Abstract
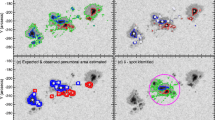
A method based on set and graph operations was developed to find and track related entities of sunspot groups on a series of consecutive solar images. Of course, if we can track entities of a sunspot group, we can also track various properties (e.g., position, area, magnetic field, and intensity) associated with them. A new higher-level sunspot-group entity belonging to the whole image series, a family, was introduced to cope with the mergings and separations of various sunspot group entities.
To demonstrate the usefulness of the method, it was applied to NOAA AR 11429 using Solar Dynamics Observatory/Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (SDO/HMI) images. This large sunspot group produced several X, M, and C class flares, among others, an X5.4 class flare on 2012 March 7. Abrupt transient and permanent variations in the mean line-of-sight (LOS) magnetic field of the large umbra families were found during the X5.4 flare. Two small umbra families immediately next to the polarity inversion line (PIL) and facing each other at opposite sides of the PIL exhibited abrupt stepwise changes in their mean LOS magnetic field during the X5.4 flare. The family with positive polarity decreased and the family with negative polarity increased. Some of the large umbra families also showed abrupt decrease in their darkness during the flare. We conjecture that an umbra family being a part of a long, narrow magnetic field strip pushing in an opposite magnetic polarity penumbral domain might be one of the triggering causes of several flares. Flare-related changes were observed at every spatial scale of the studied sunspot group. Two of the large opposite-polarity umbra families underwent shearing and converging motions. The break and the turning points of the motion curves of these families were related to flares. Some of the flares coincided with abrupt changes in the motion curves.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F., Aly, J.J., Mikic, Z., Linker, J.: 2003, Coronal mass ejection: Initiation, magnetic helicity, and flux ropes. I. Boundary motion-driven evolution. Astrophys. J. 585, 1073. DOI .
Anwar, B., Acton, L.W., Hudson, H.S., Makita, M., McClymont, A.N., Tsuneta, S.: 1993, Rapid sunspot motion during a major solar flare. Solar Phys. 147, 287. DOI .
Brown, D.S., Nightingale, R.W., Alexander, D., Schrijver, C.J., Metcalf, T.R., Shine, R.A., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J.: 2003, Observations of rotating sunspots from TRACE. Solar Phys. 216, 79. DOI .
Démoulin, P., Hénoux, J.C., Mandrini, C.H.: 1992, Development of a topological model for solar flares. Solar Phys. 139, 105. DOI .
Deng, N., Liu, C., Yang, G., Wang, H., Denker, C.: 2005, Rapid penumbral decay associated with an X2.3 flare in NOAA active region 9026. Astrophys. J. 623, 1195. DOI .
Dezső, L., Gesztelyi, L., Kondás, L., Kovács, A., Rostás, S.: 1980, Motions in the solar atmosphere associated with the white light flare of 11 July 1978. Solar Phys. 11, 67. DOI .
Ding, M.D., Qui, J., Wang, H.: 2002, Non-LTE calculation of the Ni I 676.8 nanometer line in a flaring atmosphere. Astrophys. J. Lett. 576, L83. DOI .
Fisher, G.H., Bercik, D.J., Welsch, B.T., Hudson, H.S.: 2012, Global forces in eruptive solar flares: The Lorentz force acting on solar atmosphere and solar interior. Solar Phys. 277, 59. DOI .
Gosain, S.: 2012, Evidence for collapsing fields in the corona and photosphere during the 2011 February 15 X2.2 flare: SDO/AIA and HMI observations. Astrophys. J. 749, 85. DOI .
Gosain, S., Venkatakrishnan, P., Tiwari, S.K.: 2009, Hinode observations of coherent lateral motion of penumbral filaments during an X-class flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 706, L240. DOI .
Győri, L.: 1998, Automation of area measurement of sunspots. Solar Phys. 180, 109. DOI .
Hagenaar, H.J., Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M., Shine, R.A.: 1999, Dispersal of magnetic flux in the quiet solar photosphere. Astrophys. J. 511, 932. DOI .
Hudson, H.S., Fisher, G.H., Welsh, B.T.: 2008, In: Howe, R., Komm, R.W., Balasubramaniam, K.S., Petrie, G.J.D. (eds.) Subsurface and Atmospheric Influences on Solar Activity, ASP. Conf. Ser. 383, 221.
Kosovichev, A.G., Zharkova, V.V.: 2001, Magnetic energy release and transients in the solar flare of 2000 July 14. Astrophys. J. Lett. 550, L105. DOI .
Liu, C., Deng, N., Liu, Y., Flconer, D., Goode, P.R., Denker, C., Wang, H.: 2005, Rapid change of \(\delta\) spot structure associated with seven major flares. Astrophys. J. 622, 722. DOI .
Liu, C., Deng, N., Liu, R., Lee, J., Wiegelmann, T., Wang, H.: 2012, Rapid changes of photospheric magnetic field after tether-cutting reconnection and magnetic implosion. Astrophys. J. Lett. 745, L4. DOI .
Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Hénoux, J.C., Machado, M.E.: 1991, Evidence for the interaction of large scale magnetic structures in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 250, 541.
Mandrini, C.H., Rovira, M.G., Démoulin, P., Hénoux, J.C., Machado, M.E., Wilkinson, L.K.: 1993, Evidence for magnetic reconnection in large-scale magnetic structures in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 272, 609.
Melrose, D.B.: 1997, A solar flare model based on magnetic reconnection between current-carrying loops. Astrophys. J. 486, 521.
Moore, R.L., Sterling, A.C., Hudson, H.S., Lemen, J.R.: 2001, Onset of the magnetic explosion in solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 552, 833.
Murray, S.A., Bloomfield, D.S., Gallagher, P.T.: 2012, The evolution of sunspot magnetic fields associated with a solar flare. Solar Phys. 277, 45. DOI .
Patterson, A., Zirin, H.: 1981, Transient magnetic field changes in flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 243, L99. DOI .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI .
Petrie, G.J.D.: 2013, A spatio-temporal description of the abrupt changes in the photospheric magnetic and Lorentz-force vectors during the 15 February 2011 X2.2 flare. Solar Phys. 287, 415. DOI .
Petrie, G.J.D., Sudol, J.J.: 2010, Abrupt longitudinal magnetic field changes in flaring active regions. Astrophys. J. 724, 1218. DOI .
Piddington, J.H.: 1979, Solar flares – Models and predictions of the flux-rope theory. Astrophys. J. 233, 727. DOI .
Qiu, J., Gary, D.E.: 2003, Flare-related magnetic anomaly with a sign reversal. Astrophys. J. 599, 615. DOI .
Raman, K.S., Ramesh, K.B., Selvendran, R.: 2003, The role of sunspot umbral rotation in triggerig solar flares. Bull. Astron. Soc. India 31, 101.
Schmieder, B., Hagyard, M.J., Ai, G., Zhang, H., Kálman, B., Győri, L., Rompolt, B., Démoulin, P., Machado, M.E.: 1994, Relationship between magnetic field evolution and flaring site in AR 6659 in June 1991. Solar Phys. 150, 199. DOI .
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., Wachter, R., Couvidat, S., Rabello-Soares, M.C., et al.: 2012, Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 229. DOI .
Strous, L.H., Scharmer, G., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Zwaan, C.: 1996, Phenomena in an emerging active region. I. Horizontal dynamics. Astron. Astrophys. 306, 947.
Tan, C., Chen, P.F., Abramenko, V., Wang, H.: 2009, Evolution of optical penumbral and shear flows associated with the X3.4 flare of 2006 December 13. Astrophys. J. 690, 1820. DOI .
Vemareddy, P., Ambastha, A., Maurya, R.A.: 2012, On the role of rotating sunspots in the activity of solar active region NOAA 11158. Astrophys. J. 761, 60. DOI .
Wang, H., Deng, N., Liu, C.: 2012, Rapid transition of uncombed penumbrae to faculae during large flares. Astrophys. J. 748, 76. DOI .
Wang, H., Liu, C.: 2011, In: Choudhary, D.P., Strassmeier, K.G. (eds.) The Physics of Sun and Star Spots, Proc. IAU Symp. 273, 15.
Wang, H., Spirock, T.J., Qiu, J., Ji, H., Yurchyshyn, V., Moon, Y., Denker, C., Goode, P.R.: 2002, Rapid changes of magnetic fields associated with six X-class flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 576, 497. DOI .
Wang, H., Liu, C., Deng, Y., Zhang, H.: 2005, Reevaluation of the magnetic structure and evolution associated with the Bastille day flare on 2000 July 14. Astrophys. J. 627, 1031. DOI .
Wang, S., Liu, C., Deng, N., Liu, Y., Wang, H.: 2012, Response of the photospheric magnetic field to the X2.2 flare on February 15. Astrophys. J. Lett. 745, L17. DOI .
Wang, S., Liu, C., Deng, N., Wang, H.: 2014, Sudden photospheric motion and sunspot rotation associated with the X2.2 flare on 2011 February 15. Astrophys. J. Lett. 782(2), L31. DOI .
Welsch, B.T., Longcope, D.W.: 2003, Magnetic helicity injection by horizontal flows in the quiet Sun. I. Mutual-helicity flux. Astrophys. J. 588, 620. DOI .
Yang, G., Xu, Y., Cao, W., Wang, H., Denker, C., Rimmele, T.R.: 2004, Photospheric shear flows along the magnetic neutral line of active region 10486 prior to an X10 flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 617, L151. DOI .
Zhang, J., Li, L., Song, Q.: 2007, Interaction between a fast rotating sunspot and ephemeral regions as the origin of the major solar event on 2006 December 13. Astrophys. J. Lett. 662, L35. DOI .
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the referee for comments that helped improve this manuscript. SDO images are courtesy of the Solar Dynamics Observatory (NASA). The GOES “X-ray Flare” dataset was prepared by and made available through the NOAA National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC). The GOES X-ray flare times and positions data are supplied courtesy of SolarMonitor.org. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Commissions Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under the grant agreement eHEROES (project number 284461).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Győri, L. Automation of Tracking Various Sunspot Group Entities and Demonstrating Its Usage on the Flaring NOAA AR 11429. Sol Phys 290, 1627–1645 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0714-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0714-z