Abstract
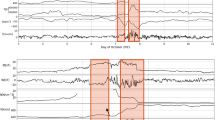
The plasma of the solar wind incident upon the Earth’s magnetosphere can produce several types of geoeffective events. Among them, an important phenomenon consists of the interrelation of the magnetospheric–ionospheric current systems and the charged-particle population of the Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts. Ultra-low-frequency (ULF) waves resonantly interacting with such particles have been claimed to play a major role in the energetic particle flux changes, particularly at the outer radiation belt, which is mainly composed of electrons at relativistic energies. In this article, we use global magnetohydrodynamic simulations along with in situ and ground-based observations to evaluate the ability of two different solar wind transient (SWT) events to generate ULF (few to tens of mHz) waves in the equatorial region of the inner magnetosphere. Magnetic field and plasma data from the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) satellite were used to characterize these two SWT events as being a sector boundary crossing (SBC) on 24 September 2013, and an interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME) in conjunction with a shock on 2 October 2013. Associated with these events, the twin Van Allen Probes measured a depletion of the outer belt relativistic electron flux concurrent with magnetic and electric field power spectra consistent with ULF waves. Two ground-based observatories apart in 90∘ longitude also showed evidence of ULF-wave activity for the two SWT events. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulation results show that the ULF-like oscillations in the modeled electric and magnetic fields observed during both events are a result from the SWT coupling to the magnetosphere. The analysis of the MHD simulation results together with the observations leads to the conclusion that the two SWT structures analyzed in this article can be geoeffective on different levels, with each one leading to distinct ring current intensities, but both SWTs are related to the same disturbance in the outer radiation belt, i.e. a dropout in the relativistic electron fluxes. Therefore, minor disturbances in the solar wind parameters, such as those related to an SBC, may initiate physical processes that are able to be geoeffective for the outer radiation belt.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, D.N., Li, X., Turner, N., Allen, J.H., Bargatze, L.F., Blake, J.B., et al.: 1997, Recurrent geomagnetic storms and relativistic electron enhancements in the outer magnetosphere: ISTP coordinated measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 102(A7), 14141. DOI .
Baker, D.N., Kanekal, S.G., Hoxie, V.C., Batiste, S., Bolton, M., Li, X., et al.: 2013, The relativistic electron-proton telescope (rept) instrument on board the radiation belt storm probes (rbsp) spacecraft: Characterization of earth’s radiation belt high-energy particle populations. Space Sci. Rev. 179(1), 337. DOI .
Borovsky, J.E., Denton, M.H.: 2016, Compressional perturbations of the dayside magnetosphere during high-speed-stream-driven geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 121(5), 4569. DOI .
Crooker, N.U.: 2000, Solar and heliospheric geoeffective disturbances. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 62(12), 1071. DOI .
De Zeeuw, D.L., Sazykin, S., Wolf, R.A., Gombosi, T.I., Ridley, A.J., Tóth, G.: 2004, Coupling of a global mhd code and an inner magnetospheric model: Initial results. J. Geophys. Res. 109(A12), A12219. DOI .
Elkington, S.R.: 2006, A review of ULF interactions with radiation belt electrons. In: Magnetospheric ULF Waves: Synthesis and New Directions, AGU, Washington. DOI .
Gombosi, T.I., Powell, K.G., De Zeeuw, D.L., Clauer, C.R., Hansen, K.C., Manchester, W.B., Ridley, A.J., Roussev, I.I., Sokolov, I.V., Stout, Q.F., Tóth, G.: 2004, Solution-adaptive magnetohydrodynamics for space plasmas: Sun-to-earth simulations. Comput. Sci. Eng. 6(2). DOI
Green, J.C., Kivelson, M.G.: 2001, A tale of two theories: How the adiabatic response and ulf waves affect relativistic electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A11), 25777. DOI .
Hao, Y.X., Zong, Q.-G., Wang, Y.F., Zhou, X.-Z., Zhang, H., Fu, S.Y., et al.: 2014, Interactions of energetic electrons with ulf waves triggered by interplanetary shock: Van allen probes observations in the magnetotail. J. Geophys. Res. 119(10), 8262. DOI .
Hudson, M.K., Elkington, S.R., Lyon, J.G., Goodrich, C.C., Rosenberg, T.J.: 1999, Simulation of radiation belt dynamics driven by solar wind variations. In: Burch, J.L., Carovillano, R.L., Antiochos, S.K. (eds.) Sun–Earth Plasma Connections, AGU, Washington. DOI .
Hudson, M.K., Baker, D.N., Goldstein, J., Kress, B.T., Paral, J., Toffoletto, F.R., Wiltberger, M.: 2014, Simulated magnetopause losses and van allen probe flux dropouts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41(4), 1113. DOI .
Ilie, R., Liemohn, M.W., Ridley, A.: 2010, The effect of smoothed solar wind inputs on global modeling results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115(A1), A01213. DOI .
Imajo, S., Yumoto, K., Uozumi, T., Kawano, H., Abe, S., Ikeda, A., et al.: 2014, Analysis of propagation delays of compressional pi 2 waves between geosynchronous altitude and low latitudes. Earth Planets Space 66(1), 1. DOI .
Kivelson, M.G., Russell, C.T. (eds.): 1995, Introduction to Space Physics, Cambridge Univ. Press, New York.
Kletzing, C.A., Kurth, W.S., Acuna, M., MacDowall, R.J., Torbert, R.B., Averkamp, T., et al.: 2013, The electric and magnetic field instrument suite and integrated science (EMFISIS) on RBSP. Space Sci. Rev. 179(1), 127. DOI .
Lyatsky, W., Khazanov, G.V.: 2008, A predictive model for relativistic electrons at geostationary orbit. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35(15), L15108. DOI .
Mathie, R.A., Mann, I.R.: 2000, A correlation between extended intervals of ulf wave power and storm-time geosynchronous relativistic electron flux enhancements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(20), 3261. DOI .
Mauk, B.H., Fox, N.J., Kanekal, S.G., Kessel, R.L., Sibeck, D.G., Ukhorskiy, A.: 2013, Science objectives and rationale for the radiation belt storm probes mission. Space Sci. Rev. 179(1), 3. DOI .
Millan, R.M., Thorne, R.M.: 2007, Review of radiation belt relativistic electron losses. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 69(3), 362. DOI .
Miyoshi, Y., Kataoka, R.: 2008, Flux enhancement of the outer radiation belt electrons after the arrival of stream interaction regions. J. Geophys. Res. 113(A3), A03S09. DOI .
Murphy, K.R., Rae, I.J., Mann, I.R., Walsh, A.P., Milling, D.K., Kale, A.: 2011, The dependence of pi2 waveforms on periodic velocity enhancements within bursty bulk flows. Ann. Geophys. 29(3), 493.
Northrop, T.G.: 1963, Adiabatic charged-particle motion. Rev. Geophys. 1(3), 283. DOI .
Paral, J., Hudson, M.K., Kress, B.T., Wiltberger, M.J., Wygant, J.R., Singer, H.J.: 2015, Magnetohydrodynamic modeling of three van Allen probes storms in 2012 and 2013. Ann. Geophys. 33(8), 1037. DOI .
Paulikas, G.A., Blake, J.B.: 1979, Effects of the solar wind on magnetospheric dynamics: Energetic electrons at the synchronous orbit. In: Olson, W.P. (ed.) Quantitative Modeling of Magnetospheric Processes, AGU, Washington. DOI .
Reeves, G.D., McAdams, K.L., Friedel, R.H.W., O’Brien, T.P.: 2003, Acceleration and loss of relativistic electrons during geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(10), 1529. DOI .
Reeves, G.D., Morley, S.K., Friedel, R.H.W., Henderson, M.G., Cayton, T.E., Cunningham, G., et al.: 2011, On the relationship between relativistic electron flux and solar wind velocity: Paulikas and Blake revisited. J. Geophys. Res. 116(A2), A02213. DOI .
Ridley, A.J., Liemohn, M.W.: 2002, A model-derived storm time asymmetric ring current driven electric field description. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A8), SMP2.
Ridley, A.J., Gombosi, T.I., DeZeeuw, D.L.: 2004, Ionospheric control of the magnetosphere: Conductance. Ann. Geophys. 22(2), 567. DOI .
Roederer, J.G.: 1970, Dynamics of Geomagnetically Trapped Radiation, Vol. 2, Springer, Berlin.
Shprits, Y.Y., Thorne, R.M., Friedel, R., Reeves, G.D., Fennell, J., Baker, D.N., Kanekal, S.G.: 2006, Outward radial diffusion driven by losses at magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. 111(A11), A11214. DOI .
Shue, J.-H., Song, P., Russell, C.T., Steinberg, J.T., Chao, J.K., Zastenker, G., et al.: 1998, Magnetopause location under extreme solar wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 103(A8), 17691. DOI .
Stone, E.C., Frandsen, A.M., Mewaldt, R.A., Christian, E.R., Margolies, D., Ormes, J.F., Snow, F.: 1998, The advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1. DOI .
Su, Z., Gao, Z., Zhu, H., Li, W., Zheng, H., Wang, Y., et al.: 2016, Nonstorm time dropout of radiation belt electron fluxes on 24 September 2013. J. Geophys. Res. 121(7), 6400. 2016JA022546. DOI .
Su, Z., Zhu, H., Xiao, F., Zheng, H., Wang, Y., He, Z., Shen, C., Shen, C., Wang, C.B., Liu, R., Zhang, M., Wang, S., Kletzing, C.A., Kurth, W.S., Hospodarsky, G.B., Spence, H.E., Reeves, G.D., Funsten, H.O., Blake, J.B., Baker, D.N., Wygant, J.R.: 2014, Intense duskside lower band chorus waves observed by van allen probes: Generation and potential acceleration effect on radiation belt electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 119(6), 4266. DOI .
Tóth, G., van der Holst, B., Sokolov, I.V., Zeeuw, D.L.D., Gombosi, T.I., Fang, F., Manchester, W.B., Meng, X., Najib, D., Powell, K.G., Stout, Q.F., Glocer, A., Ma, Y.-J., Opher, M.: 2011, Adaptive numerical algorithms in space weather modeling. J. Comput. Phys. 231(3), 870. DOI .
Tsyganenko, N.A.: 2002, A model of the near magnetosphere with a dawn-dusk asymmetry 2. parameterization and fitting to observations. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A8), SMP10. DOI .
Tsyganenko, N.A., Sitnov, M.I.: 2005, Modeling the dynamics of the inner magnetosphere during strong geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 110(A3), A03208. DOI .
Wing, S., Johnson, J.R., Camporeale, E., Reeves, G.D.: 2016, Information theoretical approach to discovering solar wind drivers of the outer radiation belt. J. Geophys. Res. DOI .
Wygant, J.R., Bonnell, J.W., Goetz, K., Ergun, R.E., Mozer, F.S., Bale, S.D., et al.: 2013, The electric field and waves instruments on the radiation belt storm probes mission. Space Sci. Rev. 179(1–4), 183. DOI .
Xiang, Z., Ni, B., Zhou, C., Zou, Z., Gu, X., Zhao, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, S., Li, X., Zuo, P., Spence, H., Reeves, G.: 2016, Multi-satellite simultaneous observations of magnetopause and atmospheric losses of radiation belt electrons during an intense solar wind dynamic pressure pulse. Ann. Geophys. 34(5), 493. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Center for Space Environment Modeling (CSEM) at the University of Michigan for providing the numerical SWMF/BATS-R-US Code available at: http://csem.engin.umich.edu/tools/swmf/downloads.php . We acknowledge the Kakioka Magnetic Observatory of the Japan Meteorological Agency and Bureau Central de Magnetisme Terrestre (France) for providing the geomagnetic field 1-second digitized data. We are also in debt to the Van Allen Probes mission teams, NASA’s CDAWeb, OMNI, and NGDC for online data access and data analysis tools. Solar wind parameters presented in Section 2 measured by ACE are available at http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/browse-data/browse-curr/ . The Van Allen Probes mission datasets presented in Sections 2 and 4 and supporting information are available at CDAWeb http://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/istp_public/ .
C.R. Braga and V.M. Souza thank the São Paulo research foundation (FAPESP) for grant 2014/24711-6 and 2014/21229-9. A. Dal Lago, M. Rockenbach, M.V. Alves, R.R.S. de Mendonça and D. Koga thank CNPq for research grant 304209/2014-7, 301495/2015-7, 305373/2010-2, 152050/2016-7, and 112886/2015-9. P.R. Jauer and L.A. da Silva thank the Research Foundation CNPq/PCI for financial support process number 313281/2015-7 and 312743/2015-7. We would also like to thank CT-INFRA-FINEP/INPE 11 number 01.12.0527.00 and EMBRACE/INPE: http://www2.inpe.br/climaespacial/portal/en/ .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Earth-Affecting Solar Transients
Guest Editors: Jie Zhang, Xochitl Blanco-Cano, Nariaki Nitta, and Nandita Srivastava
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, L.R., Souza, V.M., Jauer, P.R. et al. The Role of Solar Wind Structures in the Generation of ULF Waves in the Inner Magnetosphere. Sol Phys 292, 92 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1113-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1113-4