Abstract
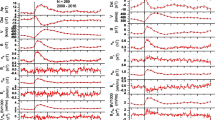
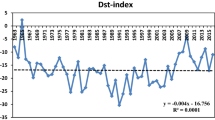
We study the interplanetary features and concomitant geomagnetic activity of the two high-speed streams (HSSs) selected by the Whole Heliosphere Interval (WHI) campaign participants: 20 March to 16 April 2008 in Carrington rotation (CR) 2068. This interval was chosen to perform a comprehensive study of HSSs and their geoeffectiveness during this “deep” solar minimum. The two HSSs within the interval were characterized by fast solar-wind speeds (peak values > 600 km s−1) containing large-amplitude Alfvénic fluctuations, as is typical of HSSs during normal solar minima. However, the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) magnitude [B o] was exceptionally low (≈3 – 5 nT) during these HSSs, leading to lower than usual IMF B z values. The first HSS (HSS1) had favorable IMF polarity for geomagnetic activity (negative during northern Spring). The average AE and Dst for the HSS1 proper (HSS1P) were + 258 nT and − 21 nT, respectively. The second HSS (HSS2) had a positive sector IMF polarity, one that is less favorable for geomagnetic activity. The AE and Dst index averages were + 188 nT and − 7 nT, both lower than corresponding numbers for the first event, as expected. The HSS1P geomagnetic activity is comparable to, and the HSS2P geomagnetic activity lower than, corresponding observations for the previous minimum (1996). Both events’ geomagnetic activities are lower than HSS events previously studied in the declining phase (in 2003). In general, V sw was faster for the HSSs in 2008 compared to 1996. The southward IMF B z was lower in the former. The product of these two parameters [V sw and IMF B z ] comprises the solar-wind electric field, which is most directly associated with the energy input into the magnetosphere during the HSS intervals. Thus the combined effects led to the solar wind energy input in 2008 being slightly less than that in 1996. A detailed analysis of magnetic-field variances and Alfvénicity is performed to explore the characteristics of Alfvén waves (a central element in the geoeffectiveness of HSSs) during the WHI. The B z variances in the proto-CIR (PCIR) were ≈ 30 nT2 and < 10 nT2 in the high speed streams proper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasofu, S.-I.:, 1981, Energy coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 28, 121.
Alves, M.V., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2006, Geoeffectiveness of corotating interaction regions as measured by Dst index. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A07S05.
Balogh, A., Bothmer, V., Crooker, N.U., Forsyth, R.J., Gloeckler, G., Hewish, A., Hilchenbach, M., Kallenbach, R., Klecker, B., Linker, J.A., Lucek, E., Mann, G., Marsch, E., Posner, A., Richardson, I.G., Schmidt, J.M., Scholer, M., Wang, Y.M., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., Aellig, M.R., Bochsler, P., Hefti, S., Mikic, Z.: 1999, The solar origin of corotating interaction regions and their formation in the inner heliosphere – Report of Working Group 1. Space Sci. Rev. 89, 141.
Belcher, J.W., Davis, L. Jr.: 1971, Large amplitude Alfven waves in the interplanetary medium, 2. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3534.
Bisi, M.M., Jackson, B.V., Buffington, A., Clover, J.M., Hick, P.P., Tokumaru, M.: 2009, Low-resolution STELab IPS 3D reconstructions of the whole heliosphere interval and comparison with in-ecliptic solar wind measurements from STEREO and Wind instrumentation. Solar Phys. 256, 201.
De Lucas, A., Gonzalez, W.D., Echer, E., Guarnieri, F.L., Dal Lago, A., da Silva, M.R., Vieira, L.E.A., Schuch, N.J.: 2007, Energy balance during intense and super-intense magnetic storms using an Akasofu ε parameter corrected by the solar wind dynamic pressure. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 69, 1851.
De Toma, G.: 2011, Evolution of corona holes and implication for high-speed solar wind during the minimum between cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9677-2 .
Dungey, J.W.: 1961, Interplanetary magnetic fields and the auroral zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Alves, M.V.: 2006, On the geomagnetic effects of solar wind interplanetary magnetic structures. Space Weather 4, S06001. doi: 10.1029/2005SW0002000 .
Echer, E., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2011, On the cause of lowest levels in geomagnetic activity in the space age. Adv. Space Res., submitted.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Guarnieri, F.L., Dal Lago, A., Vieira, L.E.A.: 2005, Introduction to space weather. Adv. Space Res. 35, 855.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, A.L.C.: 2008, Interplanetary conditions causing intense geomagnetic storms (Dst<− 100 nT) during solar cycle 23 (1996 C2006). J. Geophys. Res. 113.
Emery, B.A., Richardson, I.G., Evans, D.S., Rich, R.J., Xu, W.: 2009, Solar wind structure sources and periodicities of global electron hemispheric power over three solar cycles. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 71, 1157 – 1175. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2008.08.2005 .
Gibson, S.E., Kozyra, J.U., de Toma, G., Emery, B.A., Onsager, T., Thompson, B.J.: 2009, If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth ringing? A comparison of two solar minimum intervals. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A09105. doi: 10.1029/2009JA014342 .
Gonzalez, W.D.: 1990, A unified view of solar wind-magnetosphere coupling functions. Planet. Space Sci. 38, 627.
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Clua de Gonzalez, A.L.: 1999, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 88, 529.
Gonzalez, W.D., Joselyn, J.A., Kamide, Y., Kroehl, H.W., Rostoker, G., Tsurutani, B.T., Vasyliunas, V.M.: 1994, What is a geomagnetic storm? J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771.
Gonzalez, W.D., Guarnieri, F.L., Clua-Gonzalez, A.L., Echer, E., Alves, M.V., Ogino, T., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2006, Magnetospheric energetic during HILDCAAs. In: Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R., Gonzalez, W., Lu, G., Sobral, J.H.A., Gopalswamy, N. (eds.) Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind Streams, Geophys. Monogr. 167, AGU, Washington, 175.
Gonzalez, W.D., Echer, E., Clua-Gonzalez, A.L., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2007, Interplanetary origin of intense geomagnetic storms (Dst<− 100 nT) during solar cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L06101. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028879 .
Gopalswamy, N., Thompson, W.T., Davila, J.M., Kaiser, M.L., Yashiro, S., Makela, P., Michalek, G., Bougeret, J.-L., Howard, R.A.: 2009, Relation between type II bursts and CMEs inferred from STEREO observation. Solar Phys. 259, 227.
Guarnieri, F.L., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Echer, E., Gonzalez, A.L., Grande, M., Soraas, F.: 2006a, ICME and CIR storms with particular emphasis on HILDCAA events. In: Gopalswamy, N. (ed.) Proc. ILWS Workshop, Solar Influence on the Heliosphere and Earth’s Environment: Recent Progress and Prospects, Quest, Mumbai, 21.
Guarnieri, F.L., Tsurutani, B.T., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2006b, Geomagnetic activity and auroras caused by high-speed streams: A review. In: Adv. Geosci. 8, Solar-Terrestrial, 91.
Hathaway, D.H.: 2010, The solar cycle. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 7. http://solarphysics.livingreviews.org .
Issaultier, K., Le Chat, G., Meyer-Vernet, N., Moncuquet, M., Hoang, S., MacDowall, R.J., McComas, D.J.: 2008, Electron properties of high-speed solar wind from polar coronal holes obtained by Ulysses thermal noise spectroscopy: Not so dense, not so hot. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L19101. doi: 10.1029/2008GL034912 .
Kamide, Y., Baumjohann, W., Daglis, I.A., Gonzalez, W.D., Grande, M., Joselyn, J.A., McPherron, R.L., Phillips, J.L., Reeves, E.G.D., Rostoker, G., Sharma, A.S., Singer, H.J., Tsurutani, B.T., Vasyliunas, V.M.: 1998, Current understanding of magnetic storms: Storm-substorm relationships. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 17705.
Keller, C.U.: 2001, The SOLIS vector-spectromagnetograph (VSM). In: 20th International Sacramento Peak Summer Workshop, Advanced Solar Polarimetry-Theory, Observations and Instrumentation CS-236, Astron. Soc. Pacific, San Francisco, 16.
Kozyra, J.U., Crowley, G., Emery, B.A., Fang, X., Maris, G., Mlynczak, M.G., Niciejewski, R.J., Palo, S.E., Paxton, L.J., Randal, C.E., Rong, P.-P., Russell, J.M. III, Skinner, W., Solomon, S.C., Talaat, E.R., Wu, Q., Yee, J.-H.: 2006, Response of the upper/middle atmosphere to coronal holes and powerful high speed solar wind streams in 2003. In: Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R., Gonzalez, W., Lu, G., Sobral, J.H.A., Gopalswamy, N. (eds.) Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind Streams, Geophys. Monogr. 167, AGU, Washington, 319.
Krieger, A.S., Timothy, A.F., Roelof, E.C.: 1973, A coronal hole and its identification as the source of a high velocity solar wind stream. Solar Phys. 23, 123.
Landi, E., Raymond, J.C., Miralles, M.P., Hara, H.: 2009, Physical conditions in a CME from Hinode, STEREO and SOHO observations. Astrophys. J. 695, 221.
Lee, C.O., Luhmann, J.G., Zhao, X.P., Liu, Y., Riley, P., Arge, C.N., Russell, C.T., de Pater, I.: 2009, Effects of the weak polar fields of solar cycle 23: Investigation using OMNI for the STEREO mission period. Solar Phys. 256, 345. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9345-6 .
Luhmann, J.G., Lee, C.O., Li, Y., Arge, C.N., Galvin, A.B., Simunac, K., Russell, C.T., Howard, R.A., Petrie, G.: 2009, Solar wind sources in the late declining phase of cycle 23: Effects of the weak solar polar field on high speed streams. Solar Phys. 256, 285. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9354-5 .
Maris, G., Maris, O.: 2010, Highlights Astron. 15, Cambridge U. Press, 494.
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Baker, P., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Riley, P., Griffee, J.W.: 1998, Solar wind electron proton alpha monitor (SWEPAM) for the advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 563 – 612.
McComas, D.J., Barraclough, B.L., Funsten, H.O., Gosling, J.T., Santiago-Munoz, E., Skoug, R.M., Goldstein, B.E., Neugebauer, M., Riley, P., Balogh, A.: 2000, Solar wind observations over Ulysses’ first full polar orbit. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10419.
McComas, D.J., Ebert, R.W., Elliott, H.A., Goldstein, B.E., Gosling, J.T., Schwadron, N.A., Skoug, R.M.: 2008, Weaker solar wind from the polar coronal holes and the whole Sun. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L18103. doi: 10.1029/2008GL034896 .
Perrault, P.D., Akasofu, S.-I.: 1978, A study of geomagnetic storms. Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 54, 547.
Pizzo, V.J.: 1985, Interplanetary shocks on the large scale: A retrospective on the last decade’s theoretical efforts. In: Tsurutani, B.T., Stone, R.G. (eds.) Collisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere, Reviews of Current Research, Geophys. Monogr. 35, AGU, Washington, 51.
Richardson, I.G., Cliver, E., Cane, H.V.: 2000, Sources of geomagnetic activity over the solar cycle: relative importance of coronal mass ejections, high-speed streams and slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18203 – 18213.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996 – 2009): Catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys. 264, 189. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9568-6 .
Rostoker, G.: 1972, Geomagnetic indices. Rev. Geophys. 10, 935.
Russell, C.T.: 1971, Geophysical coordinate transformations. Cosm. Electrodyn. 2, 184.
Russell, C.T., McPherron, R.L.: 1973, Semiannual variation of geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 92.
Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Harvey, J.W., Feldman, W.C.: 1976, Coronal holes, solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic disturbances: 1973 – 1976. Solar Phys. 49, 271.
Smith, E.J., Wolfe, J.H.: 1976, Observations of interaction regions and corotating shocks between one and 5 AU-PIONEER-10 and PIONEER-11. Geophys. Res. Lett. 3, 137.
Smith, E.J., Balogh, A.: 2008, Decrease in heliospheric magnetic flux in this solar minimum: Recent Ulysses magnetic field observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L22103. doi: 10.1029/2008GL035345 .
Smith, C.W., Acuna, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Scheifele, J.: 1998, The ACE magnetic field experiment. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 613.
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Hayashi, K.: 2009, Non-dipolar solar wind structure observed in the cycle 23/24 minimum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L09101. doi: 10.1029/2009GL037461 .
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 1987, The cause of high-intensity long-duration continuous AE activity (HILDCAAs): Interplanetary Alfven wave trains. Planet. Space Sci. 35, 405.
Tsurutani, B.T., Smith, E.J., Pyle, K.R., Simpson, J.A.: 1982, Energetic protons accelerated at corotating shocks: Pioneer 10 and 11 observations from 1 to 6 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 7389.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gould, T., Goldstein, B.E., Gonzalez, W.D., Sugiura, M.: 1990, Interplanetary Alfven waves and auroral (substorm) activity: IMP-8. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 2241.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Gonzalez, A.L.C., Tang, F., Arballo, J.K., Okada, M.: 1995, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic activity in the declining phase of the solar cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 21717.
Tsurutani, B.T., Lakhina, G.S., Pickett, J.S., Guarnieri, F.L., Lin, N., Goldstein, B.E.: 2005, Nonlinear Alfvén waves, discontinuities, proton perpendicular acceleration, and magnetic holes/decreases in interplanetary space and the magnetosphere: Intermediate shocks? Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 12, 321.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Gonzalez, A.L.C., Guarnieri, F.L., Gopalswamy, N., Grande, M., Kamide, Y., Kasahara, Y., Lu, G., McPherron, R., Soraas, F., Vasyliunas, V.: 2006a, Corotating solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic activity: A review. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A07S01. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011273 .
Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R.L., Gonzalez, W.D., Lu, G., Gopalswamy, N., Guarnieri, F.L.: 2006b, Magnetic storms caused by corotating solar wind streams. In: Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R., Gonzalez, W., Lu, G., Sobral, J.H.A., Gopalswamy, N. (eds.) Recurrent Magnetic Storms, Corotating Solar Wind Streams, Geophys. Monogr. 167, AGU, Washington, 1.
Tsurutani, B.T., Echer, E., Guarnieri, F.L., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2011, The properties of two solar wind high speed streams and related geomagnetic activity during the declining phase of solar cycle 23. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 164.
Turner, N.E., Mitchell, E.J., Knipp, D.J., Emery, B.A.: 2006, Energetics of magnetic storms driven by corotating interaction regions: A study of geoeffectiveness. In: Tsurutani, B.T., McPherron, R., Gonzalez, W., Lu, G., Sobral, J.H.A., Gopalswamy, N. (eds.) Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind Streams, Geophys. Monogr. 167, AGU, Washington, 113.
Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1965, Sector structure of quiet interplanetary magnetic field. Science 148, 1592.
Winterhalter, D., Smith, E.J., Burton, M.E., Murphy, N., McComas, D.J.: 1994, The heliospheric plasma sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 6667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Sun–Earth Connection near Solar Minimum
Guest Editors: M.M. Bisi, B.A. Emery, and B.J. Thompson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echer, E., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D. et al. High Speed Stream Properties and Related Geomagnetic Activity During the Whole Heliosphere Interval (WHI): 20 March to 16 April 2008. Sol Phys 274, 303–320 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9739-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9739-0