Abstract
The volume of data anticipated from the Solar Dynamics Observatory/Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (SDO/AIA) highlights the necessity for the development of automatic-detection methods for various types of solar activity. Initially recognized in the 1970s, it is now well established that coronal dimmings are closely associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and they are particularly noted as a reliable indicator of front-side (halo) CMEs, which can be difficult to detect in white-light coronagraph data.
Existing work clearly demonstrates that several properties derived from the analysis of coronal dimmings can give useful information about the associated CME. The development and implementation of an automated coronal-dimming region detection and extraction algorithm removes visual observer bias, however unintentional, from the determination of physical quantities such as spatial location, area, and volume. This allows for reproducible, quantifiable results to be mined from very large data sets. The information derived may facilitate more reliable early space-weather detection, as well as offering the potential for conducting large-sample studies focused on determining the geo-effectiveness of CMEs, coupled with analysis of their associated coronal dimming signatures.
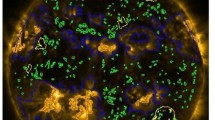
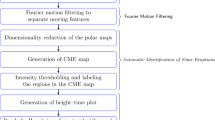
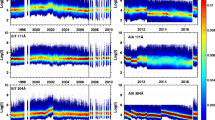
In this paper we present examples of both simple and complex dimming events extracted using our algorithm, which will be run as a module for the SDO/Computer Vision Centre. Contrasting and well-studied events at both the minimum and maximum of solar cycle 23 are identified in Solar and Heliospheric Observatory/Extreme ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SOHO/EIT) data. A more recent example extracted from Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory/Extreme Ultra-Violet Imager (STEREO/EUVI) data is also presented, demonstrating the potential for the anticipated application to SDO/AIA data. The detection part of our algorithm is based largely on the principle of operation of the NEMO software, namely the detection of significant variation in the statistics of the EUV image pixels (Podladchikova and Berghmans in Solar Phys. 228, 265 – 284, 2005). As well as running on historic data sets, the presented algorithm is capable of detecting and extracting coronal dimmings in near real-time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschwanden, M.J., Wuelser, J.P., Nitta, N.V., Lemen, J.R., Sandman, A.: 2009, First three-dimensional reconstructions of coronal loops with the STEREO A + B spacecraft. III. Instant stereoscopic tomography of active regions. Astrophys. J. 695, 12 – 29. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/695/1/12.
Attrill, G., Nakwacki, M.S., Harra, L.K., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Mandrini, C.H., Dasso, S., Wang, J.: 2006, Using the evolution of coronal dimming regions to probe the global magnetic field topology. Solar Phys. 238, 117 – 139. doi:10.1007/s11207-006-0167-5.
Attrill, G.D.R., Harra, L.K., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P., Wülser, J.P.: 2007, Coronal “wave”: A signature of the mechanism making CMEs large-scale in the low corona? Astron. Nachr. 328, 760 – 763. doi:10.1002/asna.200710794.
Attrill, G.D.R., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P., Zhukov, A.N., Steed, K., Harra, L.K., Mandrini, C.H., Linker, J.: 2008, The recovery of CME-related dimmings and the ICME’s enduring magnetic connection to the Sun. Solar Phys. 252, 349 – 372. doi:10.1007/s11207-008-9255-z.
Bewsher, D., Harrison, R.A., Brown, D.S.: 2008, The relationship between EUV dimming and coronal mass ejections. I. Statistical study and probability model. Astron. Astrophys. 478, 897 – 906. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078615.
Chertok, I.M., Grechnev, V.V.: 2003, Large-scale dimmings produced by solar coronal mass ejections according to SOHO/EIT data in four EUV lines. Astron. Rep. 47, 934 – 945. doi:10.1134/1.1626196.
Chertok, I.M., Grechnev, V.V.: 2005, Large-scale activity in the Bastille Day 2000 solar event. Solar Phys. 229, 95 – 114. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-3654-1.
Crooker, N.U., Webb, D.F.: 2006, Remote sensing of the solar site of interchange reconnection associated with the May 1997 magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 111, 8108 – 8114. doi:10.1029/2006JA011649.
Delannée, C., Aulanier, G.: 1999, CME associated with transequatorial loops and a bald patch flare. Solar Phys. 190, 107 – 129.
Démoulin, P.: 2008, A review of the quantitative links between CMEs and magnetic clouds. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3113 – 3125.
Goff, C.P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Harra, L.K., Matthews, S.A., Mandrini, C.H.: 2005, A slow coronal mass ejection with rising X-ray source. Astron. Astrophys. 434, 761 – 771. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042321.
Harrison, R.A., Lyons, M.: 2000, A spectroscopic study of coronal dimming associated with a coronal mass ejection. Astron. Astrophys. 358, 1097 – 1108.
Harrison, R.A., Sawyer, E.C., Carter, M.K., Cruise, A.M., Cutler, R.M., Fludra, A., Hayes, R.W., Kent, B.J., Lang, J., Parker, D.J., Payne, J., Pike, C.D., Peskett, S.C., Richards, A.G., Gulhane, J.L., Norman, K., Breeveld, A.A., Breeveld, E.R., Al Janabi, K.F., McCalden, A.J., Parkinson, J.H., Self, D.G., Thomas, P.D., Poland, A.I., Thomas, R.J., Thompson, W.T., Kjeldseth-Moe, O., Brekke, P., Karud, J., Maltby, P., Aschenbach, B., Bräuninger, H., Kühne, M., Hollandt, J., Siegmund, O.H.W., Huber, M.C.E., Gabriel, A.H., Mason, H.E., Bromage, B.J.I.: 1995, The coronal diagnostic spectrometer for the solar and heliospheric observatory. Solar Phys. 162, 233 – 290. doi:10.1007/BF00733431.
Howard, R.A., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Michels, D.J., Koomen, M.J.: 1985, Coronal mass ejections – 1979 – 1981. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 8173 – 8191.
Hudson, H.S., Cliver, E.W.: 2001, Observing coronal mass ejections without coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25199 – 25214. doi:10.1029/2000JA004026.
Hudson, H.S., Webb, D.F.: 1997, Soft X-Ray Signatures of Coronal Ejections, Geophys. Monogr. Ser., AGU, Washington.
Hudson, H.S., Acton, L.W., Freeland, S.L.: 1996, A long-duration solar flare with mass ejection and global consequences. Astrophys. J. 470, 629 – 635. doi:10.1086/177894.
Jackson, B.V., Hick, P.P., Buffington, A., Bisi, M.M., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M.: 2007, Comparison of the extent and mass of CME events in the interplanetary medium using IPS and SMEI Thomson scattering observations. Astron. Astrophys. Trans. 26, 477 – 487. doi:10.1080/10556790701612221.
Kahler, S.W., Hudson, H.S.: 2001, Origin and development of transient coronal holes. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29239 – 29248. doi:10.1029/2001JA000127.
Mandrini, C.H., Pohjolainen, S., Dasso, S., Green, L.M., Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Copperwheat, C., Foley, C.: 2005, Interplanetary flux rope ejected from an X-ray bright point. The smallest magnetic cloud source-region ever observed. Astron. Astrophys. 434, 725 – 740. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041079.
Mandrini, C.H., Demoulin, P., Schmieder, B., Deluca, E.E., Pariat, E., Uddin, W.: 2006, Companion event and precursor of the X17 flare on 28 October 2003. Solar Phys. 238, 293 – 312. doi:10.1007/s11207-006-0205-3.
Mandrini, C.H., Nakwacki, M.S., Attrill, G., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Elliott, H.: 2007, Are CME-related dimmings always a simple signature of interplanetary magnetic cloud footpoints? Solar Phys. 244, 25 – 43. doi:10.1007/s11207-007-9020-8.
Martens, P.C.H., Davey, A.R., Grigis, P.C., Kasper, J., Korreck, K., Saar, S.H., Su, Y., Savcheva, A., Testa, P., Wills-Davey, M., Bernasconi, P.N., Georgoulis, M.K., Delouille, V.A., Hochedez, J.F., Cirtain, J.W., DeForest, C.E., Angryk, R.A., De Moortel, I., Wiegelmann, T.: 2009, Computer vision for the solar dynamics observatory. Solar Phys., submitted.
Podladchikova, O., Berghmans, D.: 2005, Automated detection of EIT waves and dimmings. Solar Phys. 228, 265 – 284. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-5373-z.
Qiu, J., Hu, Q., Howard, T.A., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2007, On the magnetic flux budget in low-corona magnetic reconnection and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 659, 758 – 772. doi:10.1086/512060.
Reinard, A.A., Biesecker, D.A.: 2008, Coronal mass ejection-associated coronal dimmings. Astrophys. J. 674, 576 – 585. doi:10.1086/525269.
Robbrecht, E., Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, No trace left behind: STEREO observation of a coronal mass ejection without low coronal signatures. Astrophys. J. 701, 283 – 291. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/701/1/283.
Rust, D.M.: 1983, Coronal disturbances and their terrestrial effects (Tutorial Lecture). Space Sci. Rev. 34, 21 – 36.
Rust, D.M., Hildner, E.: 1976, Expansion of an X-ray coronal arch into the outer corona. Solar Phys. 48, 381 – 387.
Steed, K., Owen, C.J., Harra, L.K., Green, L.M., Dasso, S., Walsh, A.P., Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2008, Locating the solar source of 13 April 2006 magnetic cloud. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3159 – 3168.
Sterling, A.C., Hudson, H.S.: 1997, YOHKOH SXT observations of X-ray “Dimming” associated with a halo coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 491, 55 – 58. doi:10.1086/311043.
Thompson, B.J., Plunkett, S.P., Gurman, J.B., Newmark, J.S., St. Cyr, O.C., Michels, D.J.: 1998, SOHO/EIT observations of an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection on May 12, 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2465 – 2468. doi:10.1029/98GL50429.
Thompson, B.J., Cliver, E.W., Nitta, N., Delannée, C., Delaboudinière, J.P.: 2000, Coronal dimmings and energetic CMEs in April – May 1998. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1431 – 1434. doi:10.1029/1999GL003668.
Wang, T., Yan, Y., Wang, J., Kurokawa, H., Shibata, K.: 2002, The large-scale coronal field structure and source region features for a halo coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. 572, 580 – 597. doi:10.1086/340189.
Webb, D.F., Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., DeForest, C.E., Larson, D.E., Martin, S.F., Plunkett, S.P., Rust, D.M.: 2000, The origin and development of the May 1997 magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27251 – 27260. doi:10.1029/2000JA000021.
Wills-Davey, M.J.: 2006, Tracking large-scale propagating coronal wave fronts (EIT waves) using automated methods. Astrophys. J. 645, 757 – 765. doi:10.1086/504144.
Zhukov, A.N., Auchère, F.: 2004, On the nature of EIT waves, EUV dimmings and their link to CMEs. Astron. Astrophys. 427, 705 – 716. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Solar Image Processing and Analysis
Guest Editors: J. Ireland and C.A. Young.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attrill, G.D.R., Wills-Davey, M.J. Automatic Detection and Extraction of Coronal Dimmings from SDO/AIA Data. Sol Phys 262, 461–480 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-009-9444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-009-9444-4