Abstract
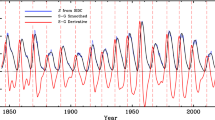
The Hilbert – Huang transform is a relatively new data analysis technique, which is able to analyze the cyclic components of a potentially nonlinear and nonstationary data series. Monthly sunspot number data from 1749 to 2010 were analyzed using this technique, which revealed the different variability inherent in the data including the 11-year (Schwabe), 20 – 50-year (quasi-Hale) and 60 – 120-year (Gleissberg) cycles. The results were compared with traditional Fourier analysis. The Hilbert – Huang transform is able to provide a local and adaptive description of the intrinsic cyclic components of sunspot number data, which are nonstationary and which are the result of nonlinear processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byron, F.W., Fuller, R.W.: 1992, Mathematics of Classical and Quantum Physics, Dover Publications, New York.
Cohen, L.: 1995, Time-Frequency Analysis, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
Flandrin, P., Rilling, G., Gonçalvès, P.: 2004, Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(2), 112.
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S., Wu, M., Shih, H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N., Tung, C., Liu, H.: 1998, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. Roy. Soc. London A 454(1971), 903.
Kolláth, Z., Oláh, K.: 2009, Multiple and changing cycles of active stars – I. Methods of analysis and application to the solar cycles. Astron. Astrophys. 501, 695.
Pegram, G.G.S., Peel, M.C., McMahon, T.A.: 2008, Empirical mode decomposition using rational splines: An application to rainfall time series. Proc. Roy. Soc. London A 464, 1483.
Qian, S.: 2002, Introduction to Time – Frequency and Wavelet Transforms, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Sonett, C.P.: 1983, J. Geophys. Res. 88(A4), 3225.
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K.: 2003, Long-term solar cycle evolution: Review of recent developments. Solar Phys. 218, 319.
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E.: 2004, A study of the characteristics of white noise using the empirical mode decomposition. Proc. Roy. Soc. London A 460(2046), 1597.
Wu, Z., Huang, N.E.: 2009, Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(1), 1. ftp://grads.iges.org/pub/ctr/ctr_193.pdf .
Wu, S., Liu, Z., Liu, B.: 2006, Enhancement of lidar backscatters signal-to-noise ratio using empirical mode decomposition. Opt. Commun. 267(1), 137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnhart, B.L., Eichinger, W.E. Analysis of Sunspot Variability Using the Hilbert – Huang Transform. Sol Phys 269, 439–449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-010-9701-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-010-9701-6