysis technique. Solar Phys. 293, 76. DOI.
Yeo, K.L., Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K., Glassmeier, K.H.: 2014, Reconstruction of total and spectral solar irradiance from 1974 to 2013 based on KPVT, SoHO/MDI, and SDO/HMI observations. Astron. Astrophys. 570, A85. DOI.
Acknowledgements
We thank the scientists and engineers that worked for more than a decade to make TSIS SIM a reality.
Furthermore, we thank the scientists and engineers that made the many solar-irradiance datasets available that we compared to. For comparison, we made use of the SATIRE-S and NRLSSI2 solar-irradiance models, SORCE SIM SSI, SORCE SOLSTICE SSI, SORCE TIM TSI, and TSIS TIM TSI.
This research was supported in part by 80GSFC18C0056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauceri, S., Richard, E., Pilewskie, P. et al. Degradation Correction of TSIS SIM. Sol Phys 295, 152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01707-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01707-y